CPP / C++ Notes - Windows API Programming Win32
Table of Contents
- 1. Windows API Programming Win32
- 1.1. Overview
- 1.2. [DRAFT] Windows API Idiosyncrasies
- 1.3. Windows Tools and Configurations
- 1.4. Windows API Main Header Files
- 1.5. Windows API Runtime Libraries
- 1.6. Windows Object Code Binary Format and Scripting Languages
- 1.7. WinAPI C Data Types
- 1.8. SAL - Source Code Annotation Language
- 1.9. Character Encoding in WinAPI - ANSI x utf8 x utf16 (wchar_t)
- 1.10. Environment Variables
- 1.11. Primitive IO - Input/Ouput
- 1.12. System Information
- 1.13. Windows Shortcut - LNK
- 1.14. Windows Registry
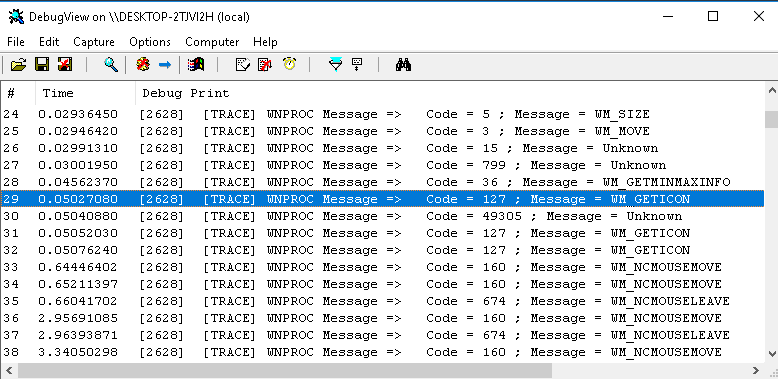
- 1.15. Capturing OutputDebugString output
- 1.16. Listing Windows and Related Processes
- 1.17. Access Tokens
- 1.18. Reading and writing process memory
- 1.19. Running machine code at runtime
- 1.20. CODE - Display information about current process
- 1.21. CODE - List processes
- 1.22. CODE - Show all DLLs or modules load by a process
- 1.23. CODE - Show files and directories attributes cmake build demo code
- 1.24. CODE - List directory files
- 1.25. CODE - Enumerate Logical Drivers
- 1.26. CODE - Launching and controlling sub-processes
- 1.27. Windows Socket - Winsock
- 1.28. WinlNet and UrlMon - APIs for HTTP and FTP protocol
- 1.29. Remote repl - telnet-like application
- 1.30. Embed Resources into Executables
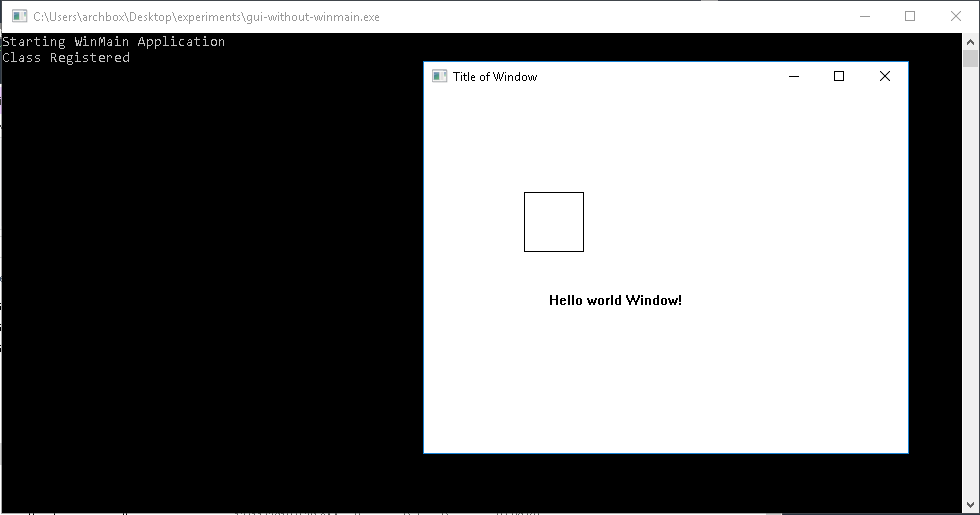
- 1.31. Graphical User Interfaces - WinAPI
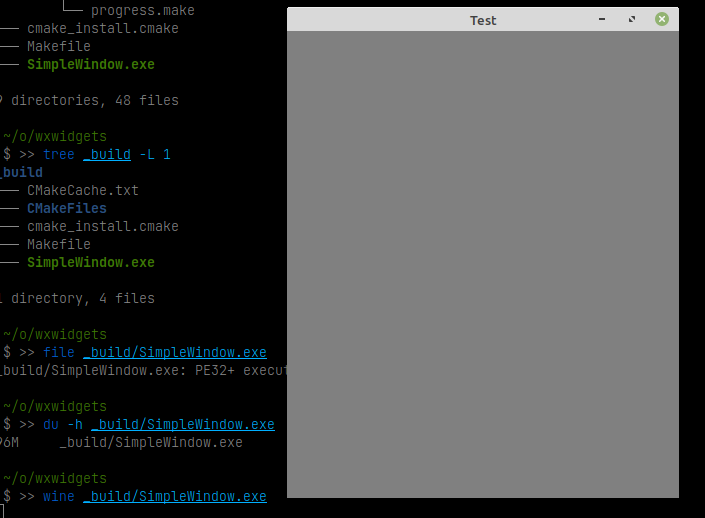
- 1.32. Cross-compiling WxWidgets for Windows from Linux
- 1.33. Loading DLLs - shared libraries at runtime
- 1.34. Runnable Shared Libraries DLLs - rundll32
- 1.35. Read metadata from Windows PE Portable Executable files
- 1.36. Install Development Tools and Compilers
- 1.37. WINAPI Map
- 1.37.1. Misc.
- 1.37.2. Header Files
- 1.37.3. Common HRESULT values
- 1.37.4. Typedefs
- 1.37.5. Console
- 1.37.6. Memory Allocation
- 1.37.7. File
- 1.37.8. Handle - Kernel "Objects"
- 1.37.9. Process Creation
- 1.37.10. Process Information
- 1.37.11. Process Manipulation
- 1.37.12. GUI _ Graphical User Interface
- 1.37.13. Dynamic Linking or Runtime Linking
- 1.38. Books
1 Windows API Programming Win32
1.1 Overview
The Windows API is very low level and obviously-Windows only, therefore it makes sense in most of cases to take advantage of higher libraries which encapsulates this API in a C++-friendly. Some of those libraries are:
Windows-Only (Microsft-only)
Windows-Only - Third party.
- WTL - Windows Template Library - Created by Microsft and later
become opensourced at 2004.
- Web site: http://wtl.sourceforge.net/
- Win32++ - "Win32++ is a C++ library used to build windows applications. Win32++ is a free alternative to MFC. It has the added advantage of being able to run on a wide range of free compilers, including Visual Studio Community, and the MinGW compiler provided with CodeBlocks and Dev-C++."
Cross-Platform:
- QT Framework - QT is not only a cross platform GUI library, it
also provides all sort of cross platform libraries for databases,
sockets, text parsing, OpenGL, XML and so on.
- Supported on: Windows, MacOSX, Linux, Android, iOS and many other operating systems.
- wxWidgets - Just a well known GUI library.
- Supported on: Windows, Linux, OSX.
- Poco - Framework - A collection of cross-platform libraries for network: HTTP protocol, FTP, ICMP; database access - SQLite, MySQL, ODBC and MongoDB; Standardized human-readable data exchange formats - JSON and XML; Zip compression; SSL and crypto utils.
1.2 [DRAFT] Windows API Idiosyncrasies
- Hungarian Notation
- Non standard types:
- LPSTRING, WORD, DWORD, BOOL, LPVOID …
- Paths: Unlike in U*nix-like operating systems which are written
with (/) forward slash, in Windows paths are written with
backward slash (\) needs to be escaped with double backward slash (\\)
since is slash is used for escape characters such as CR
\n,\sand so on. Thus, a Windows path such as"C:\Users\sombody\file.exe"must be written as "C:\\Users\\sombody\\file.exe". - Different Calling Conventions in the same OS: (Note: Only for 32 bits x86)
__stdcall__cdecl__fastcall
- Characters - ANSI X Unicode in API.
- Windows API uses 16-bits Unicode wide characters (wchar_t) instead of 8 bits Unicode UTF-8 which is common in most modern Unix-like Oses such as Linux, BSD and MacOSX.
- Windows API functions generally has two versions, an ANSI version with suffix 'A' and a wide unicode version with suffix 'W'. For instance the API CreateDirectory, has an ANSI version (which uses char) and does not work with UTF8 characteres such as 'ã', 'õ', 'ç', ' 我', 'Ж' and so on. And an wide unicode version using wide character (wchar_t) CreateDirectoryW.
- Many string types
- Many C-runtimes and entry points.
- Functions has many parameters which makes them pretty complex. The only way to understand the API is to compile and run small specific examples.
- Not all system calls are documented like open source OSes such as Linux or BSD.
1.3 Windows Tools and Configurations
1.3.1 Tools Shortcuts
This table compiles of Windows' built-in tools for enabling faster system configuration, debugging and troubleshooting. Those tools listed in the following table can be opened by typing the command at the shell (cmd.exe), powershell (powershell.exe) or by using Windows-Key + R keybind and then typing the command.
| Description | Tool/Command | |
|---|---|---|
| System Settings | ||
| Edit Environment Variables | rundll32.exe sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariables | |
| System settings and information | control.exe system | |
| Windows Registry | regedit | |
| Services and boot configuration | msconfig | |
| Security Center | wscui.cpl | |
| Services | services.msc | |
| Shared Folders | fsmgmt.msc | |
| System Information | msinfo32 | |
| User account management | Rundll32.exe keymgr.dll,KRShowKeyMgr | |
| System Properties / Remote Tab | Rundll32.exe shell32.dll,Control_RunDLL Sysdm.cpl,,5 | |
| Component Services - COM, DCOM | comexp.msc | |
| Device Manager | devmgmt.msc | |
| TPM - Trusted Platform Module management | tmp.msc | |
| Install/Unninstall new display languages | lpksetup.exe | |
| Utilities | ||
| Tool for taking screenshot | snippingtool | |
| Task manager | taskmgr | |
| Backup and Restore Utility | sdclt | |
| Certificate Manager | certmgr.msc | |
| Encrypted File System Wizard | rekeywiz | |
| Remote Desktop | mstsc | |
| General | ||
| View system logs and events | eventvwr or eventvwr.exe | |
| Windows Version | winver or winver.exe | |
| System restore | restrui.exe | |
| Details about hardware | msinfo32 | |
| DirectX and OpenGL diagnosing tool | dxdiag | |
| Disks and partitions | diskmgmt.msc | |
| Command Line (terminal-only) | ||
| Windows version | ver | |
| Summarized system information (CLI only) | systeminfo | |
| OS information and build number | wmic os list brief | |
| Show all environment variables | set | |
| Network interfaces and local IP address (CLI only) | ipconfig | |
| Show ARP table | arp -A | |
| List all active network connections TCP/IP | netstat -ano | |
| Processes and services | ||
| List all processes | tasklist | |
| Show all running services | sc query | |
| Show all running services | sc queryex | |
| List all services using WMIC tool | wmic service get processid,name,startname,pathname | |
| List all services in a concise way (brief) | wmic service list brief | |
| Terminate a process using its PID | taskkill <PID> | |
| Terminate a process by name (notepad.exe - in this case) | taskkill /F /IM notepad.exe | |
| Files and Directorires | ||
| Enter a directory | cd C:\Users\myser\directory | |
| Enter disk E: directory | E: | |
| Print a file in command line (akin to Unix's cat) | type <FILE> | |
| Delete a file | del <FILE> | |
| List current directory | dir | |
| List directory | dir <DIRECTORY> | |
| Users | ||
| Show current user | whoami | |
| Current user's privileges | whoami /priv | |
| Current user's groups | whoami /groups | |
| List user accounts | wmic useraccount | |
| List user accounts brief | wmic useraccount list brief | |
| Windwos Network and SMB | ||
| List network shares (SMB / SAMBA) | wmic share list | |
| List printers | wmic printer list brief | |
| Installed patches and hotfixes | wmic qfe | |
| Disks and BIOS | ||
| List disks | wmic diskdrive list brief | |
| List logical disks (C:, E:, …) | wmic logicaldisk list brief | |
| List all disks partitions | wmic partition get name,size,type | |
| List disks and their serial numer | wmic diskdrive get Name,Model,SerialNumber,Status | |
| Get BIOS serial number | wmic bios get name,serialnumber,version | |
| Shutdown and reboot | ||
| Reboot computer | shutdown /r | |
| Reboot immediately | shutdown /r /t 0 | |
| Shutdown computer | shutdown /s | |
| Loggof from current session | shutdown /l | |
| Abort previous shutdown command | shutdown /a | |
| System Logs | ||
| View last 5 application logs | wevtutil qe Application /f:text /rd:true /c:10 | |
| View System logs (last 5) | wevtutil qe System /f:text /rd:true | |
| View Security logs (last 5) | wevtutil qe Security /f:text /rd:true | |
| View Setup log | wevtutil qe Setup /f:text /rd:true | |
| Clean application logs | wevtutil cl Application | |
Note:
- Any executable in %PATH% variable can be called without .exe extension, for instance, $ notepad.exe can be called with $ notepad.
- (CLI only) => Command line only, the command only works on terminal (cmd.exe).
- A Windows service is similar to a Unix daemon, it is a program that continously runs in background and does not have any graphical interface
- WMIC - Windows Management Instrumentation
Shell folders shortcuts for quick access
The following commands can be run from the terminal or by using the keybind Windows-Key + R that opens the execute dialog.
| Description | shell shortcut | |
|---|---|---|
| User's directories | ||
| Open users home directory %USERPROFILE% | shell:profile |
|
| Open libraries folder | shell:libraries |
|
| Open start menu programs folders | shell:programs |
|
| View intalled windows updates | shell:AppUpdatesFolder |
|
| Open recent documents folder | shell:recent |
|
| Open sendto folder | shell:sendto |
|
| Open startup folder | shell:startup |
|
| Open templates folder | shell:templates |
|
| Open user pinned folders | shell:user pinned |
|
| System directories | ||
Open C:\Windows directory |
shell:windows |
|
Open C:\Windows\System32 folder |
shell:system |
|
| Open SysWow64 folder | shell:systemx86 |
|
Open C:\Windows\Fonts |
shell:fonts |
|
| Open Resources folder (contains windows themes) | shell:themes |
|
| Browse Implicit apps shortcut | shell:ImplicitAppShortcuts |
|
Open shell folder on terminal:
$ start "" "shell:systemx86"
Open Shell folder through Windows-Key + R:
- Type Windows-Key + R
- Type the shortcu, for instance:
shell:windows
Open shell folder through explorer.exe
- Type the shell shortcut in explorer.exe, for instance:
shell:themes
Mounting remote SMB (Server Message Block) network shares
$ net use <DISK> <HOSTNAME>\<SHARED-FOLDER> /user:<USERNAME> <PASSWORD>
Example:
# Example 1 $ net use z: \\10.0.0.2\data /user:myuser mypasswd # Example 2 - using computer Netbios name $ net use z: mycomputername\data /user:myuser mypasswd # Example 3 - using computer Netbios name and with persistence $ net use z: \\mycomputername\data /persistant:yes /user:myuser mypasswd # -------------------------------------# # Enter in the disk mapped to the network share $ z: # List files in the network share disk $ dir z:
1.3.2 File Path of Development Tools
Powershell x64
Powershell:
%SystemRoot%\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
Powershell ISE
%windir%\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\PowerShell_ISE.exe
Powershell x86
Powershell:
%windir%\syswow64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\PowerShell_ISE.exe
Powershell ISE
%windir%\syswow64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\PowerShell_ISE.exe
Loading MSVC x86-64 (64 bits) (Visual Studio Compiler)
Available at: MSCVC build tools download
# Load MSVC environment variables. $ %comspec% /k "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat" # Get tooling location $ where cl.exe C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.29.30037\bin\Hostx64\x64\cl.exe $ where link.exe C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.29.30037\bin\Hostx64\x64\link.exe C:\Users\unix\scoop\apps\git\current\usr\bin\link.exe $ where dumpbin.exe C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.29.30037\bin\Hostx64\x64\dumpbin.exe
Once MSVC configuration is loaded, sources can be compiled from command line using commands like the following:
$ cl.exe application.cpp /Fe:tkinfo.exe /EHsc /Zi /DEBUG advapi32.lib Microsoft (R) C/C++ Optimizing Compiler Version 19.29.30037 for x64 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. tokeninfo.cpp Microsoft (R) Incremental Linker Version 14.29.30037.0 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. /out:tkinfo.exe /debug tokeninfo.obj advapi32.lib
Loading MSVC x86 (32 bits) compiler tools
$ %comspec% /k "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars32.bat" ********************************************************************** ** Visual Studio 2019 Developer Command Prompt v16.10.0 ** Copyright (c) 2021 Microsoft Corporation ********************************************************************** [vcvarsall.bat] Environment initialized for: 'x86' C:\Users\unix>where cl.exe C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.29.30037\bin\Hostx86\x86\cl.exe $ where link.exe C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.29.30037\bin\Hostx86\x86\link.exe $ where dumpbin.exe C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.29.30037\bin\Hostx86\x86\dumpbin.exe
Windows Debugger Tools 64 bits ( Note: available at Windows 10 SDK )
Windbg (Windows Graphics Debugger - command line)
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Debuggers\x64\windbg.exe"
CDB Debugger (Windows command line debugger 64 bits)
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Debuggers\x64\cdb.exe"
Windows Debugger Tools 32 bits
Windbg (Windows Graphics Debugger - command line)
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Debuggers\x86\windbg.exe"
CDB Debugger (Windows command line debugger 64 bits)
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Debuggers\x86\cdb.exe"
1.3.3 Configuration
Editing Evironemnt Variables
In order to be able to launch tools from command line just by typing their name, such as MSBuild.exe or cmake.exe, the directories where are those tools need to be in the $PATH variable. This variable can be edited by using the control panel or the following command which opens the control panel at editing environment variables tab:
$ rundll32.exe sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariables
Adding tools to the %PATH% Environment Variables
STEP 1: Open the developer prompt:
**********************************************************************
** Visual Studio 2017 Developer Command Prompt v15.5.6
** Copyright (c) 2017 Microsoft Corporation
**********************************************************************
[vcvarsall.bat] Environment initialized for: 'x64'
STEP 2: Get the directory where is the executable, for instance, MSBuild.
C:\Users\archbox\source> where msbuild C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2017\Community\MSBuild\15.0\Bin\MSBuild.exe C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319\MSBuild.exe
This directory(aka path) is: C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2017\Community\MSBuild\15.0\Bin
STEP 3: Add this directory found at STEP 2 to %PATH% environment variable.
Just open the environment variables tab with the following command and add the path found at STEP 2.
- $ rundll32.exe sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariables
Now MSBuild can be launched directly from any tool or console without specifying its path.
A faster way to collect thoses paths is to redirect the output of command where to a text file.
cd %USERPROFILE%\Desktop
$ where msbuild >> paths.txt
$ where nmake >> paths.txt
$ where dumpbin >> paths.txt
1.4 Windows API Main Header Files
Most used headers:
- #include <windows.h>
- #include <wchar.h> - Wide Characters - UTF16 chars
- #include <tchar.h>
- #include <global.h>
- #include <nsfbd.h>
Other useful header files:
- windows.h
- Basic header file of Windows API
- WinError.h
- Error codes and strings
- tchar.h
- Provides the macro _T(…) and TEXT(…) for Unicode/ANSI string encoding handling.
- wchar.h
- Wide Character - UTF16 or wchar
- global.h
- ntfsb.h
- Winsock2.h
- Network sockets
- Winbase.h
- Windows types definitions
- WinUser.h
- Windows Messages
- ShellAPI.h
- Shell API
- ShFolder.h
- Folder definitions
- Commdlg.h
- Commom Controls (COM based)
- Dlgs.h
- Dialog definitions
- IUnknown.h
- COM header
- conio.h
- Console Input/Output functions - it is heritage grom MSDOS.
1.5 Windows API Runtime Libraries
- kernel32.dll
- Low level NTDLL wrappers.
- user32.dll
- User interface primitives used by graphical programs with menus, toolboxes, prompts, windows ..
- shell.dll
- gdi32.dll
- Basic drawing primitives.
- ole32.dll
- MSVCRT.DLL
- Implementation of the C standard library stdlib.
- advapi.dll
- Contains functions for system-related tasks such as registry and registry handling.
WS_32.DLL- Winsock2 library contains a socket implementation.
- Ntdll.dll
- Interface to Kernel. Not used by Windows programs directly.
- Wininet.dll
- Provides high level network APIs, for instance, HttpOpenRequest, FtpGetFile …
1.6 Windows Object Code Binary Format and Scripting Languages
Native executables, shared libraries and project files.
| Extension | Executable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Binary Format | ||
| Native Code | ||
| .exe | PE32 or PE64 | Windows Executable |
| .scr | PE32 or PE64 | Windows Executable, screen saver animation |
| .dll | PE32 or PE64 | Dynamic Linked Library - It can be Native PE32, PE64 or .NET/CLR DLL |
| .xll | PE32 or PE64 | Excel native Addin (extensio or plugin). It is a dll with .xll extension. |
| .pyd | PE32 or PE64 | Python native module on Windows - DLL with .pyd extension instead of .dll. |
| .cpl | PE32 or PE64 | Control Panel Applet - Also a DLL with .cpl extension. |
| .sys | PE32 or PE64 | Windows device driver (akin to Linux kernel modules) |
| .ocx | PE32 or PE64 | Active Control X (DLL) |
| Special Files | ||
| Ntoskrnl.exe | PE32 or PE64 | Windows-NT Kernel image |
| hall.dll | PE32 or PE64 | Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) |
| Compilation Binary Files | ||
| .obj | - | Object file -> Input to linker before building an executable. |
| .pdb | - | Program Debug Database => Contains executable or DLL debugging symbols. |
| .lib | - | Oject File Library or import library |
| .exp | - | Exports Library File |
| .RES | - | Compiled resource script |
| Source and Project Files | ||
| .def | - | Export Definition File |
| .sln | - | Visual Studio Solution (Project file). |
| .rs | - | Resource script - for embedding files into the executable. |
Scripting Languages Files:
| File Extension | Interpreter | Advantage | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| .bat | cmd.exe | Simplicity | Batch Script - Legacy technology from MSDOS, but still useful for small automation. |
| .vbs or vbe | WScript.exe or cscript.exe | COM + OOP | VBScript - Visual Basic Script |
| .js or jse | JScript.exe | COM + OOP | |
| .wcf | Windows Script File - Allows using many script engines iside the same file. | ||
| .ps1 .psm1 .ps1xml | Powershell | COM + OOP + .NET + Interactive | Powershell Script |
| .reg | regedit.exe | - | Windows registry script. Modify Windows registry when executed. |
1.7 WinAPI C Data Types
1.7.1 Hungarian Notation
Windows API uses the Hungarian notation which was intruduced by Charles Simonyi at Microsoft and Xerox PARC. This notation uses a prefix to denote the variable type.
Notes and remarks:
- Many sources advises against this notation and nowadays many IDEs can provide a variable type by just hovering the mouse over it.
- Understanding the notation can help to reason about the Windows API.
- The HN notation is not standardized.
Form:
TYPE-PREFIX + NAME + QUALIFIER
| Prefix | Type | Description | Variable Name Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| b | BYTE or BOOL | boolean | BOOL bFlag; BOOL bIsOnFocus |
| c | char | Character - 1 byte | char cLetter |
| w | WORD | word | |
| dw | DWORD | double word | |
| i | int | integer | int iNumberOfNodes |
| u32 | unsigned [int] | unsigned integer | unsigned u32Nodes |
| f or fp | float | float point - single precision | fInterestRate |
| d | double | float point - double precision | dRateOfReturn |
| n | short int | ||
| sz | char* or const char* | Pointer to null terminated char array. | char* szButtonLabel |
| H | HANDLE | Handle | HANDLE hModule; HMODULE hInstance; |
| p | - | Pointer | double* pdwMyPointer; |
| lp | - | Long Pointer | int* lpiPointer; |
| fn | - | Function pointer | |
| lpsz | Long Pointer | ||
| LP | Long Pointer | ||
| I | - | Interface (C++ interface class) | class IDrawable … |
| S | - | Struct declaration | struct SContext { … } |
| C | - | Class declaration | class CUserData{ … } |
| m_ | - | Private member variable name of some class | m_pszFileName |
| s_ | - | Static member of a class | static int s_iObjectCount |
Examples in Windows API - Function Create Process:
BOOL WINAPI CreateProcess( _In_opt_ LPCTSTR lpApplicationName, // const char* _Inout_opt_ LPTSTR lpCommandLine, // char* _In_opt_ LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes, _In_opt_ LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, // _In_ BOOL bInheritHandles, _In_ DWORD dwCreationFlags, _In_opt_ LPVOID lpEnvironment, _In_opt_ LPCTSTR lpCurrentDirectory, _In_ LPSTARTUPINFO lpStartupInfo, _Out_ LPPROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation );
- dwCreationFlags => (dw) prefix Indicates that the variable is a DWORD (int)
- lpEnvironment => (lp - Long Pointer) Indicates that variable is a void pointer => (LPVOID = void* )
- lpApplicationName => Indicates that the variable is a pointer to char or (LPCSTR = const char*)
Furthere Reading:
- Coding Conventions: The Hungarian Notation
- Why I prefer to use the Hungarian Notation
- Hungarian Notation
- Just Say mNo to Hungarian Notation - Jake Wharton
- Hungarian Notation
- Hungarian Notation
1.7.2 General Terminology
- Handle - Is a unsigned integer number assigned to processes,
windows, buttons, resources and etc. Actually, it is an opaque
pointer to some system data structure (Kernel Object), similar to
Unix's file descriptor pointer. The purpose of using handles or
opaque pointer is to hide the implementation of those data
structures allowing implementators to change their inner working
without disrupting application developers. This approach gives a
pseudo object-oriented interface to the Windows API. See also:
- Note: A handle can be an obfuscated pointer exposed as an integer, void pointer void* (also opaque pointer) or ordinary opaque pointer (pointer to a C-struct or class which implementation is not exposed).
- Types of Kernel Objects (Handle is a numeric value related to the
pointer to kernel object C-struct). The name "object" comes from
the idea that it is possible to access the kernel data structure
pointer by the handle using the Win32 API functions. It works in a
similar way to classical object oriented programming where the data
structure and internal representation can only be accessed by the
class methodos.
- Symbolic Link
- Process
- A running program, executable. A process has its own address space, data, stack and heap.
- Job
- Group of processes managed as group.
- File
- Open file or I/O device.
- Token
- Security token used by many Win32 functions.
- Event
- Synchronization object used for notification.
- Threads
- Smallest unit of execution within a process.
- Semaphore
- Mutex
- Timer
- Object which provides notification after a certain period is elapsed.
References:
- Opaque pointer - Wikipedia - Note: Opaque pointer is also called "handle classes", "pimpl idiom", "Compiler-firewall", "d-pointer" in C++.
- Handle (computing) - Wikipedia
- c++ - win32 application aren't so object oriented and why there are so many pointers? - Stack Overflow
- Object-oriented techniques in C Dmitry Frank
- Object-oriented design patterns in the kernel, part 1
1.7.3 Common Data Types
| Data Type | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BOOL | typedef int BOOL | Boolean variable true (non zero) or false (zero or 0) |
| BYTE | typedef unsigned char BYTE | A byte, 8 bits. |
| CCHAR | typedef char CHAR | An 8-bit Windows (ANSI) character. |
| DWORD | typedef unsigned long DWORD | A 32-bit unsigned integer. The range is 0 through 4294967295 decimal. |
| DWORDLONG | typedef unsigned __int64 DWORDLONG | 64 bits usigned int. |
| DWORD32 | typedef unsigned int DWORD32 | A 32-bit unsigned integer. |
| DWORD64 | typedef unsigned __int64 DWORD64 | A 64-bit unsigned integer. |
| FLOAT | typedef float FLOAT | A floating-point variable. |
| INT8 | typedef signed char INT8 | An 8-bit signed integer. |
| INT16 | typedef signed short INT16 | A 16-bit signed integer. |
| INT32 | typedef signed int INT32 | A 32-bit signed integer. The range is -2147483648 through 2147483647 decimal. |
| INT64 | typedef signed __int64 INT64 | A 64-bit signed integer. |
| LPBOOL | typedef BOOL far *LPBOOL; | A pointer to a BOOL. |
| LPBYTE | typedef BYTE far *LPBYTE | A pointer to a BYTE. |
| LPCSTR, PCSTR | typedef __nullterminated CONST CHAR *LPCSTR | pointer to a constant null-terminated string of 8-bit Windows (ANSI) characters. |
| LPCVOID | typedef CONST void *LPCVOID; | A pointer to a constant of any type. |
| LPCWSTR, PCWSTR | typedef CONST WCHAR *LPCWSTR; | A pointer to a constant null-terminated string of 16-bit Unicode characters. |
| LPDWORD | typedef DWORD *LPDWORD | A pointer to a DWORD. |
| LPSTR | typedef CHAR *LPSTR; | A pointer to a null-terminated string of 8-bit Windows (ANSI) characters. |
| LPTSTR | An LPWSTR if UNICODE is defined, an LPSTR otherwise. | |
| LPWSTR | typedef WCHAR *LPWSTR; | A pointer to a null-terminated string of 16-bit Unicode characters. |
| PCHAR | typedef CHAR *PCHAR; | A pointer to a CHAR. |
| CHAR | ANSI Char or char | |
| WCHAR | Wide character 16 bits UTF16 | |
| TCHAR | - | A WCHAR if UNICODE is defined, a CHAR otherwise. |
| UCHAR | typedef unsigned char UCHAR; | An unsigned CHAR. |
| WPARAM | typedef UINT_PTR WPARAM; | A message parameter. |
1.7.4 Other data types
| HANDLE | 32 bits integer used as a handle |
| HDC | Handle to device context |
| HWND | 32-bit unsigned integer used as handle to a window |
| LONG | |
| LPARAM | |
| LPSTR | |
| LPVOID | Generic pointer similar to void* |
| LRESULT | |
| UINT | Unsigned integer |
| WCHAR | 16-bit Unicode character or Wide-Character |
| WPARAM | |
| HINSTANCE |
1.7.5 References
General:
Windows Programming:
1.8 SAL - Source Code Annotation Language
Annotation such as __In__ or __Out__ commonly found on Windows API
documetation, as shown in the code below, is called SAL - Source Code
Annotation language. In a C code, it is hard to figure out which
parameters are used to return values or are read-only used only as
input. The SAL solves this problem by declaring which function
parameters are input, read-only and which parameters are output.
SAL is the Microsoft source code annotation language. By using source code annotations, you can make the intent behind your code explicit. These annotations also enable automated static analysis tools to analyze your code more accurately, with significantly fewer false positives and false negatives.
– http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh916383.aspx
HANDLE CreateRemoteThreadEx( __in__ HANDLE hProcess, __in__ LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, __in__ SIZE_T dwStackSize, __in__ LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE lpStartAddress, __in__ LPVOID lpParameter, __in__ DWORD dwCreationFlags, __in__ LPPROC_THREAD_ATTRIBUTE_LIST lpAttributeList, __out__ LPDWORD lpThreadId ); DWORD WINAPI FormatMessage( _In_ DWORD dwFlags, _In_opt_ LPCVOID lpSource, _In_ DWORD dwMessageId, _In_ DWORD dwLanguageId, _Out_ LPTSTR lpBuffer, _In_ DWORD nSize, _In_opt_ va_list *Arguments );
To allow those annotations in the source code, it is necessary to add the header #include <sal.h>. This SAL annotation is not standard among C++ compilers and is not defined by any C or C++ standard, as a result, the annotations only works on MSVC - Microsoft Visual C++ Compiler. This feature can be implemented in a portable way with macros.
SAL Fundamentals:
| SAL Annotatio | Description |
|---|---|
_In_ |
Input parameter - read only argument no modified inside the by the function. |
| Generally has the const qualifier such as const char*. | |
_In_Out_ |
Optional input parameter, can be ignored by passing a null pointer. |
_Out_ |
Output paramenter - Argument is written by the called function. It is generally a pointer. |
_Out_opt_ |
Optional output parameter. Can be ignored by setting it to null pointer. |
_Inout_ |
Data is passed to the function and pontentially modified. |
_Outptr_ |
Output to caller. The value returned by written to the parameter is pointer. |
_Outptr_opt_ |
Optional output pointer to caller, can be ignored by passing NULL pointer. |
Note: if the parameter is not annotated with _opt_ the caller is not
supposed to pass a NULL pointer, otherwise the parameter must be
annotated with _In_opt_, _Out_opt_ and etc.
Usage example:
- This annotation enhances the readability by telling reader which parameters are input and which parameters are output or used for returning values.
File: sal1.cpp
#include <sal.h> // Microsft's Source Code Annotation Language #include <iostream> // Computes elementwise product of two vectors void vector_element_product( _In_ size_t size, _In_ const double xs[], _In_ const double ys[], _Out_ double zs[] ){ for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){ zs[i] = xs[i] * ys[i]; } } void showArray(size_t size, double xs[]){ std::cout << "(" << size << ")[ "; for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){ std::cout << xs[i] << " "; } std::cout << "] "; } int main(){ double xs [] = {4, 5, 6, 10}; double ys [] = {4, 10, 5, 25}; double zs [4]; vector_element_product(4, xs, ys, zs); std::cout << "xs = "; showArray(4, xs); std::cout << "\n"; std::cout << "ys = "; showArray(4, ys); std::cout << "\n"; std::cout << "zs = "; showArray(4, zs); std::cout << "\n"; }
Compiling:
- MSVC (CL.EXE):
$ cl.exe sal1.cpp /nologo /Fe:sal1-a.exe && sal1-a.exe
sal1.cpp
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2017\Community\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.12.25827\include\xlocale(313): warning C4530: C++ exception handler used, but unwind semantics are not enabled. Specify /EHsc
xs = (4)[ 4 5 6 10 ]
ys = (4)[ 4 10 5 25 ]
zs = (4)[ 16 50 30 250 ]
- Mingw/G++
$ g++ sal1.cpp -o sal1-b.exe -std=c++11 && sal1-b.exe
xs = (4)[ 4 5 6 10 ]
ys = (4)[ 4 10 5 25 ]
zs = (4)[ 16 50 30 250 ]
Note: It doesn't work on Linux or other OSes. But it can be implemented with header files.
Open Source SAL Implementation:
- Source-code annotation language (SAL) compatibility header -
https://github.com/nemequ/salieri
- "Salieri is a header which provides definitions for Microsoft's source-code annotation language (SAL). Simply drop the header into your code and use it instead of including <sal.h> directly, and you can use SAL annotations even if you want your program to be portable to compilers which don't support it."
- "SAL provides lots of annotations you can use to describe the behavior of your program. There is a Best Practices and Examples (SAL) page on MSDN if you want to get a very quick idea of how it works, but the basic idea is that you end up with something like this:"
References:
- Understanding SAL - Visual Studio | Microsoft Docs
- Annotating Function Parameters and Return Values
- Using SAL Annotations to Reduce C-C++ Code Defects
- Best Practices and Examples (SAL)
- What is In in C++? - Stack Overflow
- Preventing bugs, and improving code quality with Microsoft SAL (Part 2, custom preconditions for structs & objects) | Alexander Riccio
- SQLite Source Code Annotated with SAL - https://github.com/ariccio/SQLite-Test-SAL and Using SAL in the SQLite API | Alexander Riccio
- SAL Annotations: Don’t Hate Me Because I’m Beautiful – OSR
1.9 Character Encoding in WinAPI - ANSI x utf8 x utf16 (wchar_t)
1.9.1 Overview
Unlike Linux, MacOSX and BSD where the API supports unicode UTF-8, the Windows API only supports ANSI enconding (char) and UTF16 or Unicode with 2 bytes per character wchar_t.
Macros and types for enconding portability
The following macros are widely used by Windows API for portability between ANSI and Unicode:
- Strings:
- <std::string> (UTF8 enconding) - Ordinary string (aka multi-byte string)
- std::wstring (UTF-16 enconding) - Wide string - string defined as array of wide characters wchar_t.
- TCHAR (Header: <tchar.h>) - When the UNICODE is defined TCHAR becomes wchar_t, otherwise, it becomes char.
#ifdef _UNICODE typedef wchar_t TCHAR; #else typedef char TCHAR; #endif
- String Literal _T or TEXT macro.
#ifdef _UNICODE #define _T(str) L##str #define TEXT(c) L##str #else #define _T(str) str #define TEXT(str) str #endif
- Character array type definition:
| Type | Definition | |
|---|---|---|
| LPSTR | char* | |
| LPCSTR | const char* | |
| LPWSTR | wchar_t* | |
| LPCWSTR | const wchar_t* | |
| LPTSTR | TCHAR* | |
| LPCTSTR | const TCHAR* | |
String Literals
- Utf-8 string literal (narrow characters or multibyte string) - cannot be used with Windows APIs as they will interpret those string literals as ANSI, thus not all characters will be represented.
"UTF8 - Unicode 8 bits multi-byte literal"; // Note: It doesn't work with Windows APIs (Windows specific functions) char utf8_text [] = "Random text in Georgian script (UTF8): ნუსხური";
- Utf-16 string literal (wide characters - wchar_t). Windows Unicode APIs or functions only works with wide characters (wchar_t).
L"UTF16 Wchar wide chracters literal"; wchar_t utf16_text [] = L"Random text in Georgian script (UTF16): ნუსხური";
- String prefixed with _T or TEXT. If Unicode is defined the string literal becomes an unicode UTF16 string literal and prefix 'L' is added to the string, otherwise nothing happens.
TCHAR text [] = _T("Random text in Georgian script ნუსხური"); // OR TCHAR text [] = TEXT("Random text in Georgian script ნუსხური");
If UNICODE is not defined, it becomes:
char text [] = "Random text in Georgian script ნუსხური";
If Unicode is defined, it becomes:
wchar_t text [] = L"Random text in Georgian script ნუსხური";
Windows APIs - ANSI X Unicode version
Almost every function in Windows API such as CreateDirectory has an ANSI and Unicode UTF16 (with wide chars wchar_t) version. The ANSI version of CreateDirectory API is CreateDirectoryA (suffix A) and the unicode version is CreateDirectoryW. The API CreateDirectory is expanded to CreateDirectoryW if #define UNICODE preprocessor flag is not defined, otherwise it is expanded to CreateDirectoryA.
- ANSI Version:
BOOL CreateDirectoryA( LPCSTR /* const char */ lpPathName, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpSecurityAttributes );
- Unicode Version:
BOOL CreateDirectoryW( LPCWSTR /* const wchar_t* */ lpPathName, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpSecurityAttributes );
1.9.2 Unicode UTF8 X Wide Unicode C-strign functions
In C++, it is better and safer to use std::string (UTF8 string) or std::wstring (wchar_t) wide unicode string since they can be modified at runtime and can take care of memory allocation and deallocation. However, it is worth knowing the C-functions for the purposing of reading and understanding Windows API codes which are mostly written in C rather than C++.
The following C-functions are widely used on many C-codes for Windows and Unix-like operating systems. Nowadays, the APIs of most Unix-like operating systems uses unicode UTF8 (char) by default, while most low level Windows API only supports Wide unicode (wchar_t). Windows.
| char | wchar_t - Wide character | |
|---|---|---|
| UTF8 | UTF16 - Wide Unicode | Description |
| strlen | wcslen | Get string length |
| strcmp | wcscmp | Comparre string |
| strcpy | wcsncpy | Copy N-characters from one string to another |
| strcat | wcscat | Concatenat string |
| strtod | wcstod | Convert wide string to double |
Signature of Wide unicode functions:
- Length of wide string
size_t wcslen (const wchar_t* wcs);
- Copy wide string
wchar_t* wcscpy (wchar_t* destination, const wchar_t* source);
- Concatenate wide string
wchar_t* wcscat (wchar_t* destination, const wchar_t* source
1.9.3 Example - ANSI X Unicode and Windows API
- Source Code: file:src/windows/winapi-enconding1.cpp
Compiling with GCC:
# Build $ g++ winapi-encoding1.cpp -o out-gcc.exe -std=c++14 # Compile $ out-gcc.exe
Compiling with MSVC:
- Note: If there is any unicode literal in the source, such as some text in Chinese or Hidi script, it is necessary to compile with the options (/source-charset:utf-8 /execution-charset:utf-8), otherwise the
# Build $ cl.exe winapi-encoding1.cpp user32.lib /EHsc /Zi /nologo /source-charset:utf-8 /execution-charset:utf-8 \ /Fe:out-msvc.exe # Run $ out-msvc.exe
Headers:
- To enable the expansion to unicode versions of WinAPIs, the flags
UNICODE and
_UNICODEmust be enabled. For instance, if those flags are enabled CreateDirectory is expanded to CreateDirectoryW and TCHAR is expanded to wchar_t. Otherwise, CreateDirectory is expanded to CreateDirectoryA and TCHAR to char. - Note: The unicode flags must be defined before any windows specific header such as <windows.h> or <tchar.h>.
#include <fstream> #include <string> #include <sstream> // Enable Unicode version of Windows API compile with -DWITH_UNICODE #ifdef WITH_UNICODE #define UNICODE #define _UNICODE #endif #include <windows.h> #include <tchar.h>
Experiment 1 - Print to console:
// ===========> EXPERIMENT 1 - Print to Console ============// std::cout << "\n ===>>> EXPERIMENT 1: Print to terminal [ANSI/UTF8] <<<=== " << std::endl; { std::cout << " [COUT] Some text example - указан - 读写汉字1 " << "\n"; std::wcout << L" [WCOUT] Some text example - указан - 读写汉字1 " << L"\n"; }
Output:
- This piece of code fails because the Windows' console (cmd.exe) cannot print unicode text by default. It needs to be configured before printing unicode, otherwise it will print garbage.
===>>> EXPERIMENT 1: Print to terminal [ANSI/UTF8] <<< [COUT] Some text example - указан - 读写汉字 [WCOUT] Some text example -
Experiment 2 - Print to File
// ===========> EXPERIMENT 2 - Print to File ============// std::cout << "\n ===>>> EXPERIMENT 2: Write non ANSI Chars to File <<<=== " << "\n"; std::stringstream ss; ss << " Text in Cyrllic Script: Если указан параметр " << "\n" << " Text in Chinese Script: 读写汉字1 " << "\n" << "\n"; auto dfile = std::ofstream("logging.txt"); dfile << ss.str() << std::flush;
Output: file - loggin.txt
- By opening the file logging.txt with notepad.exe, it is possible view all characters as show in the following block.
Text in Cyrllic Script: Если указан параметр Text in Chinese Script: 读写汉字1
Experiment 3 - WinAPI - CreateDirectory
This code experiment attempts to create 3 directories:
- Directory: directoryANSI-读写汉字1 with CreateDirectoryA function (ANSI version of the underlying API)
- Directory: directoryWCHAR-读写汉字 with CreateDirectoryW (Unicode version of the API).
- Directory: directoryTCHAR-读写汉字 with CreateDirectory macro which is expanded to CreateDirectoryW when UNICODE is defined, othewise it is expanded to CreateDirectoryA.
// ===========> EXPERIMENT 4 - WinAPI - CreateDirectory ============// std::cout << "\n ===>>> EXPERIMENT 3: WinAPI CreateDirectory <<<=== " << std::endl; { // -- ANSI Version of CreateDirectory API bool res; res = CreateDirectoryA("directoryANSI-读写汉字1", NULL); std::cout << "Successful 1 ?= " << std::boolalpha << res << std::endl; } { // -- Unicode (UTF16) - Wide character version of CreateDirectory API bool res; res = CreateDirectoryW(L"directoryWCHAR-读写汉字", NULL); std::cout << "Successful 2 ?= " << std::boolalpha << res << std::endl; } { // -- TCHAR Version Wide character version of CreateDirectory API bool res; #ifdef UNICODE std::cout << " [INFO] UNICODE (UTF16) CreateDirectory expanded to CreateDirectoryW" << std::endl; #else std::cout << " [INFO] ANSI CreateDirectory expanded to CreateDirectoryA" << std::endl; #endif res = CreateDirectory(_T("directoryTCHAR-读写汉字"), NULL); std::cout << "Successful 3 ?= " << std::boolalpha << res << std::endl; }
Output when compiling without -DWITH_UNICODE:
$ g++ winapi-encoding1.cpp -o out-gcc.exe -std=c++14 && out-gcc.exe
... .... ...
===>>> EXPERIMENT 3: WinAPI CreateDirectory <<<===
Successful 1 ?= true
Successful 2 ?= true
[INFO] ANSI CreateDirectory expanded to CreateDirectoryA
Successful 3 ?= true
... .... ...
Directories created:
- [FAILED]
directoryANSI-读写汉å—1 - [SUCCESS]
directoryWCHAR-读写汉字- Only the Unicode (CreateDirectoryW) function works, the ANSI function CreateDirectoryA fails even if the string is encoded with UTF-8.
- [FAILED]
directoryTCHAR-读写汉å—- Without UNICODE flag, CreateDirectory expands to CreateDirectoryA.
Output when compiling without -DWITH_UNICODE:
$ g++ winapi-encoding1.cpp -o out-gcc.exe -std=c++14 -DWITH_UNICODE && out-gcc.exe
... .... ... ... ...
===>>> EXPERIMENT 3: WinAPI CreateDirectory <<<===
Successful 1 ?= true
Successful 2 ?= true
[INFO] UNICODE (UTF16) CreateDirectory expanded to CreateDirectoryW
Successful 3 ?= true
... .... ... ... ...
Directories created:
- [FAILED]
directoryANSI-读写汉å—1 - [SUCCESS]
directoryWCHAR-读写汉字 - [SUCCESS]
directoryTCHAR-读写汉字
Experiment 4 - WinAPI MessageBox function.
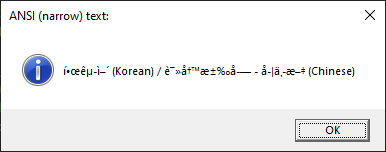
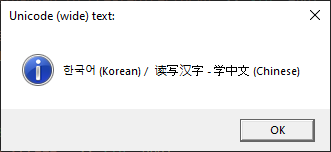
// ===========> EXPERIMENT 4 - WinAPI - MessageBox ============// std::cout << "\n ===>>> EXPERIMENT 4: MessageBox <<<=== " << std::endl; DWORD const infoboxOptions = MB_OK | MB_ICONINFORMATION | MB_SETFOREGROUND; // Text in UTF8 => Note => Windows API doesn't work with UTF8 // or multi-byte characters as the API treats the chars as they were ANSI. char narrowText [] = "한국어 (Korean) / 读写汉字 - 学中文 (Chinese)"; // Unicode text in UTF16 wchar_t wideText [] = L"한국어 (Korean) / 读写汉字 - 学中文 (Chinese)"; MessageBoxA( 0, narrowText, "ANSI (narrow) text:", infoboxOptions ); MessageBoxW( 0, wideText, L"Unicode (wide) text:", infoboxOptions );
Output of MessageBoxA (failure, it cannot deal with unicode UTF-8 chars):
Output of MessageBoxW (success):
1.10 Environment Variables
1.10.1 Overview
Environment variables are a set of key-value pairs that can be set by a command line shell or by a parent process for passing configuration and runtime parameters to applications, subprocesses and shared libraries. They are also useful for obtaining user information and locating the path of system directories.
Windows APIs for enviroment variables:
- MSDN - Environment Variables
- GetEnvironmentVariable function (winbase.h)
- SetEnvironmentVariable function (winbase.h)
Useful Windows commands (cmd.exe) for environment variables:
- $ set => Show all environment variables
- $ echo %PATH% => Show PATH environment variables.
- $ set PATH=C:\\app\bin\%PATH% => Set path environment variable.
- $ set CREDENTIAL=PASS => Set environemnt variable CREDENTIAL with value PASS.
Most important environemnt variables
- SystemDriver => Equivalent to Unix / (slash) root directory.
$ echo %SystemDrive%
C:
- SystemRoot => Path to Windows directory.
$ echo %SystemRoot%
C:\Windows
- Windir => Same as SystemRoot.
$ echo %WinDir% C:\Windows
- System32 folder (64 bits applications)
$ echo "%SystemRoot%\System32" "C:\Windows\System32"
- SysWOW64 folder (32 bits applications)
- Some files: regedit.exe (Registry editor), wscript.exe, write.exe, wusa.exe, where.exe, whoami.exe, WF.msc, tracert.exe, tracerpt.exe, tpm.msc, tcmsetup.exe, taskmgr.exe (Task Manager), runas.exe, rundll32.exe and o on.
- See: File System Redirector
- See: The SysWOW64 explained
$ echo "%SystemRoot%\SysWOW64" "C:\Windows\SysWOW64"
- ProgramFiles => Directory where 64 bits applications (Windows NT 64 bits) are installed.
$ echo %ProgramFiles%
C:\Program Files
- ProgramFiles(x86) => Directory where are installed 32-bits x86 applications. Note: x86 applications can only access up to 4GB of RAM and cannot fully harness all hardware resources.
$ echo %ProgramFiles(x86)%
C:\Program Files (x86)o
- CommonProgramFiles
$ echo "%CommonProgramFiles%" "C:\Program Files\Common Files"
- CommonProgramFiles(x86)
$ echo "%CommonProgramFiles(x86)%" "C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files"
- ProgramData
$ echo %ProgramData%
C:\ProgramData
- DriverData
$ echo "%DriverData%" "C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\DriverData"
- UserProfile => Path to current user's data directory, similar to
Unix $HOME enviroment variable.
- Note: The application 'ls' (ported from Unix) is not Windows native. It was used because the command 'dir' does not fully shows the user directory since it hides the files and directories 'ntuser.init', 'ntuser.dat', 'Applications Data/', 'Start Menu/', 'SendTo', and so on.
$ echo %UserProfile% C:\Users\ha3mx
- Temp => Directory for temporary files. Equivalent to Unix /tmp
$ echo %TEMP% C:\Users\h03fx\AppData\Local\Temp
- APPDATA =>
$ echo %AppData%
C:\Users\h03fx\AppData\Roaming
- LOCALAPPDATA =>
$ echo %LOCALAPPDATA%
C:\Users\h03fx\AppData\Local
- USERNAME => Name of current user account.
% echo %USERNAME% hafcx
- USERDOMAIN
$ echo %USERDOMAIN% DESKTOP-GMXQCB6
Directory Exploration
- Directory: %SystemDriver% (using dir command)
$ dir %SystemDrive%\ Volume in drive C has no label. Volume Serial Number is BC40-DCC4 Directory of C:\ 03/18/2019 09:52 PM <DIR> PerfLogs 02/06/2021 02:38 AM <DIR> Program Files 01/08/2021 08:25 AM <DIR> Program Files (x86) 01/05/2021 02:47 AM <DIR> Temp 01/05/2021 02:15 AM <DIR> Users 01/08/2021 03:08 PM <DIR> Windows 0 File(s) 0 bytes 6 Dir(s) 87,119,368,192 bytes free
- Directory: %SystemDriver% (using Unix 'ls' applications that comes with GIT)
$ ls -la %SystemDrive%\ total 2660600 drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 Jan 5 18:01 '$Recycle.Bin'/ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 May 3 03:37 '$WINDOWS.~BT'/ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 May 3 03:18 '$WinREAgent'/ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 May 3 2021 ./ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 May 3 2021 ../ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 May 3 2021 Config.Msi/ lrwxrwxrwx 1 hafcx 197121 8 Jan 5 00:22 'Documents and Settings' -> /c/Users/ -rw-r--r-- 1 hafcx 197121 1717768192 May 3 03:11 hiberfil.sys -rw-r--r-- 1 hafcx 197121 738197504 May 3 03:11 pagefile.sys drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 Mar 18 2019 PerfLogs/ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 Feb 6 01:38 'Program Files'/ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 Jan 8 07:25 'Program Files (x86)'/ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 Jan 8 07:33 ProgramData/ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 Jan 5 00:22 Recovery/ -rw-r--r-- 1 hafcx 197121 268435456 May 3 03:11 swapfile.sys drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 Jan 5 00:27 'System Volume Information'/ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 Jan 5 01:47 Temp/ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 Jan 5 01:15 Users/ drwxr-xr-x 1 hafcx 197121 0 Jan 8 14:08 Windows/
- Directory: %ProgramData%
λ dir %ProgramData%
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is CA82-ED51
Directory of C:\ProgramData
03/03/2021 04:35 PM <DIR> chocolatey
01/05/2021 01:49 AM <DIR> Microsoft OneDrive
01/06/2021 05:27 AM <DIR> Microsoft Visual Studio
01/06/2021 12:55 PM <DIR> Mozilla
01/06/2021 05:45 AM <DIR> Package Cache
02/04/2021 05:02 PM <DIR> Packages
01/05/2021 06:14 PM <DIR> qemu-ga
05/03/2021 03:53 AM <DIR> regid.1991-06.com.microsoft
01/08/2021 08:33 AM <DIR> shimgen
03/18/2019 09:52 PM <DIR> SoftwareDistribution
01/05/2021 02:55 AM <DIR> USOPrivate
01/05/2021 01:17 AM <DIR> USOShared
01/06/2021 05:46 AM <DIR> Windows App Certification Kit
03/18/2019 11:23 PM <DIR> WindowsHolographicDevices
0 File(s) 0 bytes
14 Dir(s) 92,218,159,104 bytes free
- Directory: %ProgramFiles%
$ dir "%ProgramFiles%" Volume in drive C has no label. Directory of C:\Program Files 02/06/2021 02:38 AM <DIR> . 03/18/2019 10:02 PM <DIR> Common Files 01/06/2021 05:58 AM <DIR> dotnet 03/18/2019 11:21 PM <DIR> Internet Explorer 03/03/2021 04:13 PM <DIR> Microsoft Update Health Tools 03/18/2019 09:52 PM <DIR> ModifiableWindowsApps ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .. .... ... ... 03/18/2019 10:02 PM <DIR> Windows NT 03/18/2019 11:23 PM <DIR> Windows Photo Viewer 03/18/2019 11:23 PM <DIR> Windows Portable Devices 03/18/2019 09:52 PM <DIR> Windows Security 03/18/2019 09:52 PM <DIR> WindowsPowerShell
- Directory: %ProgramFiles(x86)%
$ dir "%ProgramFiles(x86)%" Volume in drive C has no label. Directory of C:\Program Files (x86) 01/08/2021 08:25 AM <DIR> . 01/08/2021 08:25 AM <DIR> .. 01/06/2021 05:45 AM <DIR> Application Verifier 01/08/2021 08:26 AM <DIR> CodeBlocks 01/06/2021 05:52 AM <DIR> Common Files 01/06/2021 05:56 AM <DIR> dotnet 01/06/2021 05:50 AM <DIR> HTML Help Workshop 03/18/2019 11:21 PM <DIR> Internet Explorer 01/06/2021 05:59 AM <DIR> Microsoft SDKs 01/06/2021 05:32 AM <DIR> Microsoft Visual Studio 01/06/2021 05:55 AM <DIR> Microsoft.NET 01/08/2021 03:08 PM <DIR> Mozilla Maintenance Service 01/06/2021 05:32 AM <DIR> MSBuild 01/06/2021 05:46 AM <DIR> Reference Assemblies 01/05/2021 06:14 PM <DIR> SPICE Guest Tools 03/18/2019 11:20 PM <DIR> Windows Defender 01/06/2021 05:52 AM <DIR> Windows Kits ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
- Directory: %UserProfile% => Windows HOME directory for current user.
- Note: NTUSER.DAT is the Windows registry file of current logged user.
- Note: This file is not shown with the Windows command line '$ dir'.
$ ls "%UserProfile%" '3D Objects'/ AppData/ 'Application Data'@ Contacts/ Cookies@ Desktop/ Documents/ Downloads/ Favorites/ Links/ 'Local Settings'@ MicrosoftEdgeBackups/ Music/ 'My Documents'@ NetHood@ NTUSER.DAT ntuser.dat.LOG1 ntuser.dat.LOG2 NTUSER.DAT{fd9a35da-3abd-11e9-aa2c-908c07783950}.TxR.0.regtrans-ms NTUSER.DAT{fd9a35da-3abd-11e9-aa2c-908c07783950}.TxR.1.regtrans-ms NTUSER.DAT{fd9a35da-3abd-11e9-aa2c-908c07783950}.TxR.2.regtrans-ms NTUSER.DAT{fd9a35da-3abd-11e9-aa2c-908c07783950}.TxR.blf NTUSER.DAT{fd9a35db-3abd-11e9-aa2c-908c07783950}.TM.blf NTUSER.DAT{fd9a35db-3abd-11e9-aa2c-908c07783950}.TMContainer00000000000000000001.regtrans-ms NTUSER.DAT{fd9a35db-3abd-11e9-aa2c-908c07783950}.TMContainer00000000000000000002.regtrans-ms ntuser.ini OneDrive/ Pictures/ PrintHood@ Recent@ 'Saved Games'/ scoop/ Searches/ SendTo@ 'Start Menu'@ Templates@ Videos/
- Directory: %UserProfile%\Start Menu\Programs
$ ls "%UserProfile%\Start Menu\Programs" Accessibility/ 'Anaconda3 (64-bit)'/ Maintenance/ Startup/ Accessories/ CodeBlocks/ OneDrive.lnk* 'System Tools'/ 'Administrative Tools'/ desktop.ini 'Scoop Apps'/ 'Windows PowerShell'/ $ ls "%UserProfile%\Start Menu\Programs\System Tools" 'Administrative Tools.lnk'* computer.lnk* Desktop.ini Run.lnk* 'Command Prompt.lnk'* 'Control Panel.lnk'* 'File Explorer.lnk'* $ ls "%UserProfile%\Start Menu\Programs\Startup" desktop.ini
- Directory: %UserProfile%/AppData
$ ls "%UserProfile%/AppData/" Local/ LocalLow/ Roaming/ $ ls "%UserProfile%/AppData/Local" 'Application Data'@ IconCache.db pip/ clink/ Microsoft/ PlaceholderTileLogoFolder/ CMakeTools/ MicrosoftEdge/ Publishers/ Comms/ Mozilla/ ServiceHub/ ConnectedDevicesPlatform/ NuGet/ Temp/ D3DSCache/ Packages/ 'Temporary Internet Files'@ History@ PeerDistRepub/ VirtualStore/ $ ls "%UserProfile%/AppData/Roaming" Adobe/ Microsoft/ NuGet/ 'Code - Insiders'/ 'Microsoft Visual Studio'/ 'Visual Studio Setup'/ CodeBlocks/ Mozilla/ vstelemetry/
- Directory: %UserProfile%/SendTo
$ ls "%UserProfile%/SendTo/ 'Bluetooth File Transfer.LNK'* Documents.mydocs 'Compressed (zipped) Folder.ZFSendToTarget' 'Fax Recipient.lnk'* 'Desktop (create shortcut).DeskLink' 'Mail Recipient.MAPIMail' Desktop.ini
1.10.2 Usage of Windows environemnt variables
Environment variables can be used for global configuration, enable/disable logging detail output, setting application credentials and locating system directories. This program displays several Windows environment variables by calling the subroutines std::getenv() (standardized) and GetEvironmentVariable(). The application also demonstrates how environment variables can be used for changing the program behavior at startup time.
File: windows-envvars.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> //Note: std::get_envvar() is cross-platofrm and standardized. std::string get_envvar(std::string const& name) { const char* p = std::getenv(name.c_str()); if( p == nullptr){ return ""; } return p; } void show_envvar(std::string const& name) { auto s = get_envvar(name); std::cout << " [ENV] " << name << " = " << s << '\n'; } std::string get_envvar2(std::string const& name) { //Buffer max size in bytes constexpr size_t maximum_size = 32767; std::string buffer(maximum_size, '\0'); DWORD nread = ::GetEnvironmentVariableA(name.c_str(), buffer.data(), maximum_size); if(nread == 0){ return ""; } buffer.resize(nread); return buffer; } void show_envvar2(std::string const& name) { auto s = get_envvar2(name); std::cout << " [ENV2] " << name << " = " << s << '\n'; } bool is_logging_enabled() { // Initialized only once. static const bool enabled = []{ auto var = get_envvar2("LOGGING_ENABLED"); return var == "TRUE"; }(); return enabled; } void display_factorial(int n) { int p = 1; for(int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) { p = p * i; if( is_logging_enabled()) { std::cout << " [TRACE] p = " << p << '\n'; } } std::cout << " [RESULT] factorial( " << n << " ) = " << p << '\n'; } int main() { std::puts("\n ============= EXPERIMENT 1 =============="); show_envvar("SystemDrive"); show_envvar("USERPROFILE"); show_envvar("USERNAME"); show_envvar("USERDOMAIN"); show_envvar("WINDIR"); show_envvar("PROGRAMDATA"); show_envvar("SystemRoot"); show_envvar("AppData"); show_envvar("LocalAppData"); show_envvar("Temp"); show_envvar("ProgramFiles"); show_envvar("ProgramFiles(x86)"); show_envvar("CommonProgramFiles"); show_envvar("CommonProgramFiles(x86)"); show_envvar("CUSTOM_USER_SUPPLIED"); std::puts("\n ============= EXPERIMENT 2 =============="); show_envvar2("SystemDrive"); show_envvar2("USERPROFILE"); show_envvar2("USERNAME"); show_envvar2("USERDOMAIN"); show_envvar2("WINDIR"); show_envvar2("PROGRAMDATA"); show_envvar2("SystemRoot"); show_envvar2("AppData"); show_envvar2("LocalAppData"); show_envvar2("Temp"); show_envvar2("ProgramFiles"); show_envvar2("ProgramFiles(x86)"); show_envvar2("CommonProgramFiles"); show_envvar2("CommonProgramFiles(x86)"); show_envvar2("CUSTOM_USER_SUPPLIED"); std::puts("====== RUNTIME CONFIGURATION DEMO ========"); display_factorial(5); return 0; }
- Building with Mingw from command line:
$ g++ windows-envvars.cpp -o out.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g
- First run without setting custom environment variables.
$ .\out.exe ============= EXPERIMENT 1 ============== [ENV] SystemDrive = C: [ENV] USERPROFILE = C:\Users\hcf5 [ENV] USERNAME = hcf5 [ENV] USERDOMAIN = DESKTOP-GXMQDB8 [ENV] WINDIR = C:\Windows [ENV] PROGRAMDATA = C:\ProgramData [ENV] SystemRoot = C:\Windows [ENV] AppData = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Roaming [ENV] LocalAppData = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Local [ENV] Temp = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Local\Temp [ENV] ProgramFiles = C:\Program Files [ENV] ProgramFiles(x86) = C:\Program Files (x86) [ENV] CommonProgramFiles = C:\Program Files\Common Files [ENV] CommonProgramFiles(x86) = C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files [ENV] CUSTOM_USER_SUPPLIED = ============= EXPERIMENT 2 ============== [ENV2] SystemDrive = C: [ENV2] USERPROFILE = C:\Users\hcf5 [ENV2] USERNAME = hcf5 [ENV2] USERDOMAIN = DESKTOP-GXMQDB8 [ENV2] WINDIR = C:\Windows [ENV2] PROGRAMDATA = C:\ProgramData [ENV2] SystemRoot = C:\Windows [ENV2] AppData = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Roaming [ENV2] LocalAppData = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Local [ENV2] Temp = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Local\Temp [ENV2] ProgramFiles = C:\Program Files [ENV2] ProgramFiles(x86) = C:\Program Files (x86) [ENV2] CommonProgramFiles = C:\Program Files\Common Files [ENV2] CommonProgramFiles(x86) = C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files [ENV2] CUSTOM_USER_SUPPLIED = ======== CONFIG TEST ================= [RESULT] factorial( 5 ) = 120
- Second run after setting custom environment variables.
$ set CUSTOM_USER_SUPPLIED="Hello world! (EN) ola mundo! (PT) hola mundo! (ES) - hallo Welt! (DE)" $ set LOGGING_ENABLED=TRUE λ .\out.exe ============= EXPERIMENT 1 ============== [ENV] SystemDrive = C: [ENV] USERPROFILE = C:\Users\hcf5 [ENV] USERNAME = hcf5 [ENV] USERDOMAIN = DESKTOP-GXMQDB8 [ENV] WINDIR = C:\Windows [ENV] PROGRAMDATA = C:\ProgramData [ENV] SystemRoot = C:\Windows [ENV] AppData = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Roaming [ENV] LocalAppData = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Local [ENV] Temp = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Local\Temp [ENV] ProgramFiles = C:\Program Files [ENV] ProgramFiles(x86) = C:\Program Files (x86) [ENV] CommonProgramFiles = C:\Program Files\Common Files [ENV] CommonProgramFiles(x86) = C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files [ENV] CUSTOM_USER_SUPPLIED = "Hello world! (EN) ola mundo! (PT) hola mundo! (ES) - hallo Welt! (DE)" ============= EXPERIMENT 2 ============== [ENV2] SystemDrive = C: [ENV2] USERPROFILE = C:\Users\hcf5 [ENV2] USERNAME = hcf5 [ENV2] USERDOMAIN = DESKTOP-GXMQDB8 [ENV2] WINDIR = C:\Windows [ENV2] PROGRAMDATA = C:\ProgramData [ENV2] SystemRoot = C:\Windows [ENV2] AppData = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Roaming [ENV2] LocalAppData = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Local [ENV2] Temp = C:\Users\hcf5\AppData\Local\Temp [ENV2] ProgramFiles = C:\Program Files [ENV2] ProgramFiles(x86) = C:\Program Files (x86) [ENV2] CommonProgramFiles = C:\Program Files\Common Files [ENV2] CommonProgramFiles(x86) = C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files [ENV2] CUSTOM_USER_SUPPLIED = "Hello world! (EN) ola mundo! (PT) hola mundo! (ES) - hallo Welt! (DE)" ======== CONFIG TEST ================= [TRACE] p = 1 [TRACE] p = 2 [TRACE] p = 6 [TRACE] p = 24 [TRACE] p = 120 [RESULT] factorial( 5 ) = 120
1.11 Primitive IO - Input/Ouput
1.11.1 Overview
Unlike Unix-based operating systems, Windows NT does not use open(), read(), creat(), close() primitive IO subroutines, instead this operating system uses CreateFIle(), ReadFile(), WriteFile(), CloseHandle(). Windows NT also has asynchronous primitive IO subroutines which does not block the current thread.
- CreateFileA() / ANSI Version
- Brief MSDN: "Creates or opens a file or I/O device. The most commonly used I/O devices are as follows: file, file stream, directory, physical disk, volume, console buffer, tape drive, communications resource, mailslot, and pipe. The function returns a handle that can be used to access the file or device for various types of I/O depending on the file or device and the flags and attributes specified."
// ---- ANSI version -------------// HANDLE CreateFileA( LPCSTR lpFileName, DWORD dwDesiredAccess, DWORD dwShareMode, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpSecurityAttributes, DWORD dwCreationDisposition, DWORD dwFlagsAndAttributes, HANDLE hTemplateFile ); // -- Unicode UTF-16 -----version ----// HANDLE CreateFileW( LPCWSTR lpFileName, DWORD dwDesiredAccess, DWORD dwShareMode, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpSecurityAttributes, DWORD dwCreationDisposition, DWORD dwFlagsAndAttributes, HANDLE hTemplateFile );
- ReadFile() - Read data from handle to buffer.
- Brief: "Reads data from the specified file or input/output (I/O) device. Reads occur at the position specified by the file pointer if supported by the device. This function is designed for both synchronous and asynchronous operations. For a similar function designed solely for asynchronous operation, see ReadFileEx."
- Note: The argument lpBuffer (void*) is a pointer to any contiguous memory location or any data without any internal pointer.
BOOL ReadFile( HANDLE hFile, LPVOID lpBuffer, DWORD nNumberOfBytesToRead, LPDWORD lpNumberOfBytesRead, LPOVERLAPPED lpOverlapped );
- WriteFile() - Write a buffer to handle.
- Brief: "Writes data to the specified file or input/output (I/O) device. This function is designed for both synchronous and asynchronous operation. For a similar function designed solely for asynchronous operation, see WriteFileEx."
BOOL WriteFile( HANDLE hFile, LPCVOID lpBuffer, DWORD nNumberOfBytesToWrite, LPDWORD lpNumberOfBytesWritten, LPOVERLAPPED lpOverlapped );
- CloseHandle()
- Brief: "Closes an open object handle."
- This function can close all types of handles, including: file, I/O completion port, mutex, pipe, console input, console screen buffer, access token and so on.
BOOL CloseHandle(HANDLE hObject);
Other Windows APIs:
- DeleteFile()
- Brief: "Deletes an existing file."
BOOL DeleteFileA(LPCSTR lpFileName); BOOL DeleteFileW(LPCWSTR lpFileName);
- CreateDirectoryA()
- Brief: "Creates a new directory. If the underlying file system supports security on files and directories, the function applies a specified security descriptor to the new directory."
BOOL CreateDirectoryA( LPCSTR lpPathName, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpSecurityAttributes );
1.11.2 Sample code
Files
File: primtive-io.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> //Note: std::get_envvar() is cross-platofrm and standardized. std::string get_envvar(std::string const& name) { const char* p = std::getenv(name.c_str()); if( p == nullptr){ throw std::runtime_error("Environment variable not found"); } return std::string{p}; } struct InventoryItem { int id; float price; char product[200]; }; void run_experiment1(); void run_experiment2(); void run_experiment3(); int main() { std::puts("\n [EXPERIMENT 1] ===>> Create a text file with primitive IO ======"); run_experiment1(); std::puts("\n [EXPERIMENT 2] ===>> Create a binary file with structured data ======"); run_experiment2(); std::puts("\n [EXPERIMENT 3] ===>> Read a binary file containing structured data ==="); run_experiment3(); return 0; } void run_experiment1() { const auto desktop_dir = get_envvar("USERPROFILE") + "\\Desktop"; std::fprintf(stderr, " [TRACE] Desktop dir = %s \n", desktop_dir.c_str()); const auto fpath = desktop_dir + "\\testfile.txt"; std::fprintf(stderr, " [TRACE] File path = %s \n", fpath.c_str()); HANDLE hFile = CreateFileA( fpath.c_str() // File path ,GENERIC_WRITE // Open file for writing ,0 // File is not shared with any other process. ,NULL // Use default security - It should be nullptr ,CREATE_ALWAYS ,FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL // Normal file ,NULL ); // DO not use attribute assert( hFile != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE && "Returned invalid handle."); constexpr size_t BUFFER_SIZE = 500; size_t len = 0; BOOL error_flag = FALSE; char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; // Initialize buffer with null character memset(buffer, '\0', BUFFER_SIZE); // Copy string literal to buffer. strcpy(buffer, " =>> Buffer line 1 - test - Gotta love Windows NT \n"); // Number of bytes until '\0' null character is found. len = strlen(buffer); error_flag = WriteFile( hFile // File handle to be writtern , buffer // Buffer to be written to file handle , len // Number of bytes to be written , NULL // [OUTPUT] Number of bytes written , NULL // No overlapped structure ); assert( error_flag == TRUE && "Unable to write"); strcpy(buffer, " =>> C# CSharp, Dot net, Ponto NET - JAVA \n"); len = strlen(buffer); WriteFile( hFile, buffer, len, NULL, NULL); assert( error_flag == TRUE && "Unable to write"); // Close handle CloseHandle(hFile); } // Write binary data void run_experiment2() { InventoryItem item1; item1.id = 200; item1.price = 250.61; strcpy(item1.product, "Some unknown product"); InventoryItem item2; item2.id = 976; item2.price = 1250.61; strcpy(item2.product, "Old fashioned feature phone XYZW"); const auto desktop_dir = get_envvar("USERPROFILE") + "\\Desktop"; const auto fpath = desktop_dir + "\\inventory.dat"; HANDLE hFile = CreateFileA( fpath.c_str() ,GENERIC_WRITE ,0 ,NULL ,CREATE_ALWAYS ,FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL ,NULL ); BOOL error_flag = FALSE; error_flag = WriteFile(hFile, &item1, sizeof(struct InventoryItem), NULL, NULL ); assert( error_flag == TRUE && "Unable to write"); error_flag = WriteFile(hFile, &item2, sizeof(struct InventoryItem), NULL, NULL ); assert( error_flag == TRUE && "Unable to write"); CloseHandle(hFile); } // Read binary data. void run_experiment3() { const auto desktop_dir = get_envvar("USERPROFILE") + "\\Desktop"; const auto fpath = desktop_dir + "\\inventory.dat"; // Open file for reading HANDLE hFile = CreateFileA( fpath.c_str() ,GENERIC_READ ,0 ,NULL ,OPEN_EXISTING ,FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL ,NULL ); assert( hFile != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE && "Returned invalid handle."); BOOL error_flag = FALSE; DWORD nbytes_read = 0; InventoryItem buffer; error_flag = ReadFile(hFile, &buffer, sizeof(struct InventoryItem) , &nbytes_read, NULL); assert( error_flag == TRUE && "Unable to read."); assert( nbytes_read == sizeof(struct InventoryItem)); std::fprintf( stderr, " [ITEM 1] Id = %d ; price = %f; product = %s \n" , buffer.id, buffer.price, buffer.product); error_flag = ReadFile(hFile, &buffer, sizeof(struct InventoryItem) , &nbytes_read, NULL); assert( error_flag == TRUE && "Unable to read."); assert( nbytes_read == sizeof(struct InventoryItem)); std::fprintf( stderr, " [ITEM 2] Id = %d ; price = %f; product = %s \n" , buffer.id, buffer.price, buffer.product); CloseHandle(hFile); std::cout << " [STATUS] Type return to terminate this application \n"; std::string line; std::getline(std::cin, line); // Delete file 'inventory.dat' assert( DeleteFileA(fpath.c_str()) == TRUE ); }
Building
$ g++ primitive-io.cpp -o out.cmp -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g -static $ g++ primitive-io.cpp -o out.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g -static
Running
C:\Users\user_001\Desktop> out.cmp
[EXPERIMENT 1] ===>> Create a text file with primitive IO ======
[TRACE] Desktop dir = C:\Users\user_001\Desktop
[TRACE] File path = C:\Users\user_001\Desktop\testfile.txt
[EXPERIMENT 2] ===>> Create a binary file with structured data ======
[EXPERIMENT 3] ===>> Read a binary file containing structured data ===
[ITEM 1] Id = 200 ; price = 250.610001; product = Some unknown product
[ITEM 2] Id = 976 ; price = 1250.609985; product = Old fashioned feature phone XYZW
[STATUS] Type return to terminate this application
Check generated files from other terminal
$ type testfile.txt =>> Buffer line 1 - test - Gotta love Windows NT =>> C# CSharp, Dot net, Ponto NET - JAVA # Not possible to show file content because it contains # structured binary data (non readable bytes) $ type inventory.dat ╚)£zCSome unknown productHç√╞ ⌂☺☺☺hpKá‼↑►H^r♥╞ ⌂☺... ....
1.12 System Information
1.12.1 Oveview
Sample codes using several Windows API subroutines for obtaining system information such as path to key directories, amount of working memory, username and etc.
Documentation
- SHGetFolderLocation function
- Determine path of special folders.
- GlobalMemoryStatusEx function (sysinfoapi.h)
- Get amount of RAM memory (physical memory, aka working memory) available; amount of page file used and amount of virtual memory informations.
- System Information Functions
- Documentation functions for retrieving system information.
- GetSystemInfo()
- GetSystemDirectory()
- GetSystemWindowsDirectory()
- GetSystemWow64Directory()
- GetUserName()
- GetVersion()
- Operating System Version
- Brief: "The Version API Helper functions are used to determine the version of the operating system that is currently running. For more information, see Getting the System Version."
- GetSystemMetrics function (winuser.h)
- GetLogicalProcessorInformation function (sysinfoapi.h)
- Determines the number of logical processors available. Intel and AMD-based CPU cores can execute more than one stream of instructions simultaneously when hyper-thread is enabled. For instance, if a processor IC (Integrated Circuit) chip on the motherboard, has 4 cores and each core has 2 hyper-threads, the processor has 4 x 2 = 8 logical cores. Therefore, the processor can run up to 8 threads simultaneously and has 8 hardware threads.
1.12.2 C++ Sample Code Version
File: sysinfo.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> #include <shfolder.h> // For CSIDL_ constants #include <shlobj.h> // For CSIDL_ constants // #include <shlobj_core.h> #include <VersionHelpers.h> #include <sysinfoapi.h> std::string getSystemDirectory(); std::string getWindowsDirectory(); // Wrap functions with signature: // =>> using Func = UINT (*) (TCHAR* buffer, UINT n) // // The function returns a string by writing n bytes to the buffer // and returns the string lenght in bytes. If the buffer is not // enough larger to hold the string, the calling code should resize // it with the number of characters returned by the function call. // template<typename Func, typename T = UINT> auto wrap_fun(Func&& func) -> std::string; template<typename Func> auto wrap_fun2(Func&& func, DWORD size) -> std::string; std::string get_shfolder_path(int csidl); void show_system_memory_info(); void show_windows_version(); void show_processor_info(); int main() { std::puts("\n ======= Windows Version =================="); std::cout << std::boolalpha; show_windows_version(); std::cout << " [*] Is it Windows Sever? = " << ::IsWindowsServer() << '\n'; std::cout << " [*] Is >= Windows 10? = " << ::IsWindows10OrGreater() << '\n'; std::cout << " [*] Is >= Windows XP? = " << ::IsWindowsXPOrGreater() << '\n'; std::cout << " [*] Is >= Windows 8? = " << ::IsWindows8OrGreater() << '\n'; std::puts("\n ======== System Memory Info =============="); show_system_memory_info(); std::puts("\n ======== Hardware Info ==================="); show_processor_info(); std::puts("\n ======== System Information =============="); std::cout << " [*] Path to Windows Directory = " << wrap_fun(&GetWindowsDirectoryA) << std::endl; std::cout << " [*] Path to Windows System Directory = " << wrap_fun(&GetSystemDirectoryA) << std::endl; std::cout << " [*] Path to WOW64 Directory = " << wrap_fun(&GetSystemWow64DirectoryA) << std::endl; std::cout << " [*] Computer name = " << wrap_fun2(&GetComputerNameA, 32767) << '\n'; // Note: This function fails if the username uses // non ASCII characters such as Japanese Hiragrama //, Katakana or Kanji. std::cout << " [*] Username (account login name) = " << wrap_fun2(&GetUserNameA, 32767) << '\n'; // Documentation at: // https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/shlobj_core/nf-shlobj_core-shgetfolderpatha std::puts("\n ========= Special Directories ================="); std::cout << " =>> AdminTools = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_ADMINTOOLS) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> AppData = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_APPDATA) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> LocalAppData = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> CommonAppData = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_COMMON_APPDATA) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Common Admin Tools = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_COMMON_ADMINTOOLS) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Common Documents = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_COMMON_DOCUMENTS) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> My Pictures = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_MYPICTURES) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Personal Documents = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_PERSONAL) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Recent Folder = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_RECENT) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Internet Cache = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_INTERNET_CACHE) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> System Folder = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_SYSTEM) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Windows Folder " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_WINDOWS) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Program Files Folder = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_PROGRAM_FILES) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Program Files Common Folder = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_PROGRAM_FILES_COMMON) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Startup Folder = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_STARTUP) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Startup Menu Folder = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_STARTMENU) << '\n'; std::cout << " =>> Sendto Folder = " << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_SENDTO) << '\n'; // std::cout << " =>> Recycler Bin Folder = " // << get_shfolder_path(CSIDL_BITBUCKET) << '\n'; return 0; } //=================================// template<typename Func, typename T = UINT> auto wrap_fun(Func&& func) -> std::string { T n = 0; // Determine the size of the buffer for storing the result. n = func(nullptr, 0); assert( n != 0 && "Failure => Handle this error." ); // Create a buffer with N null characters 0x00 auto buffer = std::string(n, '\0'); n = func(buffer.data(), n); assert( n != 0); return buffer; } template<typename Func> auto wrap_fun2(Func&& func, DWORD size) -> std::string { auto buffer = std::string(size, '\0'); assert( func(buffer.data(), &size) != 0); buffer.resize(size); return buffer; } std::string get_shfolder_path(int csidl) { std::string path(MAX_PATH, 0); HRESULT h = ::SHGetFolderPathA( nullptr ,csidl ,nullptr ,0 ,path.data()); assert( SUCCEEDED(h) ); // Find position of first null char in the buffer. void* ps = memchr( &path[0], '\0', MAX_PATH); ptrdiff_t pA = reinterpret_cast<ptrdiff_t>(ps); ptrdiff_t pB = reinterpret_cast<ptrdiff_t>( path.data() ); path.resize(pA - pB); return path; } void show_system_memory_info() { MEMORYSTATUSEX st; st.dwLength = sizeof(st); ::GlobalMemoryStatusEx(&st); // Factor => Bytes to megabytes constexpr double factor = 1.0 / (1024 * 1024 ); std::printf(" [*] Percent of total physical memory used = %ld \n", st.dwMemoryLoad); std::printf(" [*] Total physical memory in Megabytes = %.3f \n", st.ullTotalPhys * factor ); std::printf(" [*] Free memory in MB form total physical memory = %.3f \n", st.ullAvailPhys * factor ); std::printf(" [*] Total size of page file in MB = %.3f \n", st.ullTotalPageFile * factor ); std::printf(" [*] Free memory of page file MB = %.3f \n", st.ullAvailPageFile * factor ); std::printf(" [*] Total virtual memory in MB = %.3f \n", st.ullTotalVirtual * factor ); std::printf(" [*] Free virtual memory MB = %.3f \n", st.ullAvailVirtual * factor ); std::printf(" [*] Amount of extended memory available in MB = %.3f \n", st.ullAvailExtendedVirtual * factor ); } void show_windows_version() { DWORD version, majorVersion, minorVersion, build; version = majorVersion = minorVersion = build = 0; version = GetVersion(); majorVersion = static_cast<DWORD>( LOBYTE( LOWORD(version) ) ); minorVersion = static_cast<DWORD>( LOBYTE( HIWORD(version) ) ); if (version < 0x80000000){ build = static_cast<DWORD>(HIWORD(version)); } std::printf(" [*] Windows Version = %ld.%ld (%ld) \n", majorVersion, minorVersion, build); } void show_processor_info() { SYSTEM_INFO info; ::GetNativeSystemInfo(&info); printf(" [*] Processor architecture = %ld \n", info.wProcessorArchitecture); printf(" [*] Processor arch is x86 = %s \n" , PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_INTEL == info.wProcessorArchitecture ? "TRUE" : "FALSE"); printf(" [*] Processor arch is AMD64 x64 (AMD or Intel = %s \n" , PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_AMD64 == info.wProcessorArchitecture ? "TRUE" : "FALSE"); #if defined(PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_ARM) printf(" [*] Processor arch is ARM = %s \n" , PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_ARM == info.wProcessorArchitecture ? "TRUE" : "FALSE"); #endif #if defined(PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_ARM64) printf(" [*] Processor arch is ARM64 = %s \n" , PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_ARM64 == info.wProcessorArchitecture ? "TRUE" : "FALSE"); #endif printf(" [*] Page size (virtual memory) in bytes = %ld \n", info.dwPageSize); printf(" [*] Number of processors = %ld \n", info.dwNumberOfProcessors); }
Building and running (MINGW compiler)
$ g++ sysinfo.cpp -o sysinfo.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g -static && .\sysinfo.exe ======= Windows Version ================== [*] Windows Version = 10.98 (19042) [*] Is it Windows Sever? = false [*] Is >= Windows 10? = true [*] Is >= Windows XP? = true [*] Is >= Windows 8? = true ======== System Memory Info ============== [*] Percent of total physical memory used = 45 [*] Total physical memory in Megabytes = 4095.484 [*] Free memory in MB form total physical memory = 2219.480 [*] Total size of page file in MB = 5503.484 [*] Free memory of page file MB = 3580.918 [*] Total virtual memory in MB = 134217727.875 [*] Free virtual memory MB = 134213543.578 [*] Amount of extended memory available in MB = 0.000 ======== Hardware Info =================== [*] Processor architecture = 9 [*] Processor arch is x86 = FALSE [*] Processor arch is AMD64 x64 (AMD or Intel = TRUE [*] Processor arch is ARM = FALSE [*] Processor arch is ARM64 = FALSE [*] Page size (virtual memory) in bytes = 4096 [*] Number of processors = 2 ======== System Information ============== [*] Path to Windows Directory = C:\WINDOWS\0 [*] Path to Windows System Directory = C:\WINDOWS\system32\0 [*] Path to WOW64 Directory = C:\WINDOWS\SysWOW64\0 [*] Computer name = DESKTOP-GLJQDB6 [*] Username (account login name) = user_001\0 ========= Special Directories ================= =>> AdminTools = C:\Users\user_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools =>> AppData = C:\Users\user_001\AppData\Roaming =>> LocalAppData = C:\Users\user_001\AppData\Local =>> CommonAppData = C:\ProgramData =>> Common Admin Tools = C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools =>> Common Documents = C:\Users\Public\Documents =>> My Pictures = C:\Users\user_001\Pictures =>> Personal Documents = C:\Users\user_001\Documents =>> Recent Folder = C:\Users\user_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Recent =>> Internet Cache = C:\Users\user_001\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\INetCache =>> System Folder = C:\WINDOWS\system32 =>> Windows Folder C:\WINDOWS =>> Program Files Folder = C:\Program Files =>> Program Files Common Folder = C:\Program Files\Common Files =>> Startup Folder = C:\Users\user_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup =>> Startup Menu Folder = C:\Users\user_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu =>> Sendto Folder = C:\Users\user_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\SendTo
1.12.3 D - DLang Sample Code Version
Definition of SYTEM_INFO struct in C (MSDN Docs)
typedef struct _SYSTEM_INFO { union { DWORD dwOemId; struct { WORD wProcessorArchitecture; WORD wReserved; } DUMMYSTRUCTNAME; } DUMMYUNIONNAME; DWORD dwPageSize; LPVOID lpMinimumApplicationAddress; LPVOID lpMaximumApplicationAddress; DWORD_PTR dwActiveProcessorMask; DWORD dwNumberOfProcessors; DWORD dwProcessorType; DWORD dwAllocationGranularity; WORD wProcessorLevel; WORD wProcessorRevision; } SYSTEM_INFO, *LPSYSTEM_INFO;
The last line: '} SYSTEM_INFO, *LPSYSTEM_INFO;' is equivalent to the following statement in C or C++:
// Equivalent statement in C or old C++-style typedef struct _SYSTEM_INFO SYSTEM_INFO; // Equivalent statement in modern C++ using SYSTEM_INFO = struct _SYSTEM_INFO; // Equivalent statement in C or old C++-style typedef struct _SYSTEM_INFO * LPSYSTEM_INFO; // Equivalent statement in modern C++ using LPSYSTEM_INFO = struct _SYSTEM_INFO *;
Definition MEMORYSTATUSEX in C: (MSDN)
typedef struct _MEMORYSTATUSEX { DWORD dwLength; DWORD dwMemoryLoad; DWORDLONG ullTotalPhys; DWORDLONG ullAvailPhys; DWORDLONG ullTotalPageFile; DWORDLONG ullAvailPageFile; DWORDLONG ullTotalVirtual; DWORDLONG ullAvailVirtual; DWORDLONG ullAvailExtendedVirtual; } MEMORYSTATUSEX, *LPMEMORYSTATUSEX;
Files
File: systeminfo.d
import std.stdio; import core.stdc.stdio; import std.range: empty; import std.string; import core.stdc.string: strlen; import std.conv : to; //---- Useful type aliases ------------// alias HANDLE = void*; alias HWND = void*; alias LPCSTR = const char*; alias LPSTR = char*; alias WORD = short; alias DWORD = int; alias DWORD_PTR = DWORD*; alias LPDWORD = DWORD*; alias UINT = uint; alias HRESULT = long; alias BOOL = int; alias ULONGLONG = long; // int64 - 64 bits alias DWORDLONG = long; alias LPVOID = void*; int main() { printf(" [TRACE] Started D application. Ok \n\n"); writeln("\n ======== General Basic Info =================\n"); writeln(" [INFO] Computer Name = ", computer_name()); writeln(" [INFO] Windows System Directory path = " , wrap_function(&GetSystemWindowsDirectoryA ) ); writeln(" [INFO] Windows Directory = " , wrap_function(&GetSystemDirectoryA)); writeln(" [INFO] Windows Wow64 Directory = " , wrap_function(&GetSystemWow64DirectoryA) ); writeln("\n ======== Processor Information ============\n"); show_processor_info(); writeln("\n ======== Memory Information ================\n"); MEMORYSTATUSEX st; st.dwLength = st.sizeof ; GlobalMemoryStatusEx(&st); // Factor => Bytes to megabytes const double factor = 1.0 / (1024 * 1024 ); printf(" [*] Percent of total physical memory used = %ld \n", st.dwMemoryLoad); printf(" [*] Total physical memory in Megabytes = %.3f \n", st.ullTotalPhys * factor ); printf(" [*] Free memory in MB form total physical memory = %.3f \n", st.ullAvailPhys * factor ); printf(" [*] Total size of page file in MB = %.3f \n", st.ullTotalPageFile * factor ); printf(" [*] Free memory of page file MB = %.3f \n", st.ullAvailPageFile * factor ); printf(" [*] Total virtual memory in MB = %.3f \n", st.ullTotalVirtual * factor ); printf(" [*] Free virtual memory MB = %.3f \n", st.ullAvailVirtual * factor ); printf(" [*] Amount of extended memory available in MB = %.3f \n", st.ullAvailExtendedVirtual * factor ); writeln("\n =========== Directory Paths ===============\n"); writeln(" [INFO] Profiles path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_PROFILE) ); writeln(" [INFO] AppData path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_APPDATA) ); writeln(" [INFO] LocalAppData path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA) ); writeln(" [INFO] Start menu path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_STARTMENU) ); writeln(" [INFO] Desktop path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_DESKTOP) ); writeln(" [INFO] Admin Tools Path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_ADMINTOOLS) ); writeln(" [INFO] Favorite path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_FAVORITES) ); writeln(" [INFO] Startup path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_STARTUP) ); writeln(" [INFO] Recent folder path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_RECENT) ); writeln(" [INFO] Sendto path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_SENDTO) ); writeln(" [INFO] Program path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_PROGRAM_FILES) ); writeln(" [INFO] Windows path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_WINDOWS) ); writeln(" [INFO] System path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_SYSTEM) ); writeln(" [INFO] Fonts folder = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_FONTS) ); writeln(" [INFO] System 86 path = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_SYSTEMX86) ); writeln(" [INFO] Progrm Files x86 = ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_PROGRAM_FILESX86)); // Display Final Message is graphical GUI modal dialog. MessageBoxA( // Pointer null // Text - content , "Application terminated Ok" // Title , "Notification" // Flags , 0x00000000 | 0x00000020 ); writeln(" [TRACE] Terminated gracefully. Ok "); return 0; } // ===========================================================================// struct MEMORYSTATUSEX { DWORD dwLength; DWORD dwMemoryLoad; DWORDLONG ullTotalPhys; DWORDLONG ullAvailPhys; DWORDLONG ullTotalPageFile; DWORDLONG ullAvailPageFile; DWORDLONG ullTotalVirtual; DWORDLONG ullAvailVirtual; DWORDLONG ullAvailExtendedVirtual; }; alias LPMEMORYSTATUSEX = MEMORYSTATUSEX*; struct SYSTEM_INFO { union DUMMYUNIONNAME { DWORD dwOemId; struct DUMMYSTRUCTNAME { WORD wProcessorArchitecture; WORD wReserved; }; DUMMYSTRUCTNAME proc; }; DUMMYUNIONNAME dummy; DWORD dwPageSize; LPVOID lpMinimumApplicationAddress; LPVOID lpMaximumApplicationAddress; DWORD_PTR dwActiveProcessorMask; DWORD dwNumberOfProcessors; DWORD dwProcessorType; DWORD dwAllocationGranularity; WORD wProcessorLevel; WORD wProcessorRevision; }; alias LPSYSTEM_INFO = SYSTEM_INFO*; extern(C) BOOL GetComputerNameA(LPSTR lpBuffer, LPDWORD nSize); extern(C) UINT GetSystemWindowsDirectoryA(LPSTR buffer, UINT size); extern(C) UINT GetSystemDirectoryA(LPSTR buffer, UINT size); extern(C) UINT GetSystemWow64DirectoryA(LPSTR buffer, UINT size); extern(Windows) int MessageBoxA(HWND hWnd, LPCSTR lpText, LPCSTR lpCaption, UINT uType); extern (Windows) HRESULT SHGetFolderPathA( HWND hwnd, int csidl, HANDLE hToken , DWORD flag, LPSTR path); extern(Windows) BOOL GlobalMemoryStatusEx(LPMEMORYSTATUSEX lpBuffer); extern(C) void GetNativeSystemInfo(LPSYSTEM_INFO lpSystemInfo); // Type alias for C function pointer alias callback_t = extern(C) UINT function(LPSTR buffer, UINT size); string wrap_function(callback_t callback) { // Stack-allocated buffer, similar to char buffer[2048] in C or C++. char[2048] buffer; UINT len = callback(&buffer[0], 2048); string res = to!string(buffer[0 .. len]); return res; } string get_sh_folder_path(int csidl) { char[600] buffer; SHGetFolderPathA(null, csidl, null, 0, &buffer[0]); // Obtain number of characters until `\0` null char is found. auto len = strlen( cast(const char*) buffer); // Remove trailing null characters string res = to!string(buffer[0 .. len]); return res; } string computer_name() { char[600] buffer; DWORD size = 600; BOOL status = GetComputerNameA(&buffer[0], &size); assert( status == 1); auto len = strlen( cast(const char*) buffer); string res = to!string(buffer[0 .. len]); return res; } const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_INTEL = 0; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_MIPS = 1; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_ALPHA = 2; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_PPC = 3; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_SHX = 4; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_ARM = 5; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_IA64 = 6; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_ALPHA64 = 7; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_MSIL = 8; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_AMD64 = 9; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_ARM64 = 12; const DWORD PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_UNKNOWN = 0xFFFF; void show_processor_info() { SYSTEM_INFO info; GetNativeSystemInfo(&info); auto arch = info.dummy.proc.wProcessorArchitecture; writeln(" [*] Processor architecture = ", arch); writeln(" [*] Processor arch is x86 = " , PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_INTEL == cast(int) arch ? "TRUE" : "FALSE"); writeln(" [*] Processor arch is AMD64 x64 (AMD or Intel) = " , PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_AMD64 == cast(int) arch ? "TRUE" : "FALSE"); writeln(" [*] Processor arch is ARM = " , PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_ARM == cast(int) arch ? "TRUE" : "FALSE"); writeln(" [*] Processor arch is ARM64 = " , PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_ARM64 == cast(int) arch ? "TRUE" : "FALSE"); writeln(" [*] Page size (virtual memory) in bytes = ", info.dwPageSize); writeln(" [*] Number of processors = ", info.dwNumberOfProcessors); } const int CSIDL_PROFILE = 0x0028; const int CSIDL_DESKTOP = 0x0000; const int CSIDL_PROGRAMS = 0x0002; const int CSIDL_STARTMENU = 0x000b; const int CSIDL_APPDATA = 0x001a; const int CSIDL_PROGRAM_FILES = 0x0026; const int CSIDL_ADMINTOOLS = 0x0030; const int CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA = 0x001c; const int CSIDL_FAVORITES = 0x0006; const int CSIDL_STARTUP = 0x0007; const int CSIDL_RECENT = 0x0008; const int CSIDL_SENDTO = 0x0009; const int CSIDL_WINDOWS = 0x0024; const int CSIDL_SYSTEM = 0x0025; const int CSIDL_FONTS = 0x0014; const int CSIDL_PROGRAM_FILESX86 = 0x002a; const int CSIDL_SYSTEMX86 = 0x0029;
Building
$ dmd sysinfo.d -m64 Kernel32.lib Ntdll.lib User32.lib
Analyzing the PE32 executable binary file
# Location of tool $ where ldd C:\Users\User_001\scoop\apps\git\current\usr\bin\ldd.exe # Location of tool $ where file C:\Users\User_001\scoop\apps\git\current\usr\bin\file.exe # Check file type $ file sysinfo.exe sysinfo.exe: PE32+ executable (console) x86-64, for MS Windows # Check file size in Kilo bytes (Kbytes) $ du -h sysinfo.exe 476K sysinfo.exe # View dependencies (Shared libraries) $ ldd sysinfo.exe ntdll.dll => /c/WINDOWS/SYSTEM32/ntdll.dll (0x7ffe52eb0000) KERNEL32.DLL => /c/WINDOWS/System32/KERNEL32.DLL (0x7ffe510c0000) KERNELBASE.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/KERNELBASE.dll (0x7ffe50b30000) USER32.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/USER32.dll (0x7ffe51920000) win32u.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/win32u.dll (0x7ffe50870000) GDI32.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/GDI32.dll (0x7ffe515c0000) gdi32full.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/gdi32full.dll (0x7ffe50e00000) msvcp_win.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/msvcp_win.dll (0x7ffe50720000) ucrtbase.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/ucrtbase.dll (0x7ffe505f0000) SHELL32.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/SHELL32.dll (0x7ffe51ac0000)
Running
$ .\sysinfo.exe [TRACE] Started D application. Ok ======== General Basic Info ================= [INFO] Computer Name = DESKTOP-GLXQAB76A [INFO] Windows System Directory path = C:\WINDOWS [INFO] Windows Directory = C:\WINDOWS\system32 [INFO] Windows Wow64 Directory = C:\WINDOWS\SysWOW64 ======== Processor Information ============ [*] Processor architecture = 9 [*] Processor arch is x86 = FALSE [*] Processor arch is AMD64 x64 (AMD or Intel) = TRUE [*] Processor arch is ARM = FALSE [*] Processor arch is ARM64 = FALSE [*] Page size (virtual memory) in bytes = 4096 [*] Number of processors = 2 ======== Memory Information ================ [*] Percent of total physical memory used = 40 [*] Total physical memory in Megabytes = 4095.484 [*] Free memory in MB form total physical memory = 2447.137 [*] Total size of page file in MB = 4799.484 [*] Free memory of page file MB = 2882.293 [*] Total virtual memory in MB = 134217727.875 [*] Free virtual memory MB = 134213528.680 [*] Amount of extended memory available in MB = 0.000 =========== Directory Paths =============== [INFO] Profiles path = C:\Users\User_001 [INFO] AppData path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming [INFO] LocalAppData path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Local [INFO] Start menu path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu [INFO] Desktop path = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop [INFO] Admin Tools Path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools [INFO] Favorite path = C:\Users\User_001\Favorites [INFO] Startup path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup [INFO] Recent folder path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Recent [INFO] Sendto path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\SendTo [INFO] Program path = C:\Program Files [INFO] Windows path = C:\WINDOWS [INFO] System path = C:\WINDOWS\system32 [INFO] Fonts folder = C:\WINDOWS\Fonts [INFO] System 86 path = C:\WINDOWS\SysWOW64 [INFO] Progrm Files x86 = C:\Program Files (x86) [TRACE] Terminated gracefully. Ok
1.12.4 Rust Sample Code Version
This rust version is an stil incomplete attempt of rewrite the C++ version.
- Note: The CSIDL_ constants are extracted from shlobj.h (React-OS source).
File: sysinfo.rs
#[allow(warnings, unused_variables)] #[allow(warnings, unused_imports)] #[allow(dead_code)] #[allow(warnings, unused_mut)] use std::os::raw::{c_int, c_char, c_long, c_void, c_uint}; use std::ffi::CString; // Useful Type aliases type HANDLE = *mut c_void; type HWND = *mut c_void; type LPCSTR = *const c_char; type LPSTR = *mut u8; type DWORD = c_int; type UINT = c_uint; type HRESULT = c_long; type BOOL = c_int; fn main() { // The type [u8, 400] => Is similar to C++ type: uint8_t var[400] // or to the type std::array<uint8_t, 400>. let mut buffer2: [u8; 400] = [0; 400]; let mut nread: UINT; unsafe { //GetSystemWindowsDirectoryA(buffer.as_mut_ptr(), buffer_size as UINT ); nread = GetSystemWindowsDirectoryA(buffer2.as_mut_ptr(), buffer2.len() as UINT); } // println!(" [INFO] Windows path = {:?}", buffer); // println!(" [INFO] Buffer2 = {:?}", buffer2); let s = std::str::from_utf8(&buffer2[..(nread as usize)]).unwrap(); println!(" [INFO] Windows System Directory Path[2] = {:?}", s); println!(" [INFO] Windows System Directory Path[1] = {}" , wrap_function(GetSystemWindowsDirectoryA) ); println!(" [INFO] Windows Directory = {} " , wrap_function(GetSystemDirectoryA) ); println!(" [INFO] Windows Wow64 Directory = {} " , wrap_function(GetSystemWow64DirectoryA) ); const CSIDL_PROFILE: c_int = 0x0028; const CSIDL_DESKTOP: c_int = 0x0000; const CSIDL_PROGRAMS: c_int = 0x0002; const CSIDL_STARTMENU: c_int = 0x000b; const CSIDL_APPDATA: c_int = 0x001a; const CSIDL_PROGRAM_FILES: c_int = 0x0026; const CSIDL_ADMINTOOLS: c_int = 0x0030; const CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA: c_int = 0x001c; const CSIDL_FAVORITES: c_int = 0x0006; const CSIDL_STARTUP: c_int = 0x0007; const CSIDL_RECENT: c_int = 0x0008; const CSIDL_SENDTO: c_int = 0x0009; const CSIDL_WINDOWS: c_int = 0x0024; const CSIDL_SYSTEM: c_int = 0x0025; const CSIDL_FONTS: c_int = 0x0014; const CSIDL_PROGRAM_FILESX86: c_int = 0x002a; const CSIDL_SYSTEMX86: c_int = 0x0029; println!("\n =========================================="); println!(" [INFO] Profiles path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_PROFILE) ); println!(" [INFO] AppData path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_APPDATA) ); println!(" [INFO] LocalAppData path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA) ); println!(" [INFO] Start menu path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_STARTMENU) ); println!(" [INFO] Desktop path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_DESKTOP) ); println!(" [INFO] Admin Tools Path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_ADMINTOOLS) ); println!(" [INFO] Favorite path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_FAVORITES) ); println!(" [INFO] Startup path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_STARTUP) ); println!(" [INFO] Recent folder path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_RECENT) ); println!(" [INFO] Sendto path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_SENDTO) ); println!(" [INFO] Program path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_PROGRAM_FILES) ); println!(" [INFO] Windows path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_WINDOWS) ); println!(" [INFO] System path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_SYSTEM) ); println!(" [INFO] Fonts folder = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_FONTS) ); println!(" [INFO] System 86 path = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_SYSTEMX86) ); println!(" [INFO] Progrm Files x86 = {} ", get_sh_folder_path(CSIDL_PROGRAM_FILESX86)); } //========================================================// #[link(name = "shell32")] extern "C" { fn SHGetFolderPathA( hwnd: HWND, csidl: c_int , hToken: HANDLE, flag: DWORD, path: LPSTR) -> HRESULT; } fn get_sh_folder_path(csidl: c_int) -> String { const max_path: usize = 260; let mut buffer: [u8; max_path] = [0; max_path]; let status: HRESULT; unsafe { status = SHGetFolderPathA( std::ptr::null_mut() , csidl , std::ptr::null_mut() , 0 , buffer.as_mut_ptr() ); } assert!( status >= 0); let st = std::str::from_utf8( &buffer[..(max_path)] ).unwrap(); let mut res: String = st.to_string(); // Remove \0 null characters. res = res.trim_matches(char::from(0)).to_string(); return res; } extern "C" { /* * UINT GetSystemWindowsDirectoryA( * LPSTR lpBuffer, * UINT uSize * ); **********************************************/ fn GetSystemWindowsDirectoryA(buffer: LPSTR, size: UINT) -> UINT; fn GetSystemDirectoryA(buffer: LPSTR, size: UINT) -> UINT; fn GetSystemWow64DirectoryA(buffer: LPSTR, size: UINT) -> UINT; } type Callback1 = unsafe extern "C" fn(buffer: LPSTR, size: UINT) -> UINT; fn wrap_function(callback: Callback1) -> String { let mut buffer2: [u8; 400] = [0; 400]; let mut nread: UINT = 0; unsafe { nread = callback(buffer2.as_mut_ptr(), buffer2.len() as UINT); } let s = std::str::from_utf8(&buffer2[..(nread as usize)]).unwrap(); return s.to_string(); }
Building
$ rustc sysinfo.rs
Analyzing the PE32 executable binary file
$ where ldd C:\Users\User_001\scoop\apps\git\current\usr\bin\ldd.exe $ where file C:\Users\User_001\scoop\apps\git\current\usr\bin\file.exe $ file sysinfo.exe sysinfo.exe: PE32+ executable (console) x86-64, for MS Windows $ du -h sysinfo.exe 172K sysinfo.exe $ ldd sysinfo.exe ntdll.dll => /c/WINDOWS/SYSTEM32/ntdll.dll (0x7ffe52eb0000) KERNEL32.DLL => /c/WINDOWS/System32/KERNEL32.DLL (0x7ffe510c0000) KERNELBASE.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/KERNELBASE.dll (0x7ffe50b30000) SHELL32.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/SHELL32.dll (0x7ffe51ac0000) msvcp_win.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/msvcp_win.dll (0x7ffe50720000) ucrtbase.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/ucrtbase.dll (0x7ffe505f0000) USER32.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/USER32.dll (0x7ffe51920000) win32u.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/win32u.dll (0x7ffe50870000) GDI32.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/GDI32.dll (0x7ffe515c0000) gdi32full.dll => /c/WINDOWS/System32/gdi32full.dll (0x7ffe50e00000) VCRUNTIME140.dll => /c/WINDOWS/SYSTEM32/VCRUNTIME140.dll (0x7ffe49e30000)
Running
$ .\sysinfo.exe
[INFO] Windows System Directory Path[2] = "C:\\WINDOWS"
[INFO] Windows System Directory Path[1] = C:\WINDOWS
[INFO] Windows Directory = C:\WINDOWS\system32
[INFO] Windows Wow64 Directory = C:\WINDOWS\SysWOW64
==========================================
[INFO] Profiles path = C:\Users\User_001
[INFO] AppData path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming
[INFO] LocalAppData path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Local
[INFO] Start menu path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu
[INFO] Desktop path = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop
[INFO] Admin Tools Path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools
[INFO] Favorite path = C:\Users\User_001\Favorites
[INFO] Startup path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup
[INFO] Recent folder path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Recent
[INFO] Sendto path = C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\SendTo
[INFO] Program path = C:\Program Files
[INFO] Windows path = C:\WINDOWS
[INFO] System path = C:\WINDOWS\system32
[INFO] Fonts folder = C:\WINDOWS\Fonts
[INFO] System 86 path = C:\WINDOWS\SysWOW64
[INFO] Progrm Files x86 = C:\Program Files (x86)
1.13 Windows Shortcut - LNK
1.13.1 Overview
The following code snippet creates several Windows shortcuts, also known as Windows Shell Link (*.lnk files), which are similar to Unix's symbolic links and Free-Desktop .desktop (FreeDesktop standard) launchers used on X11. Shell link files allows creating launchers to executable and directories. Unlike the X11 Free-Desktop standard *.desktop files, which are text files, the Windows shell link files are structured binary files, as a result, they only can be viewed by using Windows facilities or by using a hexadecimal editor.
Documentation
- Shell Links
- IUnknown COM Interface (header: unknown.h)
- Brief: "Enables clients to get pointers to other interfaces on a given object through the QueryInterface method, and manage the existence of the object through the AddRef and Release methods. All other COM interfaces are inherited, directly or indirectly, from IUnknown. Therefore, the three methods in IUnknown are the first entries in the vtable for every interface."
- IShellLinkA COM Interface (header: shobjidl_core.h)
- Brief: "Exposes methods that create, modify, and resolve Shell links."
- IPersist COM Interface (header: objidl.h)
- Brief: "Provides the CLSID of an object that can be stored persistently in the system. Allows the object to specify which object handler to use in the client process, as it is used in the default implementation of marshaling."
- CoCreateInstance()
- Brief: "Creates and default-initializes a single object of the class associated with a specified CLSID."
- Creating an Object in COM
Windows Shortcut Binary Format Specification:
- {MS-SHLLINK}: Shell Link (.LNK) Binary File Format
- Official specification of the Windows LNK file format.
- Windows shell link file: format specification
- Kaitai Format Gallery.
- The Windows Shortcut Format [PDF] (Jesse Hager)
- File: mkshelllink.c - ReactorOS implementation.
X11 Free Desktop Shortcut Specification (for comparison)
- https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Freedesktop.org
- Desktop Entry Specification
- Specification of *.desktop shortcut files used on Linux and BSD X11 or Wayland desktop environments.
- ArchLinux - Desktop Entries
- Desktop files: putting your application in the desktop menus
1.13.2 Creating shell link
This sample application instantiates an object of COM (Component Object Model) class ShellLink and obtains the two interface pointers to the object, IShellLinkA and IPersistFile for creating Windows shell links, LNK shortcut files.
Files
File: winshortcut.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #define INITGUID // Necessary for MINGW #include <windows.h> #include <shlobj.h> #include <shobjidl.h> #include <shlguid.h> #include <comdef.h> #include <comdefsp.h> // Get environment variable std::string get_envvar(std::string const& name); // Create Windows Shortcut (aka shell Link - LNK File) BOOL createWindowsShortcut( std::string const& fileName , std::string const& arguments , std::string const& path , std::string const& title); int main() { const auto homedir= get_envvar("USERPROFILE"); const auto desktop_dir = homedir + "\\Desktop"; std::fprintf(stderr, " [TRACE] Desktop dir = %s \n", desktop_dir.c_str()); // Create shortcut to Notepad.exe at user's Desktop directory. createWindowsShortcut( // Executable or command that the shortcut will launch. "notepad.exe" // Arguments used by Notepad.exe , "" // Absolute path to where the shortcut will be created. , desktop_dir + "\\Notepad.lnk" , "Shortcut for notepad.exe" ); // Create shortcut for the DxDiag.exe utility createWindowsShortcut( // Executable or command that the shortcut will launch. "dxdiag" , "" // Absolute path to where the shortcut will be created. , desktop_dir + "\\DxDiagTool.lnk" , "Shortcut for DirectX and OpenGL diagnosing tool." ); // Create shortcut to user's home directory createWindowsShortcut( homedir , "" , desktop_dir + "\\HomeDirectory.lnk" , "Shortcut for my documents" ); // Create shortcut to Device Manager for viewing user hardware settings. createWindowsShortcut( "RunDll32.exe" , "devmgr.dll DeviceManager_Execute" , desktop_dir + "\\Device_Manager.lnk" , "Shortcut for device manager." ); // Create shortcut for starting Notepad.exe automatically after reboot. createWindowsShortcut( "notepad.exe" , "" , homedir + "\\Start Menu\\Programs\\Startup\\MyNotepad.lnk" , "Notepad.exe tools" ); std::fprintf(stderr, " [TRACE] Application terminated Ok. \n"); return 0; } // ==== I M P L E M E N T A T I O N S ============== // std::string get_envvar(std::string const& name) { const char* p = std::getenv(name.c_str()); if( p == nullptr){ return ""; } return p; } BOOL createWindowsShortcut( // Executable or command launched by the Windows shortcut std::string const& filePath_ // Arguments used by the executable , std::string const& args_ // Absolute path to where the shortcut file will be created. // Note: This path must include the extenion .lnk, for instance // this argument could be: "C:\\Users\\MyUser\\Desktop\\Notepad.exe" , std::string const& path_ // Title or description of the shortcut file. , std::string const& title_ ) { const char* fileName = filePath_.c_str(); const char* args = args_.c_str(); const char* path = path_.c_str(); const char* title = title_.c_str(); std::fprintf(stderr, "\n [TRACE] Creating shortcut for command = '%s' \n", fileName); std::fprintf(stderr, " [TRACE] Creating shortcut as file = '%s' \n", path); // Intialize COM CoInitializeEx( NULL, 0 ); // Pointer to COM interface IShellLink* ptr_com = nullptr; HRESULT hres = CoCreateInstance( // CLSID =>> Unique universal identifier for Shell Link class // The class is the concrete implememntation of a COM Interface // (COM - Component Object Model) CLSID_ShellLink , NULL // This constant 'CLSCTX_INPROC_SERVER' means that the // COM server is in-process,in other words, the COM server // is provide by a DLL (Dynamic Linked Library) , CLSCTX_INPROC_SERVER // IID (Interface Identifier) => Unique universal identifier (GUID) // for the COM interface that the COM class conforms to. , IID_IShellLink // void** => [OUTPUT] Parameter that returns pointer to COM // Interface , reinterpret_cast<LPVOID*>(&ptr_com) ); if( !SUCCEEDED(hres) ){ return FALSE; } assert( ptr_com != nullptr ); IPersistFile* ptr_com2 = nullptr; // Query comp object pointed by ptr_com and check whether // it implements the interface IPersistFile. If the query is // successful, the pointer ptr_com2 will be not NULL. // LPVOID = void** hres = ptr_com->QueryInterface(IID_IPersistFile, (void**) &ptr_com2); if( !SUCCEEDED(hres) ){ return FALSE; } assert( ptr_com2 != nullptr ); ptr_com->SetPath(fileName); ptr_com->SetDescription(title); if(args_ != ""){ ptr_com->SetArguments(args); } WCHAR out_path[MAX_PATH]; // Change string to Unicode MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP, 0, path, -1, out_path, MAX_PATH); // Save Windows shortcut ptr_com2->Save(out_path, TRUE); // Release COM interface pointers ptr_com2->Release(); ptr_com->Release(); CoUninitialize(); return TRUE; }
Building with Mingw
$ g++ winshortcut.cpp -o winshortcut-mingw.exe -std=c++1z -lole32 -loleaut32 -Wall -Wextra -g
Building with MSVC CL.exe
$ cl.exe winshortcut.cpp Microsoft (R) C/C++ Optimizing Compiler Version 19.28.29335 for x64 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. winshortcut.cpp Microsoft (R) Incremental Linker Version 14.28.29335.0 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. /out:winshortcut.exe winshortcut.obj
Analyse the files with 'file' Linux tool from GIT
$ file winshortcut.exe winshortcut.exe: PE32+ executable (console) x86-64, for MS Windows $ file winshortcut-mingw.exe winshortcut-mingw.exe: PE32+ executable (console) x86-64, for MS Windows $ file winshortcut.obj winshortcut.obj: Intel amd64 COFF object file, not stripped, 881 sections, symbol offset=0x106a9, 2772 symbols
Run application for creating Windows shortcuts
- After the application is run, the shortcuts can be executed either from command line or by clicking at them at the Desktop directory.
$ .\winshortcut.exe [TRACE] Desktop dir = C:\Users\user_001\Desktop [TRACE] Creating shortcut for command = 'notepad.exe' [TRACE] Creating shortcut as file = 'C:\Users\user_001\Desktop\Notepad.lnk' [TRACE] Creating shortcut for command = 'dxdiag' [TRACE] Creating shortcut as file = 'C:\Users\user_001\Desktop\DxDiagTool.lnk' [TRACE] Creating shortcut for command = 'C:\Users\user_001' [TRACE] Creating shortcut as file = 'C:\Users\user_001\Desktop\HomeDirectory.lnk' [TRACE] Creating shortcut for command = 'RunDll32.exe' [TRACE] Creating shortcut as file = 'C:\Users\user_001\Desktop\Device_Manager.lnk' [TRACE] Creating shortcut for command = 'notepad.exe' [TRACE] Creating shortcut as file = 'C:\Users\user_001\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\MyNotepad.lnk' [TRACE] Application terminated Ok.
Run shortcuts from command line
List all shortcut files at Desktop directory:
$ ls %USERPROFILE%/Desktop/*.lnk 'C:\Users\user_001/Desktop/CodeBlocks.lnk'* 'C:\Users\user_001/Desktop/Device_Manager.lnk'* 'C:\Users\user_001/Desktop/DxDiagTool.lnk'* 'C:\Users\user_001/Desktop/HomeDirectory.lnk'* 'C:\Users\user_001/Desktop/Notepad.lnk'*
View shortcut files:
$ file Notepad.lnk Notepad.lnk: MS Windows shortcut, Item id list present , Has Description string, Has Relative path , ctime=Mon Jan 1 08:00:00 1601 , mtime=Mon Jan 1 08:00:00 1601, atime=Mon Jan 1 08:00:00 1601, length=0, window=hide $ file DxDiagTool.lnk DxDiagTool.lnk: MS Windows shortcut, Item id list present, Has Description string, Has Relative path, ctime=Mon Jan 1 08:00:00 1601, mtime=Mon Jan 1 08:00:00 1601, atime=Mon Jan 1 08:00:00 1601, length=0, window=hide
Run shortcut from command line:
# Run shortcut lnk that launches Notepad.exe $ .\\Notepad.lnk # Run shortcut lnk that launches DxDiagTool.lnk $ .\DxDiagTool.lnk # Run shortcutr that opens the directory C:\\Users\user_001 (%USERPROFILE%) directory $ HomeDirectory.lnk
1.13.3 Reading shell link
This application prints information about Windows shell link files LNK (extension .lnk). It displays the path to shell link file, the command line arguments passed to the executable, the working directory and the icon path.
Files:
File: lnkdump.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #define INITGUID // Necessary for MINGW #include <windows.h> #include <shlobj.h> #include <shobjidl.h> #include <shlguid.h> #include <comdef.h> #include <comdefsp.h> std::string guid_to_string(GUID g); int main(int argc, char** argv) { if(argc < 2) { std::fprintf( stderr , "\n Read Windows shell link shortcut files LNK (*.lnk extension) " "\n Usage: " "\n $ lnkdump <SHELL-LINK-FILE> " ); return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::string file = argv[1]; // Display UUID of COM interfaces and classes if( file == "guid" ) { std::fprintf( stderr, " [INFO] (class) CLSID_ShellLink = %s \n" , guid_to_string(CLSID_ShellLink).c_str() ); std::fprintf( stderr, " [INFO] (interface) IID_IUnknown = %s \n" , guid_to_string(IID_IUnknown).c_str()); std::fprintf( stderr, " [INFO] (interface) IID_IDispatch = %s \n" , guid_to_string(IID_IDispatch).c_str()); std::fprintf( stderr, " [INFO] (interface) IID_IShellLink = %s \n" , guid_to_string(IID_IShellLink).c_str()); std::fprintf( stderr, " [INFO] (interface) IID_IPersistFile = %s \n" , guid_to_string(IID_IPersistFile).c_str()); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } // Intialize COM CoInitializeEx( NULL, 0 ); // Pointer to COM interface IShellLinkA* ptr_com = nullptr; HRESULT hres = CoCreateInstance( CLSID_ShellLink , NULL , CLSCTX_INPROC_SERVER , IID_IShellLink , reinterpret_cast<void**>(&ptr_com) ); if( !SUCCEEDED(hres) ){ return FALSE; } assert( ptr_com != nullptr ); // Pointer to IPersisteFile => Not allocated by the caller. IPersistFile* ptr_com2; // Retrieve interface from COM object hres = ptr_com->QueryInterface( IID_IPersistFile, (void**) &ptr_com2); assert( SUCCEEDED(hres) ); assert( ptr_com2 != nullptr ); WCHAR fpath_wchar[MAX_PATH]; // Convert to UTF16 unicode wide character MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP, 0, file.c_str(), -1, fpath_wchar, MAX_PATH); hres = ptr_com2->Load(fpath_wchar, STGM_READ); assert( SUCCEEDED(hres) && "Failed to read shortcut" ); // Resolve shell link hres = ptr_com->Resolve(nullptr, 0); assert( SUCCEEDED(hres) && "Failed to resolve shell link" ); // ===== Read shortcut LNK data ======================/// std::string path, arguments, description, directory, icon; char buffer[MAX_PATH]; // Get shortcut description hres = ptr_com->GetDescription(buffer, MAX_PATH); if( !SUCCEEDED(hres) ){ std::fprintf(stderr, " [WARN] Failed to get description \n" ); } description = buffer; // Get path to shell link target, application called by the // shell link. WIN32_FIND_DATA wfd; hres = ptr_com->GetPath( buffer , MAX_PATH , reinterpret_cast<WIN32_FIND_DATA*>(&wfd) , SLGP_SHORTPATH ); assert( SUCCEEDED(hres) ); path = buffer; // Get working directory of shell link hres = ptr_com->GetWorkingDirectory(buffer, MAX_PATH); assert( SUCCEEDED(hres) ); directory = buffer; // Get working directory of shell link hres = ptr_com->GetArguments(buffer, MAX_PATH); assert( SUCCEEDED(hres) ); arguments = buffer; // Get Icon location int n = 0; hres = ptr_com->GetIconLocation(buffer, MAX_PATH, &n); assert( SUCCEEDED(hres) ); icon = buffer; // Get hotkey WORD Hotkey = 0; hres = ptr_com->GetHotkey(&Hotkey); assert( SUCCEEDED(hres) ); std::cout << " [*] Path = " << path << '\n'; std::cout << " [*] Arguments = " << arguments << '\n'; std::cout << " [*] Description = " << description << '\n'; std::cout << " [*] Working dir = " << directory << '\n'; std::cout << " [*] Icon = " << icon << '\n'; std::cout << " [*] Hotkey = " << Hotkey << '\n'; // Release COM interface pointers ptr_com->Release(); ptr_com2->Release(); // Shutdown COM CoUninitialize(); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } // ------ End of main -----------// // ================================// // Print GUID (Global Unique Identifier) //or UUID (Universal Unique Identifier) std::string guid_to_string(GUID g) { constexpr size_t size = 300; char buffer[size]; memset(buffer, '\0' ,size); snprintf( buffer, size , "{%08lX-%04hX-%04hX-%02hhX%02hhX-%02hhX%02hhX%02hhX%02hhX%02hhX%02hhX}" , g.Data1, g.Data2, g.Data3 , g.Data4[0], g.Data4[1], g.Data4[2], g.Data4[3] , g.Data4[4], g.Data4[5], g.Data4[6], g.Data4[7]); std::string out = buffer; return out; }
Building:
$ g++ lnkdump.cpp -o lnkdump.exe -lole32 -loleaut32 -lcomctl32 -luuid -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g
Running
Show help:
$ lnkdump.exe Read Windows shell link shortcut files LNK (*.lnk extension) Usage: $ lnkdump <SHELL-LINK-FILE>
Display the GUID (Global Unique Identifier) of COM interfaces and classes:
$ lnkdump.exe guid
[INFO] (class) CLSID_ShellLink = {00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}
[INFO] (interface) IID_IUnknown = {00000000-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}
[INFO] (interface) IID_IDispatch = {00020400-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}
[INFO] (interface) IID_IShellLink = {000214EE-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}
[INFO] (interface) IID_IPersistFile = {0000010B-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}
Inspect LNK (Windows shortcut) files:
$ lnkdump.exe "x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2019.lnk" [*] Path = C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe [*] Arguments = /k "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat" [*] Description = Open Visual Studio 2019 Tools Command Prompt for targeting x64 [*] Working dir = C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\BuildTools\ [*] Icon = [*] Hotkey = 0 $ lnkdump.exe "Windows PowerShell (x86).lnk" [*] Path = C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe [*] Arguments = [*] Description = Performs object-based (command-line) functions [*] Working dir = %HOMEDRIVE%%HOMEPATH% [*] Icon = %SystemRoot%\syswow64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe [*] Hotkey = 0 $ lnkdump.exe "Windows PowerShell ISE.lnk" [*] Path = C:\Windows\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\PowerShell_ISE.exe [*] Arguments = [*] Description = Windows PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment. Performs object-based (command-line) functions [*] Working dir = %HOMEDRIVE%%HOMEPATH% [*] Icon = %SystemRoot%\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell_ise.exe [*] Hotkey = 0 $ lnkdump.exe Device_Manager.lnk [*] Path = C:\WINDOWS\system32\RunDll32.exe [*] Arguments = devmgr.dll DeviceManager_Execute [*] Description = Shortcut for device manager. [*] Working dir = [*] Icon = [*] Hotkey = 0 $ lnkdump.exe "Print Management.lnk" [*] Path = C:\WINDOWS\system32\printmanagement.msc [*] Arguments = [*] Description = Manages local printers and remote print servers. [*] Working dir = [*] Icon = %systemroot%\system32\pmcsnap.dll [*] Hotkey = 0 $ lnkdump.exe "Component Services.lnk" [*] Path = C:\WINDOWS\system32\comexp.msc [*] Arguments = [*] Description = Manage COM+ applications, COM and DCOM system configuration, and the Distributed Transaction Coordinator. [*] Working dir = [*] Icon = %systemroot%\system32\comres.dll [*] Hotkey = 0
Find COM In-process Server (DLL - shared library) that provides the COM class CLSID_ShellLink by using Powershell on the Visual Studio developer's prompt.
$ powershell
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Try the new cross-platform PowerShell https://aka.ms/pscore6
PS C:\> Get-ChildItem Registry::"HKCR\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
Hive: HKCR\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}
Name Property
---- --------
Implemented Categories
InProcServer32 (default) : C:\Windows\System32\windows.storage.dll
ThreadingModel : Both
OverrideFileSystemProperties System.Kind : 1
ProgID (default) : lnkfile
shellex
View DLL symbols:
PS C:\> dumpbin.exe /exports C:\Windows\System32\windows.storage.dll Microsoft (R) COFF/PE Dumper Version 14.28.29335.0 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Dump of file C:\Windows\System32\windows.storage.dll File Type: DLL Section contains the following exports for Windows.Storage.dll 00000000 characteristics 1FA0233D time date stamp 0.00 version 2 ordinal base 2008 number of functions 242 number of names ordinal hint RVA name 8 0 000651D0 AssocCreateForClasses ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 46 28 0018BF80 DllCanUnloadNow # <=== Functions that 47 29 00184BA0 DllGetActivationFactory # must be implemented by a COM server. 48 2A 000C6FE0 DllGetClassObject 49 2B 001C1A30 DllMain 50 2C 001AEFB0 DllRegisterServer 51 2D 001AEFB0 DllUnregisterServer ... ...... ..... .... ... ...... ..... .... ... ...... ..... .... ... ...... ..... .... ... ...... ..... .... ... ...... ..... .... Summary 9000 .data 3000 .didat 52000 .pdata 184000 .rdata 1F000 .reloc 4000 .rsrc 58A000 .text
1.14 Windows Registry
1.14.1 Overview
The Windows registry is a tree-like database used by the operating system and by other applications for storing system configurations and user-specific settings. The data is stored as a tree data structure, where each child node is a key and each key may have zero or more value, which a entry comprised of a label and value.
Documentation of Windows Registry APIs
- About the registry
- Structure of the Registry
- Predefined Keys
- Function: RegOpenKeyExA()
- Brief: "Opens the specified registry key. Note that key names are not case sensitive."
- Function: RegOpenKeyExW()
- Brief: "Opens the specified registry key. Note that key names are not case sensitive."
- Function: RegEnumKeyA()
- Brief: "Enumerates the subkeys of the specified open registry key. The function retrieves the name of one subkey each time it is called."
- Function: RegEnumKeyExA()
- Brief: "Enumerates the subkeys of the specified open registry key. The function retrieves information about one subkey each time it is called."
- Function: RegEnumKeyExW()
- Brief: "Enumerates the subkeys of the specified open registry key. The function retrieves information about one subkey each time it is called."
- Function: RegGetValueA()
- Brief: "Retrieves the type and data for the specified registry value."
- Function: RegGetValueW()
- Brief: "Retrieves the type and data for the specified registry value."
- Function: RegQueryValueA()
- Brief: "Retrieves the data associated with the default or unnamed value of a specified registry key. The data must be a null-terminated string."
1.14.2 Notable Registry Locations
- Root Keys
HKLMorHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEHKCRorHKEY_CLASSES_ROOTHKCUorHKEY_CURRENT_USERHKCCorHKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\hivelist- Lists all paths to files where Windows registry data are stored.
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID- Contains all registered COM (Component Object Model) class ID as subkeys, where each subkey is a GUID (Universal Unique Identifier), a 128-bit unique random number encoded as hexadecimal.
- Example: The COM In-process server (
C:\Windows\System32\oleaut32.dll) has the CLSID - 0000002F-0000-0000-C000-000000000046 and the registry key:HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{0000002F-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}.
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Interface- Contains all COM interfaces registered in the systems. Each subkey is the interface IID (GUID - global unique identifier).
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\\Advancede- Windows Explorer settings.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\\CurrentControlSet\Services- Subkeys are services that launched at system startup time after reboot.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion- The entries (values) in this key, contains information about
the current Windows Version:
- Value: EditionID => (example: Professional)
- Value: ProductName => (example: Windows 10 Pro)
- Value: RegisteredOwner
- Value: CurrentBuild
- Value: BuildLab (example: 1941.vb_release.191206-1406)
- The entries (values) in this key, contains information about
the current Windows Version:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\App Paths- Every subkey entry is an application that can be launched without specifying the full from Windows-Key + R box or from terminal.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment- System-wide environment variables (defined for all users).
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment- User-specific environment variables.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\KnownDLLs
Windows Registry Files
The Windows registry data can be stored in several files in the system. Some of those files are:
- Directory:
%SystemRoot%\System32\config - File:
%UserProfile%\Ntuser.dat - FIle:
%UserProfile%\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\Windows\UsrClass.dat
List all files where Windows registry data are stored using PowerShell.
$ ItemProperty Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\hivelist \REGISTRY\MACHINE\HARDWARE : \REGISTRY\MACHINE\SYSTEM : \Device\HarddiskVolume2\Windows\System32\config\SYSTEM \REGISTRY\MACHINE\BCD00000000 : \Device\HarddiskVolume1\Boot\BCD \REGISTRY\MACHINE\SOFTWARE : \Device\HarddiskVolume2\Windows\System32\config\SOFTWARE \REGISTRY\USER\.DEFAULT : \Device\HarddiskVolume2\Windows\System32\config\DEFAULT \REGISTRY\MACHINE\SECURITY : \Device\HarddiskVolume2\Windows\System32\config\SECURITY \REGISTRY\MACHINE\SAM : \Device\HarddiskVolume2\Windows\System32\config\SAM \REGISTRY\USER\S-1-5-20 : \Device\HarddiskVolume2\Windows\ServiceProfiles\NetworkService\NTUSER.DAT \REGISTRY\USER\S-1-5-19 : \Device\HarddiskVolume2\Windows\ServiceProfiles\LocalService\NTUSER.DAT \REGISTRY\USER\S-1-5-21-795742887-3693175558-2200833936-1001 : \Device\HarddiskVolume2\Users\User_001\NTUSER.DAT \REGISTRY\USER\S-1-5-21-795742887-3693175558-2200833936-1001_Classes : \Device\HarddiskVolume2\Users\User_001\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\usrClass.dat PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\hivelist PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control PSChildName : hivelist PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
Query system-wide environment variables from registry:
PS C:\> ItemProperty Registry::"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" ComSpec : C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exe DriverData : C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\DriverData OS : Windows_NT PATHEXT : .COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD;.VBS;.VBE;.JS;.JSE;.WSF;.WSH;.MSC PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE : AMD64 PSModulePath : C:\Program Files\WindowsPowerShell\Modules;C:\WINDOWS\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\Modules TEMP : C:\WINDOWS\TEMP TMP : C:\WINDOWS\TEMP USERNAME : SYSTEM windir : C:\WINDOWS Path : C:\WINDOWS\system32;C:\WINDOWS;C:\WINDOWS\System32\Wbem;C:\WINDOWS\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\;C:\WINDOWS\System32\OpenSSH\;C:\Pr ogram Files\dotnet\;C:\ProgramData\chocolatey\bin;C:\D\dmd2\windows\bin ChocolateyInstall : C:\ProgramData\chocolatey NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS : 2 PROCESSOR_LEVEL : 6 PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER : Intel64 Family 6 Model 23 Stepping 3, GenuineIntel PROCESSOR_REVISION : 1703 PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager PSChildName : Environment PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
Query user-specific environment variables from registry:
$ powershell.exe Windows PowerShell Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Try the new cross-platform PowerShell https://aka.ms/pscore6 PS C:\> ItemProperty Registry::"HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment" TEMP : C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Local\Temp TMP : C:\Users\User_001\AppData\Local\Temp Path : C:\Users\User_001\.cargo\bin;C:\Users\User_001\scoop\apps\gcc\current\bin;... .... ps OneDrive : C:\Users\User_001\OneDrive GIT_INSTALL_ROOT : C:\Users\User_001\scoop\apps\git\current CMDER_ROOT : C:\Users\User_001\scoop\apps\cmder\current ConEmuDir : C:\Users\User_001\scoop\apps\cmder\current\vendor\conemu-maximus5 ChocolateyLastPathUpdate : 132545935735602224 PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER PSChildName : Environment PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
List all subkeys from the key App Paths" which are applications that can be launched without providing full path from Windows-Key+R box or from terminal:
PS C:\> Get-ChildItem -Path Registry::"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\App Paths" Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\App Paths Name Property ---- -------- cmmgr32.exe CmNative : 2 CmstpExtensionDll : C:\Windows\System32\cmcfg32.dll codeblocks.exe (default) : C:\Program Files (x86)\CodeBlocks\codeblocks.exe dfshim.dll UseURL : 1 firefox.exe (default) : C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\firefox.exe Path : C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox fsquirt.exe DropTarget : {047ea9a1-93cc-415a-a2d3-d7ffb3ca5187} IEDIAG.EXE (default) : C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\IEDIAGCMD.EXE Path : C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer; IEDIAGCMD.EXE (default) : C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\IEDIAGCMD.EXE Path : C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer; IEXPLORE.EXE (default) : C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\IEXPLORE.EXE Path : C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer; install.exe BlockOnTSNonInstallMode : 1 licensemanagershellext.exe (default) : C:\WINDOWS\System32\licensemanagershellext.exe mip.exe (default) : C:\Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Ink\mip.exe mplayer2.exe (default) : C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Media Player\wmplayer.exe Path : C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Media Player msedge.exe (default) : C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft\Edge\Application\msedge.exe Path : C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft\Edge\Application pbrush.exe (default) : C:\WINDOWS\System32\mspaint.exe Path : C:\WINDOWS\System32 PowerShell.exe (default) : C:\WINDOWS\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\PowerShell.exe setup.exe BlockOnTSNonInstallMode : 1 SnippingTool.exe (default) : C:\WINDOWS\system32\SnippingTool.exe table30.exe UseShortName : TabTip.exe (default) : C:\Program Files\Common Files\microsoft shared\ink\TabTip.exe wab.exe (default) : C:\Program Files\Windows Mail\wab.exe Path : C:\Program Files\Windows Mail wabmig.exe (default) : C:\Program Files\Windows Mail\wabmig.exe wmplayer.exe (default) : C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Media Player\wmplayer.exe Path : C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Media Player WORDPAD.EXE (default) : "C:\Program Files\Windows NT\Accessories\WORDPAD.EXE" WRITE.EXE (default) : "C:\Program Files\Windows NT\Accessories\WORDPAD.EXE"
Query all known DLLs:
$ powershell Windows PowerShell Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Try the new cross-platform PowerShell https://aka.ms/pscore6 PS> ItemProperty Registry::"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\KnownDLLs" _wow64cpu : wow64cpu.dll _wowarmhw : wowarmhw.dll _xtajit : xtajit.dll advapi32 : advapi32.dll clbcatq : clbcatq.dll combase : combase.dll COMDLG32 : COMDLG32.dll coml2 : coml2.dll DifxApi : difxapi.dll gdi32 : gdi32.dll gdiplus : gdiplus.dll IMAGEHLP : IMAGEHLP.dll IMM32 : IMM32.dll kernel32 : kernel32.dll MSCTF : MSCTF.dll MSVCRT : MSVCRT.dll NORMALIZ : NORMALIZ.dll NSI : NSI.dll ole32 : ole32.dll OLEAUT32 : OLEAUT32.dll PSAPI : PSAPI.DLL rpcrt4 : rpcrt4.dll sechost : sechost.dll Setupapi : Setupapi.dll SHCORE : SHCORE.dll SHELL32 : SHELL32.dll SHLWAPI : SHLWAPI.dll user32 : user32.dll WLDAP32 : WLDAP32.dll wow64 : wow64.dll wow64win : wow64win.dll WS2_32 : WS2_32.dll PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\KnownDLLs PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager PSChildName : KnownDLLs PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
See
1.14.3 Sample Code
Files
File: registry.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <map> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> constexpr size_t MAX_KEY_LENGTH = 255; constexpr size_t MAX_VALUE_NAME = 16383; // Read a value from registry key. std::string readRegistry_SZ( HKEY hkey , const std::string& path , const std::string& key ); std::string readRegistry_SZ( const std::string& full_path , const std::string& key ); // Read Dword from registry DWORD readRegistry_DW( HKEY hkey , const std::string& path , const std::string& key ); void enumKeyValues(HKEY root, std::string const& path) ; void enumKeys(HKEY root,std::string const& path, DWORD nmax_keys); int main() { const HKEY hkcu = HKEY_CURRENT_USER; std::puts("\n ====== [ STEP 1] ===== Show Registry Keys ====================\n"); { std::printf(" =>> Windows Explorer Settings ==== \n"); const char* path = "Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Explorer\\Advanced"; enumKeyValues(HKEY_CURRENT_USER, path); } std::puts("\n====== [ STEP 2 ] ====== Reading Windows Explorer Settings=====\n"); { std::printf(" Location of COM Server with CLSID = {EC231970-6AFD-4215-A72E-97242BB08680} \n"); const char* com_path_key = "CLSID\\{EC231970-6AFD-4215-A72E-97242BB08680}\\InProcServer32"; const HKEY hcr = HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT; std::cout << " COM Server file path = " << readRegistry_SZ(hcr, com_path_key, "") << '\n'; } std::puts("\n====== [ STEP 3 ] ====== Reading Windows Explorer Settings =======\n"); { const char* path = "Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Explorer\\Advanced"; std::printf(" Key =>> Hidden[DWORD] = %ld \n", readRegistry_DW( hkcu, path, "Hidden")); std::printf(" Key =>> HideFileExt[DWORD] = %ld \n", readRegistry_DW( hkcu, path, "HideFileExt")); } std::puts("\n====== [ STEP 4 ] ===== Listing all services that can be started after reboot ===="); { std::printf("\n Listing of services (daemons) that can be launched after reboot, at startup time. "); enumKeys( HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, "SYSTEM\\CurrentControlSet\\Services", -1); } return 0; } // ---- I M P L E M E N T A T I O N S -------------// // std::string readRegistry_SZ(HKEY hkey, const std::string& path, const std::string& key ) { HKEY key_handle; DWORD Type = REG_SZ; auto result = std::string(1024, 0); DWORD size = result.size(); if( RegOpenKeyExA( hkey, path.c_str(), 0 , KEY_QUERY_VALUE, &key_handle) != ERROR_SUCCESS ) { return "<NOT-FOUND:KEY>"; } if( RegQueryValueEx(key_handle, key.c_str() , NULL, &Type, (LPBYTE) &result[0], &size) != ERROR_SUCCESS) { RegCloseKey (key_handle); return "<NOT-FOUND:VALUE>"; } RegCloseKey (key_handle); result.resize(size-1); return result; } std::string readRegistry_SZ(const std::string& full_path, const std::string& key ) { const char* hkcu = "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\"; // Check whether string has prefix 'HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\' if( std::strncmp(full_path.c_str(), hkcu, std::strlen(hkcu)) == 0 ) { std::string path{ full_path.begin() + strlen(hkcu), full_path.end() }; std::cerr << "\n [TRACE] path = " << path << std::endl; return readRegistry_SZ(HKEY_CURRENT_USER, path, key); } return "<NOT-FOUND>"; } DWORD readRegistry_DW(HKEY hkey, const std::string& path, const std::string& key ) { HKEY key_handle; DWORD Type = REG_DWORD; DWORD result = 0; DWORD ret = 0; DWORD size = sizeof(DWORD); ret = RegOpenKeyExA( hkey, path.c_str(), 0 , KEY_QUERY_VALUE, &key_handle); assert( ret == ERROR_SUCCESS ); ret = RegQueryValueExA( key_handle, key.c_str() , NULL, &Type, (LPBYTE) &result, &size ); if( ret != ERROR_SUCCESS ) { RegCloseKey (key_handle); std::perror("Error: unable to query key"); return -1; } RegCloseKey (key_handle); return result; } // Query all values from a given registry key // Adapted from: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/sysinfo/enumerating-registry-subkeys void enumKeyValues(HKEY root, std::string const& path) { TCHAR achClass[MAX_PATH] = TEXT(""); // buffer for class name DWORD cchClassName = MAX_PATH; // size of class string DWORD cSubKeys=0; // number of subkeys DWORD cbMaxSubKey; // longest subkey size DWORD cchMaxClass; // longest class string DWORD cValues; // number of values for key DWORD cchMaxValue; // longest value name DWORD cbMaxValueData; // longest value data DWORD cbSecurityDescriptor; // size of security descriptor FILETIME ftLastWriteTime; // last write time DWORD i, retCode; TCHAR achValue[MAX_VALUE_NAME]; DWORD cchValue = MAX_VALUE_NAME; HKEY hKey{}; auto ret = RegOpenKeyEx(root, path.c_str(), 0, KEY_READ, &hKey ); if( ret != ERROR_SUCCESS ){ goto error; } // Get the class name and the value count. retCode = RegQueryInfoKey( hKey, // key handle achClass, // buffer for class name &cchClassName, // size of class string NULL, // reserved &cSubKeys, // number of subkeys &cbMaxSubKey, // longest subkey size &cchMaxClass, // longest class string &cValues, // number of values for this key &cchMaxValue, // longest value name &cbMaxValueData, // longest value data &cbSecurityDescriptor, // security descriptor &ftLastWriteTime); // last write time // Enumerate the key values. if (!cValues){ goto cleanup; } std::printf( "\n ->> Number of values: %ld \n\n ", cValues); static const auto key_types_db = std::map<DWORD, std::string>{ { REG_BINARY, "REG_BINARY" } , { REG_DWORD, "REG_DWORD" } , { REG_DWORD_LITTLE_ENDIAN, "REG_DWORD_LITTLE_ENDIAN" } , { REG_DWORD_BIG_ENDIAN, "REG_DWORD_BIG_ENDIAN" } , { REG_LINK, "REG_LINK" } , { REG_SZ, "REG_SZ(string)"} }; for (i=0, retCode=ERROR_SUCCESS; i<cValues; i++) { cchValue = MAX_VALUE_NAME; achValue[0] = '\0'; retCode = RegEnumValue(hKey, i, achValue, &cchValue, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL); assert( retCode == ERROR_SUCCESS); DWORD keyType = 0; retCode = RegGetValueA(hKey, NULL, achValue, RRF_RT_ANY, &keyType, NULL, NULL); assert( retCode == ERROR_SUCCESS); auto it = key_types_db.find(keyType); std::string keyDesc = ( it != key_types_db.end() ) ? it->second : "<UNKNOWN>"; std::printf( " =>> (%ld) %s / type = '%s' \n" , i+1, achValue, keyDesc.c_str()); } cleanup: RegCloseKey(hKey); return; error: std::cerr << " [ERRO] Unable to open Key with path = " << path << std::endl; RegCloseKey(hKey); } // Enumerate subkeys of a given Windows registry key. // Adapted from: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/sysinfo/enumerating-registry-subkeys // --------------------------------------------------- // Set max_keys to -1 in order to show all keys. void enumKeys(HKEY root,std::string const& path, DWORD nmax_keys) { TCHAR achKey[MAX_KEY_LENGTH]; // buffer for subkey name DWORD cbName; // size of name string TCHAR achClass[MAX_PATH] = TEXT(""); // buffer for class name DWORD cchClassName = MAX_PATH; // size of class string DWORD cSubKeys=0; // number of subkeys DWORD cbMaxSubKey; // longest subkey size DWORD cchMaxClass; // longest class string DWORD cValues; // number of values for key DWORD cchMaxValue; // longest value name DWORD cbMaxValueData; // longest value data DWORD cbSecurityDescriptor; // size of security descriptor FILETIME ftLastWriteTime; // last write time DWORD i, retCode; HKEY hKey{}; auto ret = RegOpenKeyEx(root, path.c_str(), 0, KEY_READ, &hKey ); assert( ret == ERROR_SUCCESS ); // Get the class name and the value count. retCode = RegQueryInfoKey( hKey, achClass, &cchClassName, NULL , &cSubKeys, &cbMaxSubKey, &cchMaxClass, &cValues , &cchMaxValue, &cbMaxValueData, &cbSecurityDescriptor ,&ftLastWriteTime); // Enumerate the subkeys, until RegEnumKeyEx fails. if( !cSubKeys ){ return; } printf( "\nNumber of subkeys: %ld\n", cSubKeys); // Show maximum of N Keys DWORD nkeys = ( cSubKeys > nmax_keys) ? nmax_keys : cSubKeys; for (i=0; i < nkeys; i++) { cbName = MAX_KEY_LENGTH; retCode = RegEnumKeyEx(hKey, i, achKey, &cbName, NULL, NULL, NULL, &ftLastWriteTime); if (retCode == ERROR_SUCCESS){ std::printf( " [*] (%ld) %s\n", i+1, achKey ); } } }
Building
$ g++ registry.cpp -o registry.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra
Running
$ registry.exe
====== [ STEP 1] ===== Show Registry Keys ====================
=>> Windows Explorer Settings ====
->> Number of values: 28
=>> (1) Start_SearchFiles / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (2) ServerAdminUI / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (3) Hidden / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (4) ShowCompColor / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (5) HideFileExt / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (6) DontPrettyPath / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (7) ShowInfoTip / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (8) HideIcons / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (9) MapNetDrvBtn / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (10) WebView / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (11) Filter / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (12) ShowSuperHidden / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (13) SeparateProcess / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (14) AutoCheckSelect / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (15) IconsOnly / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (16) ShowTypeOverlay / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (17) ShowStatusBar / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (18) StoreAppsOnTaskbar / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (19) ListviewAlphaSelect / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (20) ListviewShadow / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (21) TaskbarAnimations / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (22) StartMenuInit / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (23) TaskbarStateLastRun / type = 'REG_BINARY'
=>> (24) ShowCortanaButton / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (25) ReindexedProfile / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (26) Start_TrackProgs / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (27) StartMigratedBrowserPin / type = 'REG_DWORD'
=>> (28) TaskbarMigratedBrowserPin / type = 'REG_DWORD'
====== [ STEP 2 ] ====== Reading Windows Explorer Settings=====
Location of COM Server with CLSID = {EC231970-6AFD-4215-A72E-97242BB08680}
COM Server file path = C:\Windows\System32\wbem\Microsoft.Uev.AgentWmi.dll
====== [ STEP 3 ] ====== Reading Windows Explorer Settings =======
Key =>> Hidden[DWORD] = 2
Key =>> HideFileExt[DWORD] = 1
====== [ STEP 4 ] ===== Listing all services that can be started after reboot ====
Listing of services (daemons) that can be launched after reboot, at startup time.
Number of subkeys: 692
[*] (1) .NET CLR Data
[*] (2) .NET CLR Networking
[*] (3) .NET CLR Networking 4.0.0.0
[*] (4) .NET Data Provider for Oracle
[*] (5) .NET Data Provider for SqlServer
[*] (6) .NET Memory Cache 4.0
[*] (7) .NETFramework
[*] (8) 1394ohci
[*] (9) 3ware
[*] (10) AarSvc
[*] (11) AarSvc_2b782
[*] (12) ACPI
[*] (13) AcpiDev
[*] (14) acpiex
[*] (15) acpipagr
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
[*] (522) Telemetry
[*] (523) terminpt
[*] (524) TermService
[*] (525) Themes
[*] (526) TieringEngineService
[*] (527) TimeBrokerSvc
[*] (528) TokenBroker
[*] (529) TPM
[*] (530) TrkWks
[*] (531) TroubleshootingSvc
[*] (532) TrustedInstaller
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
1.15 Capturing OutputDebugString output
Logging and printing output to terminal with std::cout, printf or fprintf, does not work for any executable compiled for the window subsystem, even if it was launched from the terminal. As a result, applications built for the window subsystem, often uses the Windows API OutputDebugString() for logging that can be viewed using the DebugView sysinternal tool.
In this experiment, the program testprog.exe logs its execution through OutputDebugString() api and the program logview.exe waits for any OutputDebugString() call and displays the OutputDebugString message, process PID, and path to process' executable.
Apis Used:
- OpenMutexW()
- CreateMutexA()
- CreateEventA()
- CreateFileMappingA()
- Using Event Objects (Synchronization)
- MapViewOfFile()
- OutputDebugStringA() [ANSI]
- OutputDebugStringW() [UNICODE]
ReactOS implementation of OutputDebugString:
Project Files
File: logview.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> #include <tchar.h> struct alignas(4) OutputDebugStringBuffer { DWORD pid; // 4KiB - 4 Kbytes buffer char data[4096 - sizeof(DWORD)]; }; std::string get_process_path(int pid); // Link against this function without any headers containing this declaration. extern "C" void QueryFullProcessImageNameA(HANDLE hProc, int n, char* buffer, DWORD* buffer_size); int main() { static_assert( sizeof(OutputDebugStringBuffer) == 4096 ); // ---- The following constansts must have those exact name ----- // constexpr const char* strDBWinMutex = "DBWinMutex"; constexpr const char* strDBWIN_BUFFER_READY = "DBWIN_BUFFER_READY"; constexpr const char* strDBWIN_DATA_READY = "DBWIN_DATA_READY"; constexpr const char* strDBWIN_BUFFER = "DBWIN_BUFFER"; // Instatiate mutex HANDLE dbWinMutex = ::OpenMutex(MUTEX_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE, strDBWinMutex); if(dbWinMutex == nullptr) { dbWinMutex = ::CreateMutex(nullptr, FALSE, strDBWinMutex); } HANDLE bufferReady = OpenEvent(EVENT_MODIFY_STATE, FALSE, strDBWIN_BUFFER_READY); if(bufferReady == nullptr) { bufferReady = ::CreateEvent(nullptr, FALSE, TRUE, strDBWIN_BUFFER_READY); } HANDLE dataReady = ::OpenEvent(EVENT_MODIFY_STATE, FALSE, strDBWIN_DATA_READY); if(dataReady == nullptr) { dataReady = ::CreateEvent(nullptr, FALSE, FALSE, strDBWIN_DATA_READY); } HANDLE bufferMap =::OpenFileMapping(FILE_MAP_READ, FALSE, strDBWIN_BUFFER); if(bufferMap == nullptr) { std::cerr << "Creating file mapping" << std::endl; // Memory mapped file segment (shared memory) // that can be accessed by multiple processes. bufferMap = CreateFileMapping( INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE , nullptr , PAGE_READWRITE , 0 , sizeof(OutputDebugStringBuffer) , strDBWIN_BUFFER ); } auto wbuffer = reinterpret_cast<OutputDebugStringBuffer*>( ::MapViewOfFile(bufferMap, SECTION_MAP_READ, 0, 0, 0) ); if(wbuffer == nullptr) { std::cerr << "Error: failed to get buffer view" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::cout << "Waiting messages ..." << std::endl; for(;;) { // Block current thread until any other process calls OutputDebugString() // function. auto r = WaitForSingleObject(dataReady, INFINITE); if(r == WAIT_OBJECT_0) { std::fprintf( stdout , " PID = %ld ; Exe = %s \n" " >> %s \n\n" , wbuffer->pid , get_process_path(wbuffer->pid).c_str() , wbuffer->data ); } SetEvent(bufferReady); } return 0; } std::string get_process_path(int pid) { // Process handle HANDLE hProc = OpenProcess( PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ, FALSE, pid); // If hProc is null, it means that the function OpenProcess() has failed. assert( hProc != 0); DWORD size = MAX_PATH; char buffer[MAX_PATH]; // Obtain path to proces image (executable path) // Note: This function does not work with Unicode path names containing non // ascii characters such as Korean Hangul characters // For dealing with unicde use the API - QueryFullProcessImageNameW() instead. QueryFullProcessImageNameA(hProc, 0, buffer, &size); // Close proces handle disposing this reosurce. CloseHandle(hProc); return std::string{buffer}; }
File: testprog.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <windows.h> int main() { int sum = 0; char buffer[1000]; // Initialize buffer memset(buffer, '0', 1000); for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { std::snprintf(buffer, 1000, " [INFO] i = %d ; sum = %d ", i, sum); sum += sum + i * i; OutputDebugStringA(buffer); std::fprintf(stdout, "%s\n", buffer); // Block current thread for about 5 seconds. Sleep(500); } std::snprintf(buffer, 1000, " [INFO] Shutdown gracefully Ok. "); std::fprintf(stdout, "%s\n", buffer); OutputDebugStringA(buffer); return 0; }
Building
$ g++ logview.cpp -o logview.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g $ g++ testprog.cpp -o testprog.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g
Running logview.exe from terminal 1
$ .\logview.exe Creating file mapping Waiting messages ... PID = 8088 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] i = 0 ; sum = 0 PID = 8088 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] i = 1 ; sum = 0 PID = 8088 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] i = 2 ; sum = 1 PID = 8088 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] i = 3 ; sum = 6 PID = 8088 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] i = 4 ; sum = 21 PID = 8088 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] Shutdown gracefully Ok. PID = 7940 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] i = 0 ; sum = 0 PID = 7940 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] i = 1 ; sum = 0 PID = 7940 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] i = 2 ; sum = 1 PID = 7940 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] i = 3 ; sum = 6 PID = 7940 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] i = 4 ; sum = 21 PID = 7940 ; Exe = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\output_debug\testprog.exe >> [INFO] Shutdown gracefully Ok.
Running testprog.exe from terminal 2
$ .\testprog.exe [INFO] i = 0 ; sum = 0 [INFO] i = 1 ; sum = 0 [INFO] i = 2 ; sum = 1 [INFO] i = 3 ; sum = 6 [INFO] i = 4 ; sum = 21 [INFO] Shutdown gracefully Ok. $ .\testprog.exe [INFO] i = 0 ; sum = 0 [INFO] i = 1 ; sum = 0 [INFO] i = 2 ; sum = 1 [INFO] i = 3 ; sum = 6 [INFO] i = 4 ; sum = 21 [INFO] Shutdown gracefully Ok.
1.16 Listing Windows and Related Processes
The following code lists all visible windows titles, the related process ID (PID) and the path to the process' executable file.
Windows API Docs
- GetDesktopWindow()
- GetWindow()
- GetClassName()
- GetWindowText()
- FindWindowA()
- GetWindowThreadProcessId()
- GetWindowTextA()
- OpenProcess()
- QueryFullProcessImageNameA()
Files
File: enum-windows.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> int main() { HWND hDesk = GetDesktopWindow(); assert( hDesk != 0 ); // Current Winmdow HWND cwd = GetWindow(hDesk, GW_CHILD); assert ( cwd != 0 ); constexpr size_t SIZE = 2048; // 2kbytes buffer char buffer_window_title[SIZE]; char buffer_window_class[SIZE]; char buffer_executable_path[MAX_PATH]; int n = 0; DWORD pid = 0; // If true the application does not list windows // with empty titles. bool hide_empty_title = true; while( cwd ) { // Initialize and clean buffer memset(buffer_window_title, '\0', SIZE); memset(buffer_window_class, '\0', SIZE); memset(buffer_executable_path, '\0', MAX_PATH); // Get Window title GetWindowTextA(cwd, buffer_window_title, SIZE); // Get Window class GetClassName( cwd, buffer_window_class, SIZE); // Get Window PID (Process Identifier) - unique identifier. GetWindowThreadProcessId(cwd, &pid); // Window visibility bool isVisible = IsWindowVisible(cwd); // Process handle HANDLE hProc = OpenProcess( PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ, FALSE, pid); // assert( hProc != 0); DWORD size = MAX_PATH; // Obtain path to proces image (executable) QueryFullProcessImageNameA(hProc, 0, buffer_executable_path, &size); // Close proces handle disposing this reosurce. CloseHandle(hProc); // Display only visible windows with non empty title. if( !(hide_empty_title && strlen(buffer_window_title) == 0) && isVisible ) { // Display window title std::printf( " [*] => n = %d / Visible = %s " "\n => Title = '%s' " "\n => PID = %ld " "\n => Executable = %s " "\n => Class = %s \n\n" , n++, isVisible ? "TRUE" : "FALSE" , buffer_window_title, pid, buffer_executable_path , buffer_window_class ); } // GO to next window cwd = GetNextWindow(cwd, GW_HWNDNEXT); } return 0; }
Building:
g++ enum-windows.cpp -o enum-windows.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -pedantic-errors
Running
$ enum-windows.exe [*] => n = 0 / Visible = TRUE => Title = 'Cmder' => PID = 2268 => Executable = C:\Users\User_001\scoop\apps\cmder\1.3.17\vendor\conemu-maximus5\ConEmu64.exe => Class = VirtualConsoleClass [*] => n = 1 / Visible = TRUE => Title = 'emacs@DESKTOP-GLXQFC6' => PID = 7648 => Executable = C:\Users\User_001\scoop\apps\emacs\27.1\bin\emacs.exe => Class = Emacs [*] => n = 2 / Visible = TRUE => Title = 'System Configuration' => PID = 7048 => Executable = => Class = #32770 [*] => n = 3 / Visible = TRUE => Title = 'Event Viewer' => PID = 5944 => Executable = => Class = MMCMainFrame [*] => n = 4 / Visible = TRUE => Title = 'About Windows' => PID = 1368 => Executable = C:\Windows\System32\winver.exe => Class = #32770 [*] => n = 5 / Visible = TRUE => Title = 'Settings' => PID = 3704 => Executable = C:\Windows\ImmersiveControlPanel\SystemSettings.exe => Class = Windows.UI.Core.CoreWindow [*] => n = 6 / Visible = TRUE => Title = 'Settings' => PID = 6988 => Executable = C:\Windows\System32\ApplicationFrameHost.exe => Class = ApplicationFrameWindow [*] => n = 7 / Visible = TRUE => Title = 'Microsoft Text Input Application' => PID = 5896 => Executable = C:\Windows\SystemApps\MicrosoftWindows.Client.CBS_cw5n1h2txyewy\InputApp\TextInputHost.exe => Class = Windows.UI.Core.CoreWindow [*] => n = 8 / Visible = TRUE => Title = 'Program Manager' => PID = 4316 => Executable = C:\Windows\explorer.exe => Class = Progman
1.17 Access Tokens
1.17.1 Overview
An access tokens are Windows kernel objects that contain information about user identity, capabilities, privileges, domain and groups that the user belongs to. They are generated when an user logs on and is successfully authenticated. When any process is startd, it receives the user access token. As a result, the process capabilities are limited to the same permissions and capabilities granted by the user's token.
Tokens can also used for applying the principle of least privilege which advices that an application should be granted the minimum necessary privilege to perform its work. For instance, several system operations including, loading device drivers, set system time or read a process' memory, require a token to be granted with the specific privilege that enables the operation. For instance, loading device driver requies the token to have the SeLoadDriverPrivilege, reading a process' memory requires SeDugPrivilege and so on.
Some windows privileges contanst (MSDN)
- SeBackupPrivilege
- Constant:
SE_BACKUP_NAME - Privilege required for debugging operations.
- Constant:
- SeCreateGlobalPrivilege
- constant:
SE_CREATE_GLOBAL_NAME - Privilege required for creating named pipes, file mapping or shared memory namespaces in global namespace.
- constant:
- SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege
- constant:
SE_CREATE_SYMBOLIC_LINK_NAME - Privilege required for creating symbolic links.
- constant:
- SeDebugPrivilege
- Constant:
SE_DEBUG_NAME - Privilege needed for enabling debugging operations on processes not owned by the user, for instance, reading process virtual memory, writing to process virtual memory.
- Constant:
- SeLoadDriverPrivilege
- Constant:
SE_LOAD_DRIVER_NAME - Privilegy necessary for loading device drivers.
- Constant:
Widely used terminology:
- UNC - Universal Name Convention
- UAC - User Account Control
- ACE - Access Control Entries
- ACL - Access Control List
- DACL - Discretionary Access Control List
- SACL - System Access Control List
- SID - Security Identifier (User account unique identifer or ID)
- LSA - Local Security Authority
- LSAS - Local Security Subsystem Service
- SCM - Service Control Manager
Relevant documentation reading
- MSDN - Access Control (Authorization)
- MSDN - Authorization Functions (Authorization)
- How AccessCheck Works [MUST-READ]
- MSDN - Access Tokens [MUST-READ]
- MSDN - Privilege Constants [MUST-READ]
- MSDN - Well-known SIDs [MUST-READ]
- LUID structure (winnt.h)
- ACEs to Control Access to an Object's Properties
- MSDN - LSA Authentication
- MSDN - Isolated User Mode (IUM) Processes
- MSDN - Securable Objects
- Enabling and Disabling Privileges in C++–
- MSDN - Finding the Owner of a File Object in C++
Token and Process Windows APIs
- CloseHandle()
- Brief: "Closes an open object handle."
BOOL CloseHandle(HANDLE hObject);
- GetCurrentPRocessId()
- Brief: "Retrieves the process identifier of the calling process."
DWORD GetCurrentProcessId();
- OpenProcess()
- Brief: "Opens an existing local process object."
HANDLE OpenProcess( DWORD dwDesiredAccess, BOOL bInheritHandle, DWORD dwProcessId );
- IsProcessCritical()
- Brief: "Determines whether the specified process is considered critical."
BOOL IsProcessCritical(HANDLE hProcess, PBOOL Critical);
- GetCurrentProcess()
- Brief: "Retrieves a pseudo handle for the current process."
HANDLE GetCurrentProcess();
BOOL OpenProcessToken( HANDLE ProcessHandle, DWORD DesiredAccess, PHANDLE TokenHandle );
- GetTokenInformation()
- Brief: "The GetTokenInformation function retrieves a specified type of information about an access token. The calling process must have appropriate access rights to obtain the information."
BOOL GetTokenInformation( HANDLE TokenHandle, TOKEN_INFORMATION_CLASS TokenInformationClass, LPVOID TokenInformation, DWORD TokenInformationLength, PDWORD ReturnLength );
- LookupAccountSidA()
- Brief: "The LookupAccountSid function accepts a security identifier (SID) as input. It retrieves the name of the account for this SID and the name of the first domain on which this SID is found."
BOOL LookupAccountSidA( LPCSTR lpSystemName, PSID Sid, LPSTR Name, LPDWORD cchName, LPSTR ReferencedDomainName, LPDWORD cchReferencedDomainName, PSID_NAME_USE peUse );
- LookupPrivilegeValueA() [ANSI-VERSION]
- Brief: "The LookupPrivilegeValue function retrieves the locally unique identifier (LUID) used on a specified system to locally represent the specified privilege name."
BOOL LookupPrivilegeValueA( LPCSTR lpSystemName, LPCSTR lpName, PLUID lpLuid );
- LookupPrivilegeValueW() [UNICODE-VERSION]
BOOL LookupPrivilegeValueW( LPCWSTR lpSystemName, LPCWSTR lpName, PLUID lpLuid );
- AdjustTokenGroups()
- Brief: "The AdjustTokenGroups function enables or disables groups already present in the specified access token. Access to TOKEN_ADJUST_GROUPS is required to enable or disable groups in an access token."
BOOL AdjustTokenGroups( HANDLE TokenHandle, BOOL ResetToDefault, PTOKEN_GROUPS NewState, DWORD BufferLength, PTOKEN_GROUPS PreviousState, PDWORD ReturnLength );
- AdjustTokenPrivileges()
- Brief: "The AdjustTokenPrivileges function enables or disables privileges in the specified access token. Enabling or disabling privileges in an access token requires TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES access."
BOOL AdjustTokenPrivileges( HANDLE TokenHandle, BOOL DisableAllPrivileges, PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES NewState, DWORD BufferLength, PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES PreviousState, PDWORD ReturnLength );
- DuplicateToken()
- Brief: "The DuplicateToken function creates a new access token that duplicates one already in existence."
BOOL DuplicateToken( HANDLE ExistingTokenHandle, SECURITY_IMPERSONATION_LEVEL ImpersonationLevel, PHANDLE DuplicateTokenHandle );
- IsTokenRestricted()
- Brief: "The IsTokenRestricted function indicates whether a token contains a list of restricted security identifiers (SIDs)."
BOOL IsTokenRestricted( HANDLE TokenHandle );
- CreateProcessAsUserA()
- Brief: "Creates a new process and its primary thread. The new process runs in the security context of the user represented by the specified token."
BOOL CreateProcessAsUserA( HANDLE hToken, LPCSTR lpApplicationName, LPSTR lpCommandLine, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, BOOL bInheritHandles, DWORD dwCreationFlags, LPVOID lpEnvironment, LPCSTR lpCurrentDirectory, LPSTARTUPINFOA lpStartupInfo, LPPROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation );
- CreateProcessAsUserW()
- Brief: "Creates a new process and its primary thread. The new process runs in the security context of the user represented by the specified token."
BOOL CreateProcessAsUserW( HANDLE hToken, LPCWSTR lpApplicationName, LPWSTR lpCommandLine, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, BOOL bInheritHandles, DWORD dwCreationFlags, LPVOID lpEnvironment, LPCWSTR lpCurrentDirectory, LPSTARTUPINFOW lpStartupInfo, LPPROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation );
1.17.2 Inspecting access tokens
This code demmonstrates the usage of many Windows NT token APIs application programming interfaces by querying token information and privilege from system processes passed as PID command line argument.
Project Files
File: tokeninfo.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> extern "C" void QueryFullProcessImageNameA( HANDLE hProc, int n , char* buffer, DWORD* buffer_size); extern "C" BOOL IsProcessCritical(HANDLE hProcess, PBOOL Critical); extern "C" BOOL ConvertSidToStringSidA(PSID Sid, LPSTR* StringSid); bool tokenHasPrivilege( HANDLE hToken, const char* privilege); void showTokenPrivilege( HANDLE hToken, const char* privilege); void show_process_token_privilege( int pid); BOOL isTokenElevated( HANDLE hToken ); BOOL SetPrivilege( HANDLE hToken, LPCTSTR lpszPrivilege, BOOL bEnablePrivilege); // ======================================================================// int main(int argc, char** argv) { if( argc < 2 ) { std::printf("\n Usage: %s [COMMAND] [ARGUMENT]", argv[0] ); std::printf("\n => Show process token information"); std::printf("\n $ .%s proc [PID] \n", argv[0] ); std::printf("\n => Set debug privilege and show current privileges"); std::printf("\n $ %s priv \n", argv[0] ); return EXIT_FAILURE; } auto command = std::string{ argv[1] }; if( command == "proc" ) { DWORD pid = std::stoi(argv[2]); // If pid == 0 => Show privileges of current process. if( pid == 0){ pid = GetCurrentProcessId(); } show_process_token_privilege( pid ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } if( command == "priv" ) { HANDLE hProc = GetCurrentProcess(); HANDLE hToken = nullptr; if( !OpenProcessToken(hProc, TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES | TOKEN_QUERY, &hToken) ) { std::printf("Error - unable to open process Token. => Check GetLastError() error code. \n"); std::abort(); } assert( hToken != nullptr ); std::printf( " Is process elevated (admin)? = %s \n" , isTokenElevated(hToken) ? "TRUE" : "FALSE" ); // Set debug privilege => Necessary for reading or writing to/from process memory. // Note: SE_DEBUG_NAME == 'SeDebugPrivilege' SetPrivilege( hToken, SE_DEBUG_NAME, TRUE); showTokenPrivilege( hToken, SE_DEBUG_NAME ); // Backup privilege SetPrivilege( hToken, "SeBackupPrivilege", TRUE); showTokenPrivilege( hToken, "SeBackupPrivilege" ); // Privilege for creating global objects SetPrivilege( hToken, "SeCreateGlobalPrivilege", TRUE); showTokenPrivilege( hToken, "SeCreateGlobalPrivilege" ); // Privilege for loading drivers SetPrivilege( hToken, "SeLoadDriverPrivilege", TRUE); showTokenPrivilege( hToken, "SeLoadDriverPrivilege" ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } return EXIT_SUCCESS; } // ======= I M P L E M E N T A T I O N S ================ // // Check whether process is running with administrative privilege (admin) BOOL isTokenElevated( HANDLE hToken ) { TOKEN_ELEVATION elevation; DWORD size = sizeof( TOKEN_ELEVATION ); if( !GetTokenInformation( hToken, TokenElevation, &elevation , sizeof( TOKEN_ELEVATION), &size ) ) { return FALSE; } return elevation.TokenIsElevated; } bool tokenHasPrivilege(HANDLE hToken, const char* privilege) { LUID luid; PRIVILEGE_SET prvset; if( !LookupPrivilegeValue(nullptr, privilege, &luid) ) { fprintf(stderr, "Function LookipPrivilegeAndValue() failed. \n"); std::abort(); } prvset.Control = PRIVILEGE_SET_ALL_NECESSARY; prvset.Privilege[0].Luid = luid; prvset.Privilege[0].Attributes = SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED;; prvset.PrivilegeCount = 1; BOOL ret; PrivilegeCheck(hToken, &prvset, &ret); return ret == TRUE; } void showTokenPrivilege(HANDLE hToken, const char* privilege) { bool p = tokenHasPrivilege(hToken, privilege); std::fprintf( stdout, "\n [*] Has privilege? %s = %s \n" , privilege, p ? "TRUE" : "FALSE" ); } void show_process_token_privilege(int pid) { // Get handle to process // ---------------------------------------------- assert( pid > 0 ); HANDLE hProc = OpenProcess(PROCESS_QUERY_LIMITED_INFORMATION, FALSE, pid); if( hProc == nullptr ) { std::printf( " Error => Unable to open process => Error code = %ld" , GetLastError()); std::abort(); } // Get path to process // --------------------------------------------------- DWORD size = MAX_PATH; char buffer[MAX_PATH]; // Obtain path to proces image (executable path) // Note: This function does not work with Unicode path names containing non // ascii characters such as Korean Hangul characters. QueryFullProcessImageNameA(hProc, 0, buffer, &size); // Get process' access token //---------------------------------------------------------------- HANDLE hToken = nullptr; if( !OpenProcessToken(hProc, TOKEN_QUERY, &hToken) ) { std::printf("Error - unable to open process Token. => Check GetLastError() error code. \n"); std::abort(); } // Retrieve information about user which created the process //-------------------------------------------------------------- DWORD needed; // Determine the buffer size GetTokenInformation( hToken, TokenUser, NULL, 0, &needed); auto tuser = reinterpret_cast<TOKEN_USER*>( LocalAlloc( LPTR, needed) ); assert( tuser != nullptr ); GetTokenInformation( hToken, TokenUser, tuser, needed, &needed); PSID psid = tuser->User.Sid; char buffer_user[500]; char buffer_domain[500]; DWORD size_user = sizeof(buffer_user); DWORD size_domain = sizeof(buffer_domain); SID_NAME_USE snu; if( !LookupAccountSid( nullptr, psid , buffer_user, &size_user , buffer_domain, &size_domain , &snu ) ) { std::printf( "Error. Function LookupAccountSid() failed => Last error code = %ld" , GetLastError()); std::abort(); } /// Note: This string is allocated by the calee (function); char* pBuffer_sid = nullptr; // Convert SID (Security identifier) to string assert( ConvertSidToStringSidA(psid, &pBuffer_sid) ); // Display process information // ---------------------------------------------------------- std::printf(" [TOKEN] >> Pid = %d ; EXE = %s \n", pid, buffer); std::printf(" User account = %s \n", buffer_user ); std::printf(" User domain = %s \n", buffer_domain ); std::printf(" SID = %s \n", pBuffer_sid ); BOOL is_critical = FALSE; IsProcessCritical(hProc, &is_critical); std::printf(" Is process critical = %s \n", is_critical ? "TRUE" : "FALSE" ); std::printf(" Is process elevated (admin)? = %s \n", isTokenElevated(hToken) ? "TRUE" : "FALSE" ); std::printf(" Is token restricted = %s \n", IsTokenRestricted(hToken) ? "TRUE" : "FALSE" ); // Display privileges that the token grants to the process. //--------------------------------------------------- // // SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege => Allows replacing process-level token showTokenPrivilege( hToken, SE_ASSIGNPRIMARYTOKEN_NAME); // SeBackupPrivilege => Allows files and directories backup (access to any file) showTokenPrivilege( hToken, SE_BACKUP_NAME ); // SeDebugPrivilege => Allows opening process memory and performing debugging operations showTokenPrivilege( hToken, SE_DEBUG_NAME ); // SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege showTokenPrivilege( hToken, SE_INCREASE_QUOTA_NAME ); // SeTcbPrivilege => showTokenPrivilege( hToken, SE_TCB_NAME ); // Impersonate a client after authentication showTokenPrivilege( hToken, "SeImpersonatePrivilege"); // Load and unload device drivers showTokenPrivilege( hToken, "SeLoadDriverPrivilege"); // Change system time showTokenPrivilege( hToken, "SeSystemtimePrivilege" ); // Create global objects showTokenPrivilege( hToken, "SeCreateGlobalPrivilege"); // Create symbolic links showTokenPrivilege( hToken, "SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege"); // Managing and auditig the security log showTokenPrivilege( hToken, "SeSecurityPrivilege"); CloseHandle(hProc); CloseHandle(hToken); } // Source: MSDN Example BOOL SetPrivilege( HANDLE hToken // access token handle , LPCTSTR lpszPrivilege // name of privilege to enable/disable , BOOL bEnablePrivilege // to enable or disable privilege ) { TOKEN_PRIVILEGES tp; LUID luid; if ( !LookupPrivilegeValue(NULL, lpszPrivilege, &luid ) ) { printf("LookupPrivilegeValue error: %ld\n", GetLastError() ); return FALSE; } tp.PrivilegeCount = 1; tp.Privileges[0].Luid = luid; if (bEnablePrivilege) tp.Privileges[0].Attributes = SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED; else tp.Privileges[0].Attributes = 0; // Enable the privilege or disable all privileges. if ( !AdjustTokenPrivileges( hToken, FALSE, &tp, sizeof(TOKEN_PRIVILEGES), (PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES) NULL, (PDWORD) NULL) ) { printf("AdjustTokenPrivileges error: %ld\n", GetLastError() ); return FALSE; } if (GetLastError() == ERROR_NOT_ALL_ASSIGNED) { printf("The token does not have the specified privilege. \n"); return FALSE; } return TRUE; }
Building:
$ g++ tokeninfo.cpp -o tokeninfo.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g
Experiment 1 - run as non administrator - querying process privileges.
λ .\tokeninfo.exe proc 0 [TOKEN] >> Pid = 3100 ; EXE = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\tokeninfo.exe User account = User_001 User domain = DESKTOP-FA8FC0Q SID = S-1-5-20-3640651439-4294530408-2125417441-1261 Is process critical = FALSE Is process elevated (admin)? = FALSE Is token restricted = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeBackupPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeDebugPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeTcbPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeImpersonatePrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeLoadDriverPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeSystemtimePrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeCreateGlobalPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeSecurityPrivilege = FALSE
Check user privileges with command whoami:
$ whoami /priv PRIVILEGES INFORMATION ---------------------- Privilege Name Description State ============================= ==================================== ======== SeShutdownPrivilege Shut down the system Disabled SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled SeUndockPrivilege Remove computer from docking station Disabled SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Disabled SeTimeZonePrivilege Change the time zone Disabled
Experiment 2 - run as administrator - querying process own privilge
$ .\tokeninfo.exe proc 0 [TOKEN] >> Pid = 7784 ; EXE = C:\Users\User_001\Desktop\tokeninfo.exe User account = User_001 User domain = DESKTOP-FA8FC0Q SID = S-1-5-20-3640651439-4294530408-2125417441-1261 Is process critical = FALSE Is process elevated (admin)? = TRUE Is token restricted = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeBackupPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeDebugPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeTcbPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeImpersonatePrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeLoadDriverPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeSystemtimePrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeCreateGlobalPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeSecurityPrivilege = FALSE
Check user privileges with command whoami:
$ whoami /priv
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
========================================= ================================================================== ========
SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege Adjust memory quotas for a process Disabled
SeSecurityPrivilege Manage auditing and security log Disabled
SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege Take ownership of files or other objects Disabled
SeLoadDriverPrivilege Load and unload device drivers Disabled
SeSystemProfilePrivilege Profile system performance Disabled
SeSystemtimePrivilege Change the system time Disabled
SeProfileSingleProcessPrivilege Profile single process Disabled
SeIncreaseBasePriorityPrivilege Increase scheduling priority Disabled
SeCreatePagefilePrivilege Create a pagefile Disabled
SeBackupPrivilege Back up files and directories Disabled
SeRestorePrivilege Restore files and directories Disabled
SeShutdownPrivilege Shut down the system Disabled
SeDebugPrivilege Debug programs Disabled
SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege Modify firmware environment values Disabled
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege Force shutdown from a remote system Disabled
SeUndockPrivilege Remove computer from docking station Disabled
SeManageVolumePrivilege Perform volume maintenance tasks Disabled
SeImpersonatePrivilege Impersonate a client after authentication Enabled
SeCreateGlobalPrivilege Create global objects Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Disabled
SeTimeZonePrivilege Change the time zone Disabled
SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege Create symbolic links Disabled
SeDelegateSessionUserImpersonatePrivilege Obtain an impersonation token for another user in the same session Disabled
Experiment 3 - Enable debug, backup and load driver privileges checking whether they are enabled.
# Note: Executed as administrator. $ .\tokeninfo.exe priv Is process elevated (admin)? = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeDebugPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeBackupPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeCreateGlobalPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeLoadDriverPrivilege = TRUE
Experiment 4
List system services and their PIDs (Process unique identifiers):
$ sc queryex SERVICE_NAME: WSearch DISPLAY_NAME: Windows Search TYPE : 10 WIN32_OWN_PROCESS STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, ACCEPTS_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0 PID : 5508 FLAGS : SERVICE_NAME: cbdhsvc_3c648 DISPLAY_NAME: Clipboard User Service_3c648 TYPE : f0 ERROR STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0 PID : 4120 FLAGS : SERVICE_NAME: CDPUserSvc_3c648 DISPLAY_NAME: Connected Devices Platform User Service_3c648 TYPE : f0 ERROR STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0 PID : 4388 FLAGS : ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Inspect token information of process (PID = 2664)
$ .\tokeninfo.exe proc 2664 [TOKEN] >> Pid = 2664 ; EXE = C:\Program Files (x86)\SPICE Guest Tools\drivers\Balloon\w10\amd64\blnsvr.exe User account = SYSTEM User domain = NT AUTHORITY SID = S-1-5-18 Is process critical = FALSE Is process elevated (admin)? = TRUE Is token restricted = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeBackupPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeDebugPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeTcbPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeImpersonatePrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeLoadDriverPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeSystemtimePrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeCreateGlobalPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeSecurityPrivilege = FALSE
Inspect token information of process (PID = 636)
$ .\tokeninfo.exe proc 636 [TOKEN] >> Pid = 636 ; EXE = C:\Windows\System32\lsass.exe User account = SYSTEM User domain = NT AUTHORITY SID = S-1-5-18 Is process critical = FALSE Is process elevated (admin)? = TRUE Is token restricted = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeBackupPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeDebugPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeTcbPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeImpersonatePrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeLoadDriverPrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeSystemtimePrivilege = FALSE [*] Has privilege? SeCreateGlobalPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege = TRUE [*] Has privilege? SeSecurityPrivilege = FALSE
1.18 Reading and writing process memory
1.18.1 Overview
Windows NT family operating systems provide APIs OpenProcess(), ReadProcessMemory() and WriteProcessMemory() which allow the calling code to manipulate the memory of other processes. Those functions are meant to support the implementation of debuggers such as Visual Studio Debugger, Windb or GDB (GNU Debugger), which need to be able to read, write and inspect the virtual memory of any process.
Note: Debug privilege is required for inspecting the memory of processes not created by the user of the calling code.
Documentation of APIs used:
- OpenProcess()
- CloseHandle()
- GetCurrentProcessId()
- Brief: "Retrieves the process identifier of the calling process."
- GetCurrentProcess()
- Brief: "Retrieves a pseudo handle for the current process."
- ReadProcessMemory()
- Brief: "ReadProcessMemory copies the data in the specified address range from the address space of the specified process into the specified buffer of the current process. Any process that has a handle with PROCESS_VM_READ access can call the function."
- WriteProcessMemory()
- Brief: "Writes data to an area of memory in a specified process. The entire area to be written to must be accessible or the operation fails."
- GetModuleBaseName()
- Brief: "Retrieves the base name of the specified module."
- IsWow64Process()
- Brief: "Determines whether the specified process is running under WOW64 or an Intel64 of x64 processor."
- NtQueryInformationProcess() [INTERNAL-API] [UNDOCUMENTED-API]
- Brief: "Retrieves information about the specified process."
- Note: It is unstable internal Windows API, as a result, it may removed without notice on future Windows releases. This API is not supposed to be used by any application code. However, there is no way to get a process full command line path without this "undocumented function".
- PEB structure [INTERNAL-API] [UNDOCUMENTED-API]
- Brief: Process Enviroment Block data structure.
- PEB_LDR_DATA structure [INTERNAL-API] [UNDOCUMENTED-API]
- Brief: Contains information about the loaded modules for the process.
- RTL_USER_PROCESS_PARAMETERS structure [INTERNAL-API] [UNDOCUMENTED-API]
- Brief: Contains process parameter information.
- Note: Contains process command line arguments.
Structs:
typedef struct _PEB { BYTE Reserved1[2]; BYTE BeingDebugged; BYTE Reserved2[1]; PVOID Reserved3[2]; PPEB_LDR_DATA Ldr; PRTL_USER_PROCESS_PARAMETERS ProcessParameters; PVOID Reserved4[3]; PVOID AtlThunkSListPtr; PVOID Reserved5; ULONG Reserved6; PVOID Reserved7; ULONG Reserved8; ULONG AtlThunkSListPtr32; PVOID Reserved9[45]; BYTE Reserved10[96]; PPS_POST_PROCESS_INIT_ROUTINE PostProcessInitRoutine; BYTE Reserved11[128]; PVOID Reserved12[1]; ULONG SessionId; } PEB, *PPEB; typedef struct _RTL_USER_PROCESS_PARAMETERS { BYTE Reserved1[16]; PVOID Reserved2[10]; UNICODE_STRING ImagePathName; UNICODE_STRING CommandLine; } RTL_USER_PROCESS_PARAMETERS, *PRTL_USER_PROCESS_PARAMETERS; typedef struct _PEB_LDR_DATA { BYTE Reserved1[8]; PVOID Reserved2[3]; LIST_ENTRY InMemoryOrderModuleList; } PEB_LDR_DATA, *PPEB_LDR_DATA; struct UNICODE_STRING { USHORT Length; // unsigned short (16 bits) USHORT MaximumLength; // unsigned short (16 bits) PWSTR Buffer; // type WCHAR* };
1.18.2 Sample code
This sample code uses memory inspection APIs for manipulating the virtual memory of a target process and also for obtaining the full command line used for instantiating a given process.
Project files
File: target.cpp => Sample target process.
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <windows.h> char static_allocated_buffer[300]; int main() { int number = 300; std::string cppstr = "Hallo Welt"; strcpy(static_allocated_buffer, "Strcpy is an unsafe C function! BE AWARE!"); const DWORD pid = GetCurrentProcessId(); std::printf(" [*] Number = %d \n", number ); std::printf(" [*] cppstr = %s \n", cppstr.c_str()); std::printf(" [*] Global buffer = %s \n", static_allocated_buffer); std::printf(" [*] Current process PID = %ld \n", pid); std::printf(" [*] Number address = %p \n", &number ); std::printf(" [*] cppstr address = %p \n", cppstr.data()); std::printf(" [*] Global buffer address = %p \n", static_allocated_buffer); std::printf("\n =>> Type RETURN to resume execution \n"); std::cin.ignore(); std::printf(" [*] Number = %d \n", number ); std::printf(" [*] cppstr = %s \n", cppstr.c_str()); std::printf(" [*] Global buffer = %s \n", static_allocated_buffer); std::printf("\n =>> Type RETURN to resume execution \n"); std::cin.ignore(); }
File: memorydump.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> #include <psapi.h> #include <winternl.h> // Declare linkage to C symbol only when using on MING (GCC) compiler. #if !defined(__MINGW64__) || defined(__MINGW32__) extern "C" BOOL QueryFullProcessImageNameA(HANDLE hProcess, DWORD dwFlags , LPSTR lpExeName, PDWORD lpdwSize ); #endif std::string process_basename(HANDLE hProc); std::string process_full_path(HANDLE hProc); void enableDebugPrivilege(BOOL enable); BOOL setPrivilege(HANDLE hToken, LPCTSTR privilege, BOOL enable_privilege); // Type alias to Windows API function pointer. using NtQueryInformationProcess_t = NTSTATUS (*) ( HANDLE ProcessHandle, PROCESSINFOCLASS ProcessInformationClass, PVOID ProcessInformation, ULONG ProcessInformationLength, PULONG ReturnLength ); // Show process command line arguments by reading its virtual memory. // Note: This function requires debug privilege enabled if the process // does not belong to the current user. void show_process_cli(DWORD pid); int main(int argc, char** argv) { if( argc < 2) { std::fprintf(stderr, "Error: expected process PID \n"); return -1; } // Set debug privilege for current process token // Note: It only works if this application is run with // administrative privilege. //--------------------------------------------------- enableDebugPrivilege( TRUE ); auto command = std::string{ argv[1] }; // Obains information about commmand line used to start the process. if( command == "cli" ) { int pid = std::stoi( argv[2] ); show_process_cli(pid); return 0; } // Dump a buffer from target process memory. if( command == "read-str" ) { // Pid of target process . int pid = std::stoi( argv[2] ); // Buffer memory address to be read from target process // (in hexadecimal base, base 16) int address = std::stoi( argv[3], 0, 16 ); // Buffer Lenght int lenght = std::stoi( argv[4] ); HANDLE hProc = OpenProcess( PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ, FALSE, pid); assert( hProc != nullptr ); // Create heap-allocated string buffer with length characters // set as '\0' null characters. auto buffer = std::string(lenght, '\0'); ReadProcessMemory( hProc, (LPVOID) address, buffer.data(), lenght, nullptr); std::printf(" Buffer value = %s \n", buffer.c_str()); std::printf(" Address = %x \n", address); CloseHandle( hProc ); return 0; } // Write to buffer from target process if( command == "write-str" ) { // Pid of target process . int pid = std::stoi( argv[2] ); // Buffer memory address to be read from target process // (in hexadecimal base, base 16) int address = std::stoi( argv[3], 0, 16 ); // Data to be written to buffer process memory auto str = std::string{ argv[4] }; const DWORD flags = PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ | PROCESS_VM_WRITE; const HANDLE hProc = OpenProcess( flags, FALSE, pid); assert( hProc != nullptr ); WriteProcessMemory( hProc, (LPVOID) address, str.data(), str.length(), nullptr); auto buffer = std::string(str.length(), '\0'); ReadProcessMemory( hProc, (LPVOID) address, buffer.data(), str.length(), nullptr); std::printf(" Buffer value = %s \n", buffer.c_str()); std::printf(" Address = %x \n", address); CloseHandle( hProc ); return 0; } // Read number from target process memory. if( command == "read-num" ) { // Pid of target process . int pid = std::stoi( argv[2] ); // Buffer memory address to be read from target process // (in hexadecimal base, base 16) int address = std::stoi( argv[3], 0, 16 ); HANDLE hProc = OpenProcess( PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ, FALSE, pid); assert( hProc != nullptr ); int buffer = 0; ReadProcessMemory( hProc, (LPVOID) address, &buffer, sizeof(buffer), nullptr); std::printf(" [*] Number value = %d \n", buffer); return 0; } // Write number to target process memory. if( command == "write-num" ) { // Pid of target process . int pid = std::stoi( argv[2] ); // Buffer memory address to be read from target process // (in hexadecimal base, base 16) int address = std::stoi( argv[3], 0, 16 ); int number = std::stoi( argv[4] ); const DWORD flags = PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ | PROCESS_VM_WRITE; const HANDLE hProc = OpenProcess( flags, FALSE, pid); assert( hProc != nullptr ); WriteProcessMemory( hProc, (LPVOID) address, &number, sizeof(number), nullptr); int buffer = 0; ReadProcessMemory( hProc, (LPVOID) address, &buffer, sizeof(buffer), nullptr); std::printf(" [*] Number value = %d \n", buffer); return 0; } std::fprintf(stderr, " [TRACE] Error => Unable to find command."); return -1; } // ============= I M P L E M E N T A T I O N S ================= // std::string process_basename(HANDLE hProc) { // Note: This function fails if the process executable uses non aciii characters // such as Japanese Kanji, Hiragrama or Katakana. But this function was // chosen due to it be easier to deal with than GetModuleBaseNameW(). size_t size = 260; auto buffer = std::string('0', size); assert( GetModuleBaseNameA(hProc, nullptr, buffer.data(), size) != 0 ); return buffer; } std::string process_full_path(HANDLE hProc) { DWORD size = MAX_PATH; char buffer[MAX_PATH]; QueryFullProcessImageNameA(hProc, 0, buffer, &size); CloseHandle(hProc); return std::string{buffer}; } BOOL setPrivilege(HANDLE hToken, LPCTSTR privilege, BOOL enable_privilege) { TOKEN_PRIVILEGES tp; LUID luid; if ( !LookupPrivilegeValue(NULL, privilege, &luid ) ) { printf("LookupPrivilegeValue error: %ld\n", GetLastError() ); return FALSE; } tp.PrivilegeCount = 1; tp.Privileges[0].Luid = luid; if (enable_privilege) tp.Privileges[0].Attributes = SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED; else tp.Privileges[0].Attributes = 0; // Enable the privilege or disable all privileges. if ( !AdjustTokenPrivileges( hToken, FALSE, &tp, sizeof(TOKEN_PRIVILEGES), (PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES) NULL, (PDWORD) NULL) ) { printf("AdjustTokenPrivileges error: %ld\n", GetLastError() ); return FALSE; } if (GetLastError() == ERROR_NOT_ALL_ASSIGNED) { printf("The token does not have the specified privilege. \n"); return FALSE; } return TRUE; } // Enable Debug privilege for current process void enableDebugPrivilege(BOOL enable) { // Current process' hProc handle HANDLE hProc = GetCurrentProcess(); // Current process' token HANDLE hToken = nullptr; if( !OpenProcessToken(hProc, TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES | TOKEN_QUERY, &hToken) ) { std::printf("Error - unable to open process Token. => Check GetLastError() error code. \n"); std::abort(); } setPrivilege( hToken, "SeDebugPrivilege" , enable); std::printf(" [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. \n"); } void show_process_cli(DWORD pid) { HANDLE hProc = OpenProcess( PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ, FALSE, pid); if( hProc == nullptr ) { std::fprintf(stderr, "Error: unable to open process"); std::exit(-1); } // Check whether proces is wow64 (32 bits) BOOL is_wow64; IsWow64Process( hProc, &is_wow64); std::printf(" [*] Is Wow64 (32 bits) process = %s \n", is_wow64 == TRUE ? "TRUE" : "FALSE" ); // Check whether current process is 32 bits (wow64) HANDLE hThisProc = GetCurrentProcess(); IsWow64Process( hThisProc, &is_wow64); std::printf(" [*] Is this process Wow64 (32 bits) process = %s \n", is_wow64 == TRUE ? "TRUE" : "FALSE" ); // Load function native function NtQueryInformationProcess from Ntdll.dll //----------------------------------------- HMODULE hnd = LoadLibraryA("Ntdll.dll"); assert( hnd != nullptr ); FARPROC hnd_fun = GetProcAddress(hnd, "NtQueryInformationProcess"); assert( hnd_fun != nullptr ); auto func_NtQueryInformationProcess = reinterpret_cast<NtQueryInformationProcess_t>(hnd_fun); PROCESS_BASIC_INFORMATION pinfo; DWORD pinfo_size = sizeof(PROCESS_BASIC_INFORMATION); DWORD needed = 0; NTSTATUS result = func_NtQueryInformationProcess( hProc , ProcessBasicInformation , &pinfo , pinfo_size , &needed ); assert( result >= 0 && "NtQuery failed." ); DWORD res = 0; // PEB - Process Environment Block data structure. _PEB peb; // Proces parameter - field of PEB. RTL_USER_PROCESS_PARAMETERS param; // Read PEB from target process' memory. res = ReadProcessMemory( hProc , pinfo.PebBaseAddress , &peb , sizeof(_PEB) , nullptr ); assert( res != 0 ); // Read RTL_USER_PROCESS_PARAMETERS from process' memory. res = ReadProcessMemory( hProc , peb.ProcessParameters , ¶m , sizeof(param) , nullptr ); assert( res != 0 ); auto cmdline = param.CommandLine; auto buffer = std::wstring(cmdline.Length, 0); res = ReadProcessMemory( hProc, cmdline.Buffer, buffer.data(), cmdline.Length, nullptr); assert( res != 0 ); std::printf("\n [*] Process base name = %s ", process_basename(hProc).c_str() ); std::printf("\n [*] Process full path = %s \n", process_full_path(hProc).c_str() ); std::printf(" [*] Unique process ID (PID) = %d \n", pinfo.UniqueProcessId ); std::printf(" [*] Parent process ID (PPID) = %d \n", pinfo.InheritedFromUniqueProcessId ); std::printf(" [*] Process PEB address = 0x%X \n", pinfo.PebBaseAddress ); // Display process command line arguments std::wcout << L"\n Cmdline = " << buffer << L"\n"; // Dispose library handle FreeLibrary( hnd ); }
Building
Building target.exe:
$ g++ target.cpp -o target.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g -O3
Building memdump.exe:
$ g++ memdump.cpp -o memdump.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g -pedantic-errors -lpsapi
Experiment 1 => Obtain process full command line arguments
STEP 1 - List all processes with tasklist.
$ tasklist Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage ========================= ======== ================ =========== ============ ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... LockApp.exe 7632 Console 1 8,456 K RuntimeBroker.exe 2024 Console 1 3,372 K dllhost.exe 1244 Console 1 3,220 K svchost.exe 7096 Services 0 1,548 K svchost.exe 6528 Services 0 1,000 K YourPhone.exe 5376 Console 1 12,340 K RuntimeBroker.exe 2168 Console 1 2,672 K svchost.exe 1416 Services 0 4,120 K dllhost.exe 684 Console 1 860 K DataExchangeHost.exe 8012 Console 1 672 K svchost.exe 1992 Services 0 2,356 K SecurityHealthHost.exe 3880 Console 1 616 K SearchUI.exe 5136 Console 1 98,284 K RuntimeBroker.exe 6352 Console 1 11,000 K smartscreen.exe 5716 Console 1 17,440 K MicrosoftEdge.exe 1412 Console 1 540 K browser_broker.exe 7924 Console 1 392 K Windows.WARP.JITService.e 7508 Services 0 348 K MicrosoftEdgeSH.exe 2324 Console 1 208 K MicrosoftEdgeCP.exe 5080 Console 1 476 K Windows.WARP.JITService.e 3472 Services 0 340 K svchost.exe 1336 Services 0 3,064 K svchost.exe 8424 Services 0 7,484 K .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... .... ....
STEP 2 - Show process information. Note: This procedure requires running a terminal with elevated privilege.
$ .\memdump.exe cli 1992 [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. [*] Is Wow64 (32 bits) process = FALSE [*] Is this process Wow64 (32 bits) process = FALSE [*] Process base name = svchost.exe [*] Process full path = C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe [*] Unique process ID (PID) = 1992 [*] Parent process ID (PPID) = 628 [*] Process PEB address = 0x244F2000 Cmdline = C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe -k netsvcs -p -s lfsvc $ .\memdump.exe cli 5080 [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. [*] Is Wow64 (32 bits) process = FALSE [*] Is this process Wow64 (32 bits) process = FALSE [*] Process base name = MicrosoftEdgeCP.exe [*] Process full path = C:\Windows\System32\MicrosoftEdgeCP.exe [*] Unique process ID (PID) = 5080 [*] Parent process ID (PPID) = 828 [*] Process PEB address = 0x88D6000 Cmdline = "C:\Windows\System32\MicrosoftEdgeCP.exe" -ServerName:Windows.Internal.WebRuntime.ContentProcessServer $ .\memdump.exe cli 1208 [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. [*] Is Wow64 (32 bits) process = TRUE [*] Is this process Wow64 (32 bits) process = FALSE [*] Process base name = OneDrive.exe [*] Process full path = C:\Users\unix\AppData\Local\Microsoft\OneDrive\OneDrive.exe [*] Unique process ID (PID) = 1208 [*] Parent process ID (PPID) = 4220 [*] Process PEB address = 0x68D000 Cmdline = /updateInstalled /background $ .\memdump.exe cli 5376 [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. [*] Is Wow64 (32 bits) process = FALSE [*] Is this process Wow64 (32 bits) process = FALSE [*] Process base name = YourPhone.exe [*] Process full path = C:\Program Files\WindowsApps\Microsoft.YourPhone_1.21042.137.0_x64__8wekyb3d8bbwe\YourPhone.exe [*] Unique process ID (PID) = 5376 [*] Parent process ID (PPID) = 828 [*] Process PEB address = 0xD05D8000 Cmdline = "C:\Program Files\WindowsApps\Microsoft.YourPhone_1.21042.137.0_x64__8wekyb3d8bbwe\YourPhone.exe" -ServerName:App.AppX9yct9q388jvt4h7y0gn06smzkxcsnt8m.mca
Experiment 2 - Manipulate target process virtula memory
STEP 1 => Run target.exe executable.
C:\Users\unix\Desktop>.\target.exe [*] Number = 300 [*] cppstr = Hallo Welt [*] Global buffer = Strcpy is an unsafe C function! BE AWARE! [*] Current process PID = 1536 [*] Number address = 000000000063fdec [*] cppstr address = 000000000063fe00 [*] Global buffer address = 000000000040c040 =>> Type RETURN to resume execution [*] Number = 98164 [*] cppstr = Windows NT [*] Global buffer = Replace strcpy with strncpy! NOWBE AWARE! =>> Type RETURN to resume execution
STEP 2 => Run the following commands from another terminal.
## ========= Read process memory ================// $ .\memdump.exe read-num 1536 0x63fdec [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. [*] Number value = 300 $ .\memdump.exe read-str 1536 0x63fe00 20 [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. Buffer value = Hallo Welt Address = 63fe00 $ .\memdump.exe read-str 1536 0x40c040 50 [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. Buffer value = Strcpy is an unsafe C function! BE AWARE! Address = 40c040 ## ========= Write to process memory ================// $ .\memdump.exe write-num 1536 0x63fdec 98164 [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. [*] Number value = 98164 $ .\memdump.exe write-str 1536 0x63fe00 "Windows NT" [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. Buffer value = Windows NT Address = 63fe00 $ .\memdump.exe write-str 1536 0x40c040 "Replace strcpy with strncpy! NOW" [INFO] Enable debug privilege Ok. Buffer value = Replace strcpy with strncpy! NOW Address = 40c040
1.19 Running machine code at runtime
This code uses the windows APIs VirtuaAlloc, for allocating memory for the machine code payload which is copied to the allocated memory, and VirtualProtect for making the allocated memory executable allowing the machine code to be run. This technique is used by JIT compilers from interpreted languages, such as C# or Java, for speeding up computations and reduce the byte code interpretation overhead.
Documentation:
- VirtualAlloc()
- "Reserves, commits, or changes the state of a region of pages in the virtual address space of the calling process. Memory allocated by this function is automatically initialized to zero."
- VirtualProtect()
- "Changes the protection on a region of committed pages in the virtual address space of the calling process. To change the access protection of any process, use the VirtualProtectEx function."
- VirtualFree()
- Brief: "Releases, decommits, or releases and decommits a region of pages within the virtual address space of the calling process.To free memory allocated in another process by the VirtualAllocEx function, use the VirtualFreeEx function."
Sample code
File: winmmap.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <cassert> #include <cstring> // std::memcpy() #include <windows.h> void* load_machine_code(const std::uint8_t* buffer, size_t size) { void* pmap = VirtualAlloc( // lpAddress nullptr // dwSize - Size of memory to be allocated. , size // , MEM_COMMIT | MEM_RESERVE // Memory is writeable, readable, but not executable. , PAGE_READWRITE ); assert( pmap != nullptr && "Allocation failed." ); // Copy machine code to allocated memory std::memcpy(pmap, buffer, size); // Set memory permission to executable. BOOL result = FALSE; // Sto9res previous memory protection flags. DWORD prev_protection = 0; // Set the allocated memory only as readable and executable (code is data!) // ,but not writeable. result = VirtualProtect( pmap, size, PAGE_EXECUTE_READ , &prev_protection ); assert( result == TRUE && "Failed to change memory protection flags." ); return pmap; } /** 0000000000401550 <factorial>: 401550: 55 push rbp 401551: 48 89 e5 mov rbp,rsp 401554: 48 83 ec 10 sub rsp,0x10 401558: 89 4d 10 mov DWORD PTR [rbp+0x10],ecx 40155b: c7 45 fc 01 00 00 00 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],0x1 401562: c7 45 f8 01 00 00 00 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],0x1 401569: eb 0e jmp 401579 <factorial+0x29> 40156b: 8b 45 fc mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4] 40156e: 0f af 45 f8 imul eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8] 401572: 89 45 fc mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],eax 401575: 83 45 f8 01 add DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],0x1 401579: 8b 45 f8 mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8] 40157c: 3b 45 10 cmp eax,DWORD PTR [rbp+0x10] 40157f: 7c ea jl 40156b <factorial+0x1b> 401581: 8b 45 fc mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4] 401584: 48 83 c4 10 add rsp,0x10 401588: 5d pop rbp 401589: c3 ret */ std::uint8_t asm_factorialA[] = { 0x55 ,0x48, 0x89, 0xe5 ,0x48, 0x83, 0xec, 0x10 ,0x89, 0x4d, 0x10 ,0xc7, 0x45, 0xfc, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 ,0xc7, 0x45, 0xf8, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00 ,0xeb, 0x0e ,0x8b, 0x45, 0xfc ,0x0f, 0xaf, 0x45, 0xf8 ,0x89, 0x45, 0xfc ,0x83, 0x45, 0xf8, 0x01 ,0x8b, 0x45, 0xf8 ,0x3b, 0x45, 0x10 ,0x7c, 0xea ,0x8b, 0x45, 0xfc ,0x48, 0x83, 0xc4, 0x10 ,0x5d ,0xc3 }; // Same as asm_factorialA but encoded as hexadecimal. std::uint8_t asm_factorialB[] = "\x55\x48\x89\xe5\x48\x83\xec\x10\x89\x4d\x10\xc7" "\x45\xfc\x01\x00\x00\x00\xc7\x45\xf8\x01\x00\x00" "\x00\xeb\x0e\x8b\x45\xfc\x0f\xaf\x45\xf8\x89\x45" "\xfc\x83\x45\xf8\x01\x8b\x45\xf8\x3b\x45\x10\x7c" "\xea\x8b\x45\xfc\x48\x83\xc4\x10\x5d\xc3" ; int main() { auto data_size = std::size(asm_factorialA); std::printf(" Data size in bytes = %d \n", data_size); // Function pointer alias. using funptr_factorial = int (*) (int n); auto factorialA = (funptr_factorial) load_machine_code( asm_factorialA , std::size(asm_factorialA)); std::printf(" [*] Factorial(4)(A) = %d \n", factorialA(4)); std::printf(" [*] Factorial(5)(A) = %d \n", factorialA(5)); std::printf(" [*] Factorial(6)(A) = %d \n", factorialA(6)); std::printf(" [*] Factorial(7)(A) = %d \n", factorialA(7)); std::printf(" [*] Factorial(8)(A) = %d \n", factorialA(8)); auto factorialB = (funptr_factorial) load_machine_code( asm_factorialB , std::size(asm_factorialB)); std::printf(" [*] Factorial(4)(B) = %d \n", factorialB(4)); std::printf(" [*] Factorial(5)(B) = %d \n", factorialB(5)); std::printf(" [*] Factorial(6)(B) = %d \n", factorialB(6)); std::printf(" [*] Factorial(7)(B) = %d \n", factorialB(7)); std::printf(" [*] Factorial(8)(B) = %d \n", factorialB(8)); std::printf("\n ====== Finish Execution Ok. [ PART 1 ] =======\n"); return 0; }
Building and running
$ g++ winmmap.cpp -o winmmap.exe -std=c++1z -Wall -Wextra -g $ .\winmmap.exe Data size in bytes = 58 [*] Factorial(4)(A) = 6 [*] Factorial(5)(A) = 24 [*] Factorial(6)(A) = 120 [*] Factorial(7)(A) = 720 [*] Factorial(8)(A) = 5040 [*] Factorial(4)(B) = 6 [*] Factorial(5)(B) = 24 [*] Factorial(6)(B) = 120 [*] Factorial(7)(B) = 720 [*] Factorial(8)(B) = 5040 # Display message box containing 'Hast la vista' text.
1.20 CODE - Display information about current process
Print information about current process and copy itself to desktop directory.
File: file:src/windows/currentProcess.cpp
Files
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> // Return true if program was launched by clicking on it, // return false if this program was launched from command line. auto isInOwnConsole() -> bool { DWORD procIDs[2]; DWORD maxCount = 2; DWORD result = GetConsoleProcessList((LPDWORD)procIDs, maxCount); return result != 1; } auto ExecutablePath = [](int pid){ HANDLE hProc = OpenProcess( PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ, FALSE, pid ); // Get process file path std::string process_path(MAX_PATH, 0); DWORD size = MAX_PATH; QueryFullProcessImageNameA(hProc, 0, &process_path[0], &size); process_path.resize(size); CloseHandle(hProc); return process_path; }; auto CurrentDirectory = []{ DWORD size = ::GetCurrentDirectory(0, nullptr); assert(size != 0); std::string path(size + 1, 0x00); size = ::GetCurrentDirectory(path.size(), &path[0]); path.resize(size); return path; }; int main() { // Get current process ID DWORD pid = GetCurrentProcessId(); // Return module handle of current process HMODULE hProc = GetModuleHandleA(nullptr); // Get process module std::cout << "=========== Current Process Info ========" << std::endl; std::cout << "PID = " << pid << std::endl; std::cout << "hProc = 0x" << hProc << std::endl; std::cout << "Executable path = " << ExecutablePath(pid) << std::endl; std::cout << "Current path = " << CurrentDirectory() << std::endl; // Copy itself to Desktop CopyFile(ExecutablePath(pid).c_str(), "C:\\Users\\archbox\\Desktop\\appinfo.exe", false) ; // Stop program from exiting if it was launched by clicking on it. if(!isInOwnConsole()){ std::cout << "\n ==> Type RETURN to exit." << std::endl; std::cin.get(); } return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Building
Compile: MSVC
$ cl.exe currentProcess.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /Fe:currentProcess.exe && currentProcess.exe
Running on console (from cmd.exe or cmder terminal):
$ currentProcess.exe =========== Current Process Info ======== PID = 5712 hProc = 0x00007FF65D890000 Executable path = C:\Users\archbox\Desktop\experiments\currentProcess.exe Current path = c:\Users\archbox\Desktop\experiments
Running program by clicking on it:
- If program checks whether it was launched by click, it waits for the user to type RETURN before terminating.
=========== Current Process Info ======== PID = 6916 hProc = 0x00007FF72C300000 Executable path = C:\Users\archbox\Desktop\experiments\currentProcess.exe Current path = C:\Users\archbox\Desktop\experiments ==> Type RETURN to exit.
Code:
- Function: isInOwnConsole - returns true if program was launched by click. Returns false if it was launched from any type console such as cmd.exe or cmder.
// Return true if program was launched by clicking on it, // return false if this program was launched from command line. auto isInOwnConsole() -> bool { DWORD procIDs[2]; DWORD maxCount = 2; DWORD result = GetConsoleProcessList((LPDWORD)procIDs, maxCount); return result != 1; }
- Lambda function ExecutablePath - Returns the path of some process executable given its PID (Process ID).
auto ExecutablePath = [](int pid){ HANDLE hProc = OpenProcess( PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ, FALSE, pid ); // Get process file path std::string process_path(MAX_PATH, 0); DWORD size = MAX_PATH; QueryFullProcessImageNameA(hProc, 0, &process_path[0], &size); process_path.resize(size); CloseHandle(hProc); return process_path; };
- Lambda function CurrentDirectory - returns current directory.
auto CurrentDirectory = []{ DWORD size = ::GetCurrentDirectory(0, nullptr); assert(size != 0); std::string path(size + 1, 0x00); size = ::GetCurrentDirectory(path.size(), &path[0]); path.resize(size); return path; };
- Main function:
// Get current process ID DWORD pid = GetCurrentProcessId(); // Return module handle of current process HMODULE hProc = GetModuleHandleA(nullptr); // Get process module std::cout << "=========== Current Process Info ========" << std::endl; std::cout << "PID = " << pid << std::endl; std::cout << "hProc = 0x" << hProc << std::endl; std::cout << "Executable path = " << ExecutablePath(pid) << std::endl; std::cout << "Current path = " << CurrentDirectory() << std::endl; // Copy itself to Desktop CopyFile(ExecutablePath(pid).c_str(), "C:\\Users\\archbox\\Desktop\\appinfo.exe", false) ; // Stop program from exiting if it was launched by clicking on it. if(!isInOwnConsole()){ std::cout << "\n ==> Type RETURN to exit." << std::endl; std::cin.get(); } return EXIT_SUCCESS;
1.21 CODE - List processes
This code prints to stdout (console) and to a file the list of running processes in current machine:
Source:
FIle: showProcesses.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <sstream> #include <fstream> // Windows Headers #include <windows.h> #include <tlhelp32.h> auto showProcessInfo(std::ostream& os) -> int; int main() { // Log file auto plog = std::ofstream("process-log.txt"); // Print all processes to stdout. showProcessInfo(std::cout); // Write all processes to file showProcessInfo(plog); // Flush buffer - force data to be written to file. plog.flush(); std::cout << "\n ==> Type return to exit." << std::endl; std::cin.get(); return 0; } //=======================/// // Show all processes in current machine auto showProcessInfo(std::ostream& os) -> int { // Get snapshot with process listing. HANDLE hProcessSnapShot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPPROCESS, 0); // Instnatiate process' entry structure. PROCESSENTRY32 ProcessEntry = { 0 }; ProcessEntry.dwSize = sizeof( ProcessEntry ); BOOL Return = FALSE; Return = Process32First( hProcessSnapShot, &ProcessEntry ); // Returns -1 if process failed if(!Return ) { return -1;} do { // print process' data os << "EXE File = " << ProcessEntry.szExeFile << "\n" << "PID = " << ProcessEntry.th32ProcessID << "\n" << "References = " << ProcessEntry.cntUsage << "\n" << "Thread Count = " << ProcessEntry.cntThreads << "\n" << "-----------------------------------------------\n"; } while( Process32Next( hProcessSnapShot, &ProcessEntry )); // Close handle releasing resource. CloseHandle( hProcessSnapShot ); return 1; }
Analysis
Parts:
- Function which prints all processes to any output stream:
// Show all processes in current machine auto showProcessInfo(std::ostream& os) -> int { // Get snapshot with process listing. HANDLE hProcessSnapShot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPPROCESS, 0); // Instnatiate process' entry structure. PROCESSENTRY32 ProcessEntry = { 0 }; ProcessEntry.dwSize = sizeof( ProcessEntry ); BOOL Return = FALSE; Return = Process32First( hProcessSnapShot, &ProcessEntry ); // Returns -1 if process failed if(!Return ) { return -1;} do { // print process' data os << "EXE File = " << ProcessEntry.szExeFile << "\n" << "PID = " << ProcessEntry.th32ProcessID << "\n" << "References = " << ProcessEntry.cntUsage << "\n" << "Thread Count = " << ProcessEntry.cntThreads << "\n" << "-----------------------------------------------\n"; } while( Process32Next( hProcessSnapShot, &ProcessEntry )); // Close handle releasing resource. CloseHandle( hProcessSnapShot ); return 1; }
- Main function:
// Log file auto plog = std::ofstream("process-log.txt"); // Print all processes to stdout. showProcessInfo(std::cout); // Write all processes to file showProcessInfo(plog); // Flush buffer - force data to be written to file. plog.flush(); std::cout << "\n ==> Type return to exit." << std::endl; std::cin.get(); return 0;
- Compiling and running:
# Build $ cl.exe showProcesses.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /Fe:showProcesses.exe # Run: $ showProcesses # Run $ showProcesses.exe
- Output:
$ showProcesses.exe ... ... ... ... ----------------------------------------------- EXE File = Registry PID = 68 References = 0 Thread Count = 3 ----------------------------------------------- EXE File = smss.exe PID = 308 References = 0 Thread Count = 2 ----------------------------------------------- EXE File = csrss.exe PID = 412 References = 0 Thread Count = 10 ----------------------------------------------- EXE File = wininit.exe PID = 484 References = 0 Thread Count = 1 ----------------------------------------------- ... ... ...
API DOCS:
1.22 CODE - Show all DLLs or modules load by a process
This example program shows all modules, aka DLLs (Dynamic Linked Libraries) loaded by some process given its PID.
- Source: file:src/windows/showModulesDLL.cpp
Gist: showModulesDLL.cpp
Files
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <iomanip> #include <functional> //- Windows Headers --- #include <windows.h> #include <psapi.h> // RAAI for managing Handler template<class HANDLER> class ResourceHandler { public: using Disposer = std::function<void (HANDLER)>; ResourceHandler(HANDLER hnd, Disposer disposer) : m_hnd(hnd), m_fndisp(disposer) { } auto get() -> HANDLER { return m_hnd; } ~ResourceHandler(){ m_fndisp(m_hnd); } // Disable copy-constructor and copy-assignment operator ResourceHandler(const ResourceHandler&) = delete; auto operator= (const ResourceHandler&) -> ResourceHandler& = delete; // Move member functios ResourceHandler(ResourceHandler&& rhs) : m_hnd(rhs.m_hnd), m_fndisp(rhs.m_fndisp){ } auto operator= (ResourceHandler&& rhs){ std::swap(this->m_hnd, rhs.m_hnd); this->m_fndisp = rhs->m_fndisp; } private: HANDLER m_hnd; Disposer m_fndisp; }; auto utf8_encode(const std::wstring& wstr) -> std::string; auto utf8_decode(const std::string& str) -> std::wstring; namespace WProcess{ using ModuleConsumer = std::function<auto (HMODULE, const std::string&) -> void>; auto GetName(HANDLE hProc) -> std::string; auto GetExecutablePath(HANDLE hProc) -> std::string; auto ForEachModule(HANDLE hProc, ModuleConsumer FunIterator) -> void; } int main(int argc, char **argv){ if(argc < 2){ std::cerr << "Error: missing Process ID <PID>."; return EXIT_FAILURE; } DWORD pid; DWORD flags = PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ; try{ pid = std::stoi(argv[1]); } catch(const std::invalid_argument& ex){ std::cerr << "Error invalid PID" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } auto hProc = ResourceHandler<HANDLE>{ ::OpenProcess(flags, FALSE, pid), ::CloseHandle }; if(hProc.get() == nullptr){ std::cerr << "Error: process of pid = <" << pid << "> not found." << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::cout << "Process base name = " << WProcess::GetName(hProc.get()) << std::endl; std::cout << "Process path = " << WProcess::GetExecutablePath(hProc.get()) << std::endl; std::cout << std::endl; // Print all DLLs used by some process WProcess::ForEachModule( hProc.get(), [](HMODULE hmod, const std::string& path) -> void { std::cout << std::setw(10) << hmod << std::setw(5) << " " << std::left << std::setw(45) << path << "\n"; } ); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } // ================= End of Main =================// auto utf8_encode(const std::wstring &wstr) -> std::string { int size_needed = WideCharToMultiByte( CP_UTF8, 0, &wstr[0], (int)wstr.size(), NULL, 0, NULL, NULL); std::string strTo(size_needed, 0); WideCharToMultiByte( CP_UTF8, 0, &wstr[0], (int)wstr.size(), &strTo[0], size_needed, NULL, NULL); return strTo; } auto utf8_decode(const std::string &str) -> std::wstring { int size_needed = MultiByteToWideChar( CP_UTF8, 0, &str[0], (int)str.size(), NULL, 0); std::wstring wstrTo(size_needed, 0); MultiByteToWideChar( CP_UTF8, 0, &str[0], (int) str.size(), &wstrTo[0], size_needed); return wstrTo; } namespace WProcess{ using ModuleConsumer = std::function<auto (HMODULE, const std::string&) -> void>; auto GetName(HANDLE hProc) -> std::string { std::wstring basename(MAX_PATH, 0); int n1 = ::GetModuleBaseNameW(hProc, NULL, &basename[0], MAX_PATH); basename.resize(n1); return utf8_encode(basename); } auto GetExecutablePath(HANDLE hProc) -> std::string { std::wstring path(MAX_PATH, 0); int n2 = ::GetModuleFileNameExW(hProc, NULL, &path[0], MAX_PATH); path.resize(n2); return utf8_encode(path); } auto ForEachModule(HANDLE hProc, ModuleConsumer FunIterator) -> void { HMODULE hMods[1024]; DWORD cbNeeded; if (::EnumProcessModules(hProc, hMods, sizeof(hMods), &cbNeeded)){ int n = cbNeeded / sizeof(HMODULE); std::wstring path(MAX_PATH, 0); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ DWORD nread = ::GetModuleFileNameExW(hProc, hMods[i], &path[0], MAX_PATH); path.resize(nread); if(nread) FunIterator(hMods[i], utf8_encode(path)); } } } } // --- End of namespace WProcess ---- //
Building
Compile with MSVC (cl.exe)
$ cl.exe showModulesDLL.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /Fe:showModulesDLL.exe
Compile with MingW/GCC:
$ g++ showModulesDLL.cpp -o showModulesDLL.exe -std=c++14 -lpsapi
Running:
- List PID of all processes
# Get PID of all processes $ tasklist ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... svchost.exe 88 Services 0 5,920 K dllhost.exe 4572 Console 1 9,520 K notepad.exe 5272 Console 1 14,048 K vctip.exe 3564 Console 1 10,920 K svchost.exe 1112 Services 0 5,572 K svchost.exe 2996 Services 0 7,140 K SearchProtocolHost.exe 5636 Services 0 11,964 K SearchFilterHost.exe 1832 Services 0 6,104 K mspdbsrv.exe 3416 Console 1 5,888 K ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
- Show DLLs loaded by process dllhost.exe (PID 4572)
$ showModulesDLL.exe 4572 Process base name = DllHost.exe Process path = C:\Windows\System32\dllhost.exe 00007FF734720000 C:\WINDOWS\system32\DllHost.exe 00007FFBFA8C0000 C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\ntdll.dll 00007FFBF98C0000 C:\WINDOWS\System32\KERNEL32. 00007FFBF78C0000 C:\WINDOWS\System32\KERNELBASE.d 00007FFBF6C90000 C:\WINDOWS\System32\ucrtbase.dll 00007FFBF7EE0000 C:\WINDOWS\System32\combase.dll ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 00007FFBEDBA0000 C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\iertutil. 00007FFBF65C0000 C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\CRYPTBASE.DL
Parts:
- Class ResourceHandler<HANDLER> is a RAII (Resource Aquisition Is Initialization) for any generic resource which may not be a pointer such as an integer for a file descriptor.
template<class HANDLER> class ResourceHandler { public: using Disposer = std::function<void (HANDLER)>; ResourceHandler(HANDLER hnd, Disposer disposer) : m_hnd(hnd), m_fndisp(disposer) { } auto get() -> HANDLER { return m_hnd; } ~ResourceHandler(){ m_fndisp(m_hnd); } // Disable copy-constructor and copy-assignment operator ResourceHandler(const ResourceHandler&) = delete; auto operator= (const ResourceHandler&) -> ResourceHandler& = delete; // Move member functios ResourceHandler(ResourceHandler&& rhs) : m_hnd(rhs.m_hnd), m_fndisp(rhs.m_fndisp){ } auto operator= (ResourceHandler&& rhs){ std::swap(this->m_hnd, rhs.m_hnd); this->m_fndisp = rhs->m_fndisp; } private: HANDLER m_hnd; Disposer m_fndisp; };
Namespace WProcess contains functions for querying processes:
namespace WProcess{ using ModuleConsumer = std::function<auto (HMODULE, const std::string&) -> void>; auto GetName(HANDLE hProc) -> std::string; auto GetExecutablePath(HANDLE hProc) -> std::string; auto ForEachModule(HANDLE hProc, ModuleConsumer FunIterator) -> void; }
Main function
- Get PID (Process ID) as program argument.
DWORD pid; DWORD flags = PROCESS_QUERY_INFORMATION | PROCESS_VM_READ; try{ pid = std::stoi(argv[1]); } catch(const std::invalid_argument& ex){ std::cerr << "Error invalid PID" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } // Automatically closes this handle when it goes out of scope. auto hProc = ResourceHandler<HANDLE>{ ::OpenProcess(flags, FALSE, pid), ::CloseHandle };
Print process name:
std::cout << "Process base name = " << WProcess::GetName(hProc.get()) << std::endl;
Print path to executable:
std::cout << "Process path = " << WProcess::GetExecutablePath(hProc.get()) << std::endl;
Print all DLLs used by the process:
using ModuleConsumer = std::function<auto (HMODULE, const std::string&) -> void>; // Print all DLLs used by some process WProcess::ForEachModule( hProc.get(), [](HMODULE hmod, const std::string& path) -> void { std::cout << std::setw(10) << hmod << std::setw(5) << " " << std::left << std::setw(45) << path << "\n"; } );
Functions in namespace WProcess
- WProcess::GetName
auto GetName(HANDLE hProc) -> std::string { std::wstring basename(MAX_PATH, 0); int n1 = ::GetModuleBaseNameW(hProc, NULL, &basename[0], MAX_PATH); basename.resize(n1); return utf8_encode(basename); }
- WProcess::GetExecutablePath
auto GetExecutablePath(HANDLE hProc) -> std::string { std::wstring path(MAX_PATH, 0); int n2 = ::GetModuleFileNameExW(hProc, NULL, &path[0], MAX_PATH); path.resize(n2); return utf8_encode(path); }
- WProcess::ForEachModule
auto ForEachModule(HANDLE hProc, ModuleConsumer FunIterator) -> void { HMODULE hMods[1024]; DWORD cbNeeded; if (::EnumProcessModules(hProc, hMods, sizeof(hMods), &cbNeeded)){ int n = cbNeeded / sizeof(HMODULE); std::wstring path(MAX_PATH, 0); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ DWORD nread = ::GetModuleFileNameExW(hProc, hMods[i], &path[0], MAX_PATH); path.resize(nread); if(nread) FunIterator(hMods[i], utf8_encode(path)); } } }
1.23 CODE - Show files and directories attributes cmake build demo code
Gist:
File: attrib.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <windows.h> #include <string> #define disp(expr) std::cerr << std::boolalpha << __FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__ << ":" \ << " ; " << #expr << " = " << (expr) << std::endl void showFileAttributes(std::string path) { DWORD attr = GetFileAttributesA(path.c_str()); disp(attr); bool isInvalid = attr == INVALID_FILE_ATTRIBUTES; bool exists = !isInvalid; bool isDirectory = exists && static_cast<bool>(attr & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY); bool isFile = exists && !static_cast<bool>(attr & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY); std::cout << "File attributes for path = " << path << std::endl; std::cout << std::boolalpha << "Is invalid file attribute = " << isInvalid << std::endl << "File exists = " << exists << std::endl << "Is directory = " << isDirectory << std::endl << "Is file = " << isFile << std::endl; std::cout << "--------------------------------" << std::endl << std::endl; } bool fileExists(std::string path) { DWORD attr = GetFileAttributesA(path.c_str()); return !(attr == INVALID_FILE_ATTRIBUTES) && !(attr & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY); } bool dirExists(std::string path) { DWORD attr = GetFileAttributesA(path.c_str()); return !(attr == INVALID_FILE_ATTRIBUTES) && (attr & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY); } // Get Path to current program / Application std::string pathToThisProgram() { std::string result(MAX_PATH, 0); int n = GetModuleFileNameA(NULL, &result[0], MAX_PATH); result.resize(n); return result; } std::string getEnvironment(std::string varname) { static int size = 32767; std::string result(size, 0); DWORD n = GetEnvironmentVariableA(varname.c_str(), &result[0], size); result.resize(n); return result; } int main() { std::cout << "Path to this program = " << pathToThisProgram() << std::endl; std::cout << "Evironment variable => %USERPROFILE% = " << getEnvironment("USERPROFILE") << std::endl; std::cout << "Evironment variable => %SYSTEMROOT% = " << getEnvironment("SYSTEMROOT") << std::endl; std::cout << "Evironment variable => %WRONGVAR% = " << getEnvironment("WRONGVAR") << std::endl; std::string thisprog = pathToThisProgram(); std::string dest = getEnvironment("USERPROFILE") + "\\Desktop\\app.exe"; // Copy file to Desktop if (fileExists(dest)) { std::cout << " ==> File " << dest << " exists - removing it ... " << std::endl; DeleteFileA(dest.c_str()); } bool result = CopyFileA(thisprog.c_str(), dest.c_str(), TRUE); std::cout << "Copy successful? = " << std::boolalpha << result << std::endl; //Delete this executable bool result2 = DeleteFileA(thisprog.c_str()); std::cout << "Delete successful? = " << std::boolalpha << result2 << std::endl; std::cout << "-------------------------------" << std::endl; showFileAttributes("C:\\Windows\\System32"); showFileAttributes("C:/Windows/System32"); showFileAttributes("C:\\Windows\\System32\\cmd.exe"); showFileAttributes("C:\\Windows\\System32DONOT_EXISTS"); disp(fileExists("C:\\Windows\\System32")); disp(fileExists("C:/Windows/System32")); // Windows file system is case insensitive! disp(fileExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\cmd.exe")); disp(fileExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\CMD.EXE")); disp(fileExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\kernel32.dll")); disp(fileExists("C:\\Windows\\System32DONOT_EXISTS")); std::cout << std::endl; disp(dirExists("C:\\Windows\\System32")); disp(dirExists("C:/Windows/System32")); disp(dirExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\cmd.exe")); disp(dirExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\CMD.EXE")); disp(dirExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\kernel32.dll")); disp(dirExists("C:\\Windows\\System32DONOT_EXISTS")); disp(dirExists("C:\\$Recycle.bin")); return 0; }
File: CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.9) project(WindowsExploration) #========== Global Configurations =============# #----------------------------------------------# set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17) set(CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON) #========== Targets Configurations ============# add_executable(attrib attrib.cpp)
Download sources:
$ git clone https://gist.github.com/bad57134dd6e95e394a04b8b727a825f attrib $ cd attrib $ ls CMakeLists.txt Makefile attrib.cpp build_msvc.bat
Building manually with MINGW (GCC ported to Windows):
$ g++ attrib.cpp -o attrib.exe -std=c++1z -ggdb -Wall -Wextra $ g++ attrib.cpp -o attrib.scr -std=c++1z -ggdb -Wall -Wextra $ file attrib.exe attrib.exe: PE32+ executable (console) x86-64, for MS Windows
Building manually with MSVC-2019 (cl.exe) via developer command prompt at start menu.
$ cl.exe attrib.cpp /out:attrib.exe /ZI /std:c++latest
Building via CMake and Visual Studio Code Vscode:
# Open the directory with source files in Vscode, Select the toolchain (called KIT) # ,then build the application. $ cd attrib $ vscode .
Building with CMake and "Visual" Studio Compiler (MSVC-15) from command line:
$ cmake -H. -B_build -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug -G "Visual Studio 14 2015 Win64" $ cmake --build _build --target all # Command file comes from GIT installation that provides some Linux/UNIX tools # for Windows. $ file _build/Debug/atrib.exe _build/Debug/atrib.exe: PE32+ executable (console) x86-64, for MS Windows
Building with CMake and MSVC 2019 (Only works if this compiler is already installed.)
$ cmake -B_build -H. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug $ cmake --build _build --target all
Building with CMake and Mingw:
$ cmake -H. -B_build_mingw -G "MinGW Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug -DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=TRUE
$ cmake --build _build_mingw --target
$ dir _build_mingw/
CMakeCache.txt CMakeFiles Makefile cmake_install.cmake compile_commands.json
Program output:
$ _build\Debug\attrib.exe Path to this program = Z:\windows-experiments\build\attrib.exe Evironment variable => %USERPROFILE% = C:\Users\myuser Evironment variable => %SYSTEMROOT% = C:\Windows Evironment variable => %WRONGVAR% = ==> File C:\Users\myuser\Desktop\app.exe exists - removing it ... Copy successful? = true Delete successful? = false ------------------------------- ..\application1.cpp:11: ; attr = 16 File attributes for path = C:\Windows\System32 Is invalid file attribute = false File exists = true Is directory = true Is file = false -------------------------------- ..\application1.cpp:11: ; attr = 16 File attributes for path = C:/Windows/System32 Is invalid file attribute = false File exists = true Is directory = true Is file = false -------------------------------- ..\application1.cpp:11: ; attr = 32 File attributes for path = C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe Is invalid file attribute = false File exists = true Is directory = false Is file = true -------------------------------- ..\application1.cpp:11: ; attr = 4294967295 File attributes for path = C:\Windows\System32DONOT_EXISTS Is invalid file attribute = true File exists = false Is directory = false Is file = false -------------------------------- ..\application1.cpp:90: ; fileExists("C:\\Windows\\System32") = false ..\application1.cpp:91: ; fileExists("C:/Windows/System32") = false ..\application1.cpp:93: ; fileExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\cmd.exe") = true ..\application1.cpp:94: ; fileExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\CMD.EXE") = true ..\application1.cpp:95: ; fileExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\kernel32.dll") = true ..\application1.cpp:96: ; fileExists("C:\\Windows\\System32DONOT_EXISTS") = false ..\application1.cpp:100: ; dirExists("C:\\Windows\\System32") = true ..\application1.cpp:101: ; dirExists("C:/Windows/System32") = true ..\application1.cpp:102: ; dirExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\cmd.exe") = false ..\application1.cpp:103: ; dirExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\CMD.EXE") = false ..\application1.cpp:104: ; dirExists("C:\\Windows\\System32\\kernel32.dll") = false ..\application1.cpp:105: ; dirExists("C:\\Windows\\System32DONOT_EXISTS") = false ..\application1.cpp:106: ; dirExists("C:\\$Recycle.bin") = true
1.24 CODE - List directory files
Program for listing directories, similar to U*nix's ls or Windows' dir usign Win32 API.
Source:
- File: file:src/windows/listFiles.cpp
- Gist: listFiles.cpp
Files
File: listFiles.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <sstream> #include <iomanip> #include <functional> //- Windows Headers --- #include <windows.h> //----------------------------------------------// // Uses RAII for setting console to UTF8 // and restoring its previous settings. class ConsoleUTF8{ public: // Constructor saves context ConsoleUTF8(){ m_config = ::GetConsoleOutputCP(); ::SetConsoleOutputCP(CP_UTF8); std::cerr << " [TRACE] Console set to UTF8" << std::endl; } // Destructor restores context ~ConsoleUTF8(){ std::cerr << " [TRACE] Console restored." << std::endl; ::SetConsoleOutputCP(m_config); } private: unsigned int m_config; }; struct CloseHandleRAAI{ using Disposer = std::function<void ()>; Disposer m_dispose; CloseHandleRAAI(Disposer dispose): m_dispose(dispose){ } ~CloseHandleRAAI(){ m_dispose(); } }; void CloseHandleLog(HANDLE h, const std::string& name){ ::CloseHandle(h); std::cerr << " [LOG] Handler <" << name << "> closed OK." << std::endl; } auto utf8_encode(const std::wstring &wstr) -> std::string; auto utf8_decode(const std::string &str) -> std::wstring; using FileEnumerator = std::function<bool (const std::string&)>; auto getLastErrorAsString() -> std::string; auto EnumerateFiles(const std::string& path, FileEnumerator Enumerator) -> int; int main(int argc, char** argv){ if(argc < 2){ std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " " << "[PATH]" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } auto utf8Console = ConsoleUTF8(); auto directoryPath = std::string{argv[1]}; std::cout << "directoryPath = " << directoryPath << "\n"; int count = 0; // Show 50 first files. int status = EnumerateFiles( directoryPath, [&count](const auto& file){ std::cout << " => " << file << "\n"; if(count++ < 50) return true; else return false; }); if(status != ERROR_SUCCESS){ std::cout << " => Error code = " << ::GetLastError() << std::endl; std::cout << " => Error message = " << getLastErrorAsString() << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::puts(" [LOG] End sucessfully"); // FindClose(hFile); //CloseHandle(hFind); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } //---------------------------------------------------------// /** Enumerate files of some directory util enumerator function (callback) returns false. * - path - Directory path to be listed * - Enumerator - Functions which consumes a string (file listed) and returns bool. * this function returns false when it is no longer interested in * being called. When it returns false the iteration stops. * * - Return - Returns error code from GetLastError(). If it is successful, * the function returns ERROR_SUCCESS. */ auto EnumerateFiles(const std::string& path, FileEnumerator Enumerator) -> int { WIN32_FIND_DATAW fdata; HANDLE hFind = INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE; // Ensure that resource hFind is always disposed. auto close_hFind = CloseHandleRAAI(std::bind(CloseHandleLog, hFind, "hFile")); hFind = FindFirstFileW(utf8_decode(path).c_str(), &fdata); if(hFind == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) return GetLastError(); do { //Consumer function if(!Enumerator(utf8_encode(fdata.cFileName))) break; } while(FindNextFileW(hFind, &fdata) != 0); return ERROR_SUCCESS; } // Print human-readable description of GetLastError() - Error Code // Source: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1387064 // Requires: <string>, <sstream>, <windows.h>, auto getLastErrorAsString() -> std::string { //Get the error message, if any. DWORD errorMessageID = ::GetLastError(); if(errorMessageID == 0) return std::string(); LPSTR messageBuffer = nullptr; static const DWORD flags = FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS; size_t size = FormatMessageA( flags, NULL, errorMessageID, MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), (LPSTR)&messageBuffer, 0, NULL); auto message = std::string(messageBuffer, size); auto ss = std::stringstream(message); auto line = std::string{}; std::getline(ss, line, '\r'); //Free the buffer. LocalFree(messageBuffer); return line; } auto utf8_encode(const std::wstring &wstr) -> std::string { int size_needed = WideCharToMultiByte( CP_UTF8, 0, &wstr[0], (int)wstr.size(), NULL, 0, NULL, NULL); std::string strTo(size_needed, 0); WideCharToMultiByte( CP_UTF8, 0, &wstr[0], (int)wstr.size(), &strTo[0], size_needed, NULL, NULL); return strTo; } // Credits: https://gist.github.com/pezy/8571764 auto utf8_decode(const std::string &str) -> std::wstring { int size_needed = MultiByteToWideChar( CP_UTF8, 0, &str[0], (int)str.size(), NULL, 0); std::wstring wstrTo(size_needed, 0); MultiByteToWideChar( CP_UTF8, 0, &str[0], (int) str.size(), &wstrTo[0], size_needed); return wstrTo; }
Building
- MSVC
$ cl.exe listFiles.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /Fe:listFiles.exe
- Mingw/GCC
$ g++ listFiles.cpp -o listFiles.exe -std=c++14
Usage:
$ listFiles.exe "C:\*" [TRACE] Console set to UTF8 directoryPath = C:\* => $GetCurrent => $Recycle.Bin ... . ... ... .... .. .. ... => pagefile.sys => PerfLogs => Program Files => Program Files (x86) ... ... ... ... => Users => Windows => Windows10Upgrade [LOG] Handler <hFile> closed OK. [LOG] End sucessfully [TRACE] Console restored. $ listFiles.exe "E:\*" [TRACE] Console set to UTF8 directoryPath = E:\* [LOG] Handler <hFile> closed OK. => Error code = 3 => Error message = The system cannot find the path specified. [TRACE] Console restored. $ listFiles.exe "C:\windows\system32\*.dll" 2> log directoryPath = C:\windows\system32\*.dll => aadauthhelper.dll => aadcloudap.dll => aadjcsp.dll => aadtb.dll => aadWamExtension.dll => AboutSettingsHandlers.dll => AboveLockAppHost.dll ... ... ... ... [LOG] End sucessfully
Parts
- Function: getLastErrorAsString - Returns a human readable std::string description of GetLastError().
// Print human-readable description of GetLastError() - Error Code // Source: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1387064 Requires: // <string>, <sstream>, <windows.h>, auto getLastErrorAsString() -> std::string { //Get the error message, if any. DWORD errorMessageID = ::GetLastError(); if(errorMessageID == 0) return std::string(); LPSTR messageBuffer = nullptr; static const DWORD flags = FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS; size_t size = FormatMessageA( flags, NULL, errorMessageID, MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), (LPSTR)&messageBuffer, 0, NULL); auto message = std::string(messageBuffer, size); auto ss = std::stringstream(message); auto line = std::string{}; std::getline(ss, line, '\r'); //Free the buffer. LocalFree(messageBuffer); return line; }
- Function EnumereFiles encapsulates the WinAPIs FindFileFirstW and FindNextFileW. This function iterate over files of some directory and applies an Enumerator function taking a string (file name) and returning a boolean. The iteration continues until the enumerator function returns false.
using FileEnumerator = std::function<bool (const std::string&)>; /** Enumerate files of some directory util enumerator function (callback) returns false. * - path - Directory path to be listed * - Enumerator - Functions which consumes a string (file listed) and returns bool. * this function returns false when it is no longer interested in * being called. When it returns false the iteration stops. * * - Return - Returns error code from GetLastError(). If it is successful, * the function returns ERROR_SUCCESS. */ auto EnumerateFiles(const std::string& path, FileEnumerator Enumerator) -> int { WIN32_FIND_DATAW fdata; HANDLE hFind = INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE; // Ensure that resource hFind is always disposed. auto close_hFind = CloseHandleRAAI(std::bind(CloseHandleLog, hFind, "hFile")); hFind = FindFirstFileW(utf8_decode(path).c_str(), &fdata); if(hFind == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) return GetLastError(); do { //Consumer function if(!Enumerator(utf8_encode(fdata.cFileName))) break; } while(FindNextFileW(hFind, &fdata) != 0); return ERROR_SUCCESS; }
Main function:
if(argc < 2){ std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " " << "[PATH]" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } auto utf8Console = ConsoleUTF8(); auto directoryPath = std::string{argv[1]}; std::cout << "directoryPath = " << directoryPath << "\n"; int count = 0; // Show 50 first files. int status = EnumerateFiles( directoryPath, [&count](const auto& file){ std::cout << " => " << file << "\n"; if(count++ < 50) return true; else return false; }); if(status != ERROR_SUCCESS){ std::cout << " => Error code = " << ::GetLastError() << std::endl; std::cout << " => Error message = " << getLastErrorAsString() << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::puts(" [LOG] End sucessfully"); return EXIT_SUCCESS;
WinAPIs used:
1.25 CODE - Enumerate Logical Drivers
This code enumerates all logical drivers in the current Windows machine, for instance, C:, D:, E: … and so on.
Source:
Files:
File: GetLogicalDrivers.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <sstream> #include <deque> #include <vector> #include <functional> #include <Windows.h> using DriverEnumerator = std::function<auto (std::string) -> void>; auto EnumerateLogicalDriver(DriverEnumerator Consumer) -> void; template<template<class, class> class Container = std::vector> auto LogicalDriverList() -> Container<std::string, std::allocator<std::string>>; int main() { std::puts("Logical Drivers or Disks found in the current installation"); std::puts("------------------------------------------------"); EnumerateLogicalDriver( [](const std::string& name){ std::cout << "Driver = " << name << std::endl; }); auto driverList1 = LogicalDriverList<std::deque>(); std::cout << " *=> Driver list in STL container std::deque = "; for(const auto& d: driverList1){ std::cout << d << ", "; } std::cout << std::endl;; auto driverList2 = LogicalDriverList<std::vector>(); std::cout << " *=> Driver list in STL container std::vector = "; for(const auto& d: driverList2){ std::cout << d << ", "; } std::cout << std::endl;; return 0; } //---------------------------------------------------// using DriverEnumerator = std::function<auto (std::string) -> void>; auto EnumerateLogicalDriver(DriverEnumerator Consumer) -> void { size_t size = ::GetLogicalDriveStringsA(0, nullptr); std::string buffer(size, 0x00); ::GetLogicalDriveStringsA(buffer.size(), &buffer[0]); std::stringstream ss{buffer}; while(std::getline(ss, buffer, '\0') && !buffer.empty()) Consumer(buffer); } // Remember: Template always in header files // The user can choose the type of container used to return // the computer drivers. template<template<class, class> class Container = std::vector> auto LogicalDriverList() -> Container<std::string, std::allocator<std::string>> { Container<std::string, std::allocator<std::string>> list{}; EnumerateLogicalDriver( [&](const std::string& name){ list.push_back(name); }); return list; }
Analysis
Main Function:
std::puts("Logical Drivers or Disks found in the current installation"); std::puts("------------------------------------------------"); EnumerateLogicalDriver( [](const std::string& name){ std::cout << "Driver = " << name << std::endl; }); auto driverList1 = LogicalDriverList<std::deque>(); std::cout << " *=> Driver list in STL container std::deque = "; for(const auto& d: driverList1){ std::cout << d << ", "; } std::cout << std::endl;; auto driverList2 = LogicalDriverList<std::vector>(); std::cout << " *=> Driver list in STL container std::vector = "; for(const auto& d: driverList2){ std::cout << d << ", "; } std::cout << std::endl;; return 0;
Function EnumerateDriver:
- Takes a function as argument which consumes the logical driver names passed as string.
using DriverEnumerator = std::function<auto (std::string) -> void>; auto EnumerateLogicalDriver(DriverEnumerator Consumer) -> void { size_t size = ::GetLogicalDriveStringsA(0, nullptr); std::string buffer(size, 0x00); ::GetLogicalDriveStringsA(buffer.size(), &buffer[0]); std::stringstream ss{buffer}; while(std::getline(ss, buffer, '\0') && !buffer.empty()) Consumer(buffer); }
Function LogicalDriverList;
- Templated functions which takes an STL container as type argument. It allows choosing the type of stl container which will be returned.
// Remember: Template always in header files The user can choose the // type of container used to return the computer drivers. template<template<class, class> class Container = std::vector> auto LogicalDriverList() -> Container<std::string, std::allocator<std::string>> { Container<std::string, std::allocator<std::string>> list{}; EnumerateLogicalDriver( [&](const std::string& name){ list.push_back(name); }); return list; }
Program output:
# Compiling and running with MingW/GCC $ g++ GetLogicalDrivers.cpp -std=c++1z -o out.exe && out.exe Logical Drivers or Disks found in the current installation ------------------------------------------------ Driver = C:\ Driver = D:\ *=> Driver list in STL container std::deque = C:\, D:\, *=> Driver list in STL container std::vector = C:\, D:\,
1.26 CODE - Launching and controlling sub-processes
This sample program contains a class process builder which encapsulates the complexity of Windows API process. It can be used for launching processes, streaming process output line by line, wait for process execution, get PID and also terminate the subprocess.
Source:
- File: file:src/windows/winprocess.cpp
- GIST: winprocess.cpp
Files
File: winprocess.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <cstdio> #include <sstream> #include <functional> #include <fstream> #include <windows.h> //========= File: ProcessBuilder.hpp - Header ===================// /** Requires: <iostream> <string>, <functional> <vector> <windows.h> */ class ProcessBuilder { private: // Program to be run std::string m_program; // Arguments passed to the program std::vector<std::string> m_args = {}; // If this flag is true, the program is launched on console bool m_console = true; std::string m_cwd; STARTUPINFO m_si = { sizeof(STARTUPINFO)}; PROCESS_INFORMATION m_pi; public: using SELF = ProcessBuilder&; using LineConsumer = std::function<bool (std::string)>; ProcessBuilder() = default; ProcessBuilder(const std::string& program, const std::vector<std::string>& args = {}); ProcessBuilder(const ProcessBuilder&) = delete; auto operator=(const ProcessBuilder&) = delete; ~ProcessBuilder(); ProcessBuilder(ProcessBuilder&& rhs); auto operator=(ProcessBuilder&& rhs) -> SELF; auto SetProgram(const std::string& program) -> SELF; auto SetConsole(bool flag) -> SELF; /** Set process directory. * @param path - Process directory path. */ auto SetCWD(const std::string& path) -> SELF; /** Start process without waiting for its termination. */ auto Run() -> bool; auto Wait() -> void; // Start process and wait for its termination. auto RunWait() -> bool; auto GetPID() -> DWORD; auto Terminate() -> bool; auto isRunning() -> bool; auto StreamLines(LineConsumer consumer) -> bool; auto GetOutput() -> std::string; private: auto ReadLineFromHandle(HANDLE hFile) -> std::pair<bool, std::string>; }; //========= End of Class ProcessBuilder ===== // //========= File: main.cpp ===================// int main(int argc, char** argv) { if(argc < 2) { std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " [test0 | test1 | test2 | test3 | test4 ]" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } auto tryExit = [&argc, &argv](std::function<int ()> Action) -> void { try { // End current process with exit code returned // from function int status = Action(); std::cerr << "[SUCCESS] End gracefully"; std::exit(status); }catch(const std::runtime_error& ex) { std::cerr << "[ERROR ] " << ex.what() << std::endl; std::exit(1); } }; /** Stream process output to stdout line by line. Print line read form subprocess * output as soon as it arrives. */ if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test0") tryExit([]{ auto p = ProcessBuilder(); p.SetProgram("ping 8.8.8.8"); std::puts("Stream output of process ping to stdout."); p.StreamLines([](std::string line){ std::cout << " line = " << line << std::endl; return true; }); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }); /** Read whole process output and then print it to console and to a file. * run $ dir . at path C:\\windows\\system32, read the whole process output * as string printing it and saving it to a log file. (output.log) */ if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test1") tryExit([]{ std::puts("Get output of tasklist."); auto p = ProcessBuilder("dir ."); p.SetCWD("C:\\windows\\system32"); std::cout << "Process output = " << std::endl; auto out = p.GetOutput(); std::cout << out << std::endl; std::ofstream fs("output.log"); fs << " ==>>> Process output = " << "\n"; fs << " +=================+ " << "\n"; fs << out; return EXIT_SUCCESS; }); /** Launch a process (for window subsystem) and wait for its termination. */ if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test2") tryExit([]{ std::puts("Launch process and wait for its termination"); auto p = ProcessBuilder("notepad"); p.Run(); std::cout << "Waiting for process termination" << std::endl; p.Wait(); std::cout << "Process terminated. OK." << std::endl; return EXIT_SUCCESS; }); /** Launch a process and terminate it when user hit RETURN. */ if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test3") tryExit([]{ std::puts("Launch process and wait for its termination"); auto p = ProcessBuilder("notepad"); p.Run(); std::cout << "Enter RETURN to terminate process => PID = " << p.GetPID() << std::endl; std::cin.get(); p.Terminate(); std::cout << " Process terminated OK."; return EXIT_SUCCESS; }); /** Simulate failure. */ if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test4") tryExit([]{ std::puts("Launch process and wait for its termination"); auto p = ProcessBuilder("notepad-error-failure"); p.Run(); std::cout << "Enter RETURN to terminate process => PID = " << p.GetPID() << std::endl; std::cin.get(); p.Terminate(); std::cout << " Process terminated OK."; return EXIT_SUCCESS; }); std::cerr << "Error: invalid option " << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE;; } //========= File: ProcessBuilder.cpp - Implementation ===================// ProcessBuilder::ProcessBuilder(const std::string& program, const std::vector<std::string>& args) : m_program(std::move(program)) , m_args(std::move(args)) , m_si() { } ProcessBuilder::~ProcessBuilder(){ ::CloseHandle( m_pi.hProcess ); ::CloseHandle( m_pi.hThread ); } ProcessBuilder::ProcessBuilder(ProcessBuilder&& rhs) { m_program = std::move(rhs.m_program); m_args = std::move(rhs.m_args); m_console = std::move(rhs.m_console); m_cwd = std::move(m_cwd); m_si = std::move(m_si); m_pi = std::move(m_pi); } auto ProcessBuilder::operator=(ProcessBuilder&& rhs) -> SELF { std::swap(m_program, rhs.m_program); std::swap(m_args, rhs.m_args); std::swap(m_console, rhs.m_console); std::swap(m_cwd, rhs.m_cwd); std::swap(m_si, rhs.m_si); std::swap(m_pi, rhs.m_pi); return *this; } auto ProcessBuilder::SetProgram(const std::string& program) -> ProcessBuilder& { m_program = program; return *this; } auto ProcessBuilder::SetConsole(bool flag) -> ProcessBuilder& { m_console = flag; return *this; } /** Set process directory. * @param path - Process directory path. */ auto ProcessBuilder::SetCWD(const std::string& path) -> ProcessBuilder& { m_cwd = path; return *this; } /** Start process without waiting for its termination. */ auto ProcessBuilder::Run() -> bool { std::string cmdline = m_program; for(const auto& s: m_args) cmdline = cmdline + " " + s; bool status = ::CreateProcessA( // lpApplicationName nullptr // lpCommandLine ,&cmdline[0] // lpProcessAttributes ,nullptr // lpThreadAttributes ,nullptr // bInheritHandles ,m_console ? true : false // dwCreationFlags ,m_console ? 0 : CREATE_NO_WINDOW // lpEnvironment - Pointer to environment variables ,nullptr // lpCurrentDirectory - Pointer to current directory ,m_cwd.empty() ? nullptr : &m_cwd[0] // lpStartupInfo ,&m_si // lpProcessInformation ,&m_pi ); DWORD code; // Wait 10 milliseconds ::WaitForSingleObject(m_pi.hProcess, 10); ::GetExitCodeProcess(m_pi.hProcess, &code); if(code != STILL_ACTIVE) throw std::runtime_error(std::string("Failed to create process = ") + m_program); return status; } auto ProcessBuilder::Wait() -> void { ::WaitForSingleObject( m_pi.hProcess, INFINITE ); } // Start process and wait for its termination. auto ProcessBuilder::RunWait() -> bool { bool status = this->Run(); this->Wait(); return status; } auto ProcessBuilder::GetPID() -> DWORD { return m_pi.dwProcessId; } auto ProcessBuilder::Terminate() -> bool { return ::TerminateProcess(m_pi.hProcess, 0); } auto ProcessBuilder::isRunning() -> bool { DWORD code; ::GetExitCodeProcess(m_pi.hProcess, &code); return code == STILL_ACTIVE; } auto ProcessBuilder::StreamLines(ProcessBuilder::LineConsumer consumer) -> bool { HANDLE hProcStdoutRead = INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE; HANDLE hProcStdoutWrite = INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE; SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES sattr; sattr.nLength = sizeof(SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES); sattr.bInheritHandle = true; sattr.lpSecurityDescriptor = nullptr; if(!::CreatePipe(&hProcStdoutRead, &hProcStdoutWrite, &sattr, 0)) throw std::runtime_error("Error: failed to create pipe"); if(!::SetHandleInformation(hProcStdoutRead, HANDLE_FLAG_INHERIT, 0)) throw std::runtime_error("Error: failed to set handle information"); m_si.hStdOutput = hProcStdoutWrite; m_si.dwFlags |= STARTF_USESTDHANDLES; bool status = this->Run(); // The writing handler must be closed befored reading the ::CloseHandle(hProcStdoutWrite); auto lin = std::pair<bool, std::string>{}; while(lin = ReadLineFromHandle(hProcStdoutRead), lin.first) if(!consumer(std::move(lin.second))) break; return status; } //--- EOf ReadOutput --- // auto ProcessBuilder::GetOutput() -> std::string { std::stringstream ss; StreamLines([&ss](std::string line){ ss << line << '\n'; return true; }); return ss.str(); } auto ProcessBuilder::ReadLineFromHandle(HANDLE hFile) -> std::pair<bool, std::string> { std::stringstream ss; DWORD bytesRead; char c; bool result; while(true){ result = ::ReadFile(hFile, &c, 1, &bytesRead, nullptr); //, result if(GetLastError() == ERROR_HANDLE_EOF || GetLastError() == ERROR_BROKEN_PIPE){ // std::cerr << " [TRACE] Reach END OF FILE." << std::endl; return std::make_pair(false, ""); } if(c == '\n') break; ss << c; } // Return (NOTEOF?, string) => Flag returns false while end of file is not reached. std::string line = ss.str(); char last = line[line.size()-1]; if(last == '\r' || last == '\n') line = line.substr(0, line.size() - 2); return std::make_pair(!(bytesRead == 0 && result), ss.str()); };
Building
Compiling MSVC:
$ cl.exe winprocess.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /Fe:winprocess.exe
Compiling Mingw/GCC:
$ g++ winprocess.cpp -o winprocess.exe -Wall -Wextra -std=c++14
Main function
The main function accepts a single argument which can be test0, test1, test2, test3 and test4. Each argument tests a different action.
int main(int argc, char** argv){ if(argc < 2){ std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " [test0 | test1 | test2 | test3 | test4 ]" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } auto tryExit = [&argc, &argv](std::function<int ()> Action) -> void { try { // End current process with exit code returned // from function int status = Action(); std::cerr << "[SUCCESS] End gracefully"; std::exit(status); } catch(const std::runtime_error& ex) { std::cerr << "[ERROR ] " << ex.what() << std::endl; std::exit(1); } }; /** Stream process output to stdout line by line. Print line read form subprocess * output as soon as it arrives. */ if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test0") tryExit([]{ auto p = ProcessBuilder(); p.SetProgram("ping 8.8.8.8"); std::puts("Stream output of process ping to stdout."); p.StreamLines([](std::string line){ std::cout << " line = " << line << std::endl; return true; }); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }); /** Read whole process output and then print it to console and to a file. * run $ dir . at path C:\\windows\\system32, read the whole process output * as string printing it and saving it to a log file. (output.log) */ if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test1") ... ... ... ... std::cerr << "Error: invalid option " << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; }
Command test0
The command test0 stream process (ping.exe) output line by line read from the sub-process as soon as the process prints the line.
if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test0") tryExit([]{ auto p = ProcessBuilder(); p.SetProgram("ping 8.8.8.8"); std::puts("Stream output of process ping to stdout."); p.StreamLines([](std::string line){ std::cout << " line = " << line << std::endl; return true; }); return EXIT_SUCCESS; });
Output: $ winprocess.exe test0
$ winprocess.exe test0 Stream output of process ping to stdout. line = line = Pinging 8.8.8.8 with 32 bytes of data: line = Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=105ms TTL=127 line = Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=106ms TTL=127 line = Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=105ms TTL=127 line = Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=106ms TTL=127 line = line = Ping statistics for 8.8.8.8: line = Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), line = Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: line = Minimum = 105ms, Maximum = 106ms, Average = 105ms [SUCCESS] End gracefully
Command test1
Runs the process $ dir . (dir.exe) at the directory
C::\Windows\\System32\\, reads the whole process output containing the
directory listening saving it to a string and writing it to a file named
output.log.
if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test1") tryExit([]{ std::puts("Get output of tasklist."); auto p = ProcessBuilder("dir ."); p.SetCWD("C:\\windows\\system32"); std::cout << "Process output = " << std::endl; auto out = p.GetOutput(); std::cout << out << std::endl; std::ofstream fs("output.log"); fs << " ==>>> Process output = " << "\n"; fs << " +=================+ " << "\n"; fs << out; return EXIT_SUCCESS; });
Output: $ winprocess.exe test1
$ winprocess.exe test1 ... ... ... ... wwanprotdim.dll wwansvc.dll wwapi.dll xbgmengine.dll xbgmsvc.exe xboxgipsvc.dll xboxgipsynthetic.dll xcopy.exe xh-ZA xmlfilter.dll xmllite.dll ... .... ... .... ... ....
Command test2
Launch a process (for window subsystem), notepad.exe and wait for its termination.
if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test2") tryExit([]{ std::puts("Launch process and wait for its termination"); auto p = ProcessBuilder("notepad"); p.Run(); std::cout << "Waiting for process termination" << std::endl; p.Wait(); std::cout << "Process terminated. OK." << std::endl; return EXIT_SUCCESS; });
Output: $ winprocess.exe test2
- The sub-process notepad.exe (window subsystem) is launched and then the program waits for its termination.
$ winprocess.exe test2 Launch process and wait for its termination Waiting for process termination Process terminated. OK. [SUCCESS] End gracefully
Command test3
Launch sub-process notepad.exe without waiting and waits for user to type RETURN. When user types this key, the process is terminated.
if(std::string(argv[1]) == "test3") tryExit([]{ std::puts("Launch process and wait for its termination"); auto p = ProcessBuilder("notepad"); p.Run(); std::cout << "Enter RETURN to terminate process => PID = " << p.GetPID() << std::endl; std::cin.get(); p.Terminate(); std::cout << " Process terminated OK."; return EXIT_SUCCESS; });
Output:
$ winprocess.exe test3 Launch process and wait for its termination Enter RETURN to terminate process => PID = 2324 Process terminated OK.[SUCCESS] End gracefully
Class ProcessBuilder
//========= File: ProcessBuilder.hpp - Header ===================// /** Requires: <iostream> <string>, <functional> <vector> <windows.h> */ class ProcessBuilder { private: // Program to be run std::string m_program; // Arguments passed to the program std::vector<std::string> m_args = {}; // If this flag is true, the program is launched on console bool m_console = true; std::string m_cwd; STARTUPINFO m_si = { sizeof(STARTUPINFO)}; PROCESS_INFORMATION m_pi; public: using SELF = ProcessBuilder&; using LineConsumer = std::function<bool (std::string)>; ProcessBuilder() = default; ProcessBuilder(const std::string& program, const std::vector<std::string>& args = {}); ProcessBuilder(const ProcessBuilder&) = delete; auto operator=(const ProcessBuilder&) = delete; ~ProcessBuilder(); ProcessBuilder(ProcessBuilder&& rhs); auto operator=(ProcessBuilder&& rhs) -> SELF; auto SetProgram(const std::string& program) -> SELF; auto SetConsole(bool flag) -> SELF; /** Set process directory. * @param path - Process directory path. */ auto SetCWD(const std::string& path) -> SELF; /** Start process without waiting for its termination. */ auto Run() -> bool; auto Wait() -> void; // Start process and wait for its termination. auto RunWait() -> bool; auto GetPID() -> DWORD; auto Terminate() -> bool; auto isRunning() -> bool; auto StreamLines(LineConsumer consumer) -> bool; auto GetOutput() -> std::string; private: auto ReadLineFromHandle(HANDLE hFile) -> std::pair<bool, std::string>; }; //========= End of Class ProcessBuilder ===== //
1.27 Windows Socket - Winsock
1.27.1 Overview
Winsock API
- Winsock 1.x - Adapation from BSD Berkley Socket API used by most Unix-like operating systems.
- Winsock 2.x - Provides new features:
- Overlapped IO
- Asynchrnous calls and callbacks
- Layered service provided - LSP architechture.
- Note: Unlike Unix implementation of sockets - BSD sockets, Winsocks API doesn't allow read/write operations with sockets as they where files, as a result, casting to file pointer from <stdio.h> doesn't work and leads to the program crashing at runtime. However, socket can be casted to Windows HANDLES and manipulated with Win32 File IO functions.
- Note: Windows Sockets are not portable and specific to only Windows, so in order to write an operating system agnostic network code, it is necessary to use an high level network library such as Boost-ASIO library or POCO frameworks.1
Headers and Libraries
- <windows.h>
- <winsock2.h>
Library:
Ws2_32.libWs2_32.dll
Main System Calls
| System Call | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|
| socket() | client or server socket | Create a socket |
| listen() | server socket | Server socket listen for incoming connections. |
| accept() | server socket | Make a server socket ccept a connection from a client socket. |
| connect() | client socket | Stablish a connection from a client socket to a server socket. |
| send() | client or server socket | Send data to socket |
| sednto() | client or server socket | Send data to non connected socket |
| recev() | client or server socket | Receives data/bytes from connected socket |
| recevfrom() | client or server socket | Receives data from non connected socket |
| shutdown() | client or server socket | Disables send and receive on socket |
| closesocket() | client or server socket | Close a socket, closing the connection. |
Creating a socket:
- af : Address familty
PF_INETAF_INET- IP Protocol
- type: Connection-oriented (TCP) or Datagra-oriented (UDP)
SOCK_STREAM- (TCP) Connection-Oriented.SOCK_DGRAM- (UDP) Datagram-Oriented.
- protocol: Unecessary when the af is
AF_INETand can be set to 0. - Return: Socket handler and returns the constant
INVALID_SOCKETon failure.
SOCKET socket(int af, int type, int protocol)
Socket-Client Function
- s - socket object created with the function socket.
- lpName - Hostname of machine to be connected, IP address.
- nNameLen -
sizeof(struct sockaddr_in) - RETURN: Returns 0 to indicate a successfull connection and
SOCKET_ERRORfor connection failure.
int connect(SOCKET s, LPSOCKADDR lpName, int nNameLen);
Byte Ordering Functions – Beej's Guide to Network Programming
- htons() - Host to network short
- htonl() - Host ot network long
- ntohs() - Network to Host Short
- ntohl() - Network to host long
Data Structure hostent
struct hostent { // Official name of the host (PC). char FAR * h_name; // A NULL -terminated array of alternate names. char FAR * FAR *h_aliases; // The type of address being returned; for Windows Sockets this is always PF_INET. short h_addrtype; // The length, in bytes, of each address; for PF_INET, this is always 4. short h_length; // A NULL-terminated list of addresses for the host. Addresses are returned in network byte order. char FAR * FAR *h_addr_list; };
Data Structure in_addr
/* * Internet address (old style... should be updated) */ struct in_addr { union { struct { u_char s_b1,s_b2,s_b3,s_b4; } S_un_b; struct { u_short s_w1,s_w2; } S_un_w; u_long S_addr; } S_un;
Data structures - sockaddr and sockaddr_6
See: https://www.tenouk.com/Winsock/Winsock2example7.html
- IPv4
struct sockaddr { ushort sa_family; char sa_data[14]; }; struct sockaddr_in { short sin_family; u_short sin_port; struct in_addr sin_addr; char sin_zero[8]; };
- IPv6
struct sockaddr_in6 { short sin6_family; u_short sin6_port; u_long sin6_flowinfo; struct in6_addr sin6_addr; u_long sin6_scope_id; }; typedef struct sockaddr_in6 SOCKADDR_IN6; typedef struct sockaddr_in6 *PSOCKADDR_IN6; typedef struct sockaddr_in6 FAR *LPSOCKADDR_IN6;
Data Structure WSAData
Before using Winsocks, it is necessary to initialize the library with the function WSAStartup and the data structure WSDATA. After the program has finished its execution, it necessary to run WSACleanup function.
typedef struct WSAData { WORD wVersion; WORD wHighVersion; char szDescription[WSADESCRIPTION_LEN+1]; char szSystemStatus[WSASYS_STATUS_LEN+1]; unsigned short iMaxSockets; unsigned short iMaxUdpDg; char FAR* lpVendorInfo; } WSADATA, *LPWSADATA;
Example:
WSADATA wd; // Intialize with Winsocks 1.0 WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(1, 0), &wd); // Intialize with Winsocks 2.0 WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wd); // Intialize with Winsocks 2.0 WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 0), &wd);
References:
- Windows Programming/Winsock - Wikibooks, open books for an open world
- An introduction to Windows socket/Winsock 2/Windows network programming tutorial with practical C program examples
- Receive full data with recv socket function in C – BinaryTides
- Beej's Guide to Network Programming
- Winsock Socket Programming
1.27.2 CODE - Show IPv4 address of a hostname
File: showIP.cpp
/* Show IPV4 Address of a given hostname *===================================*/ #include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <windows.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if(argc != 2){ std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <hostname> " << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } // Initialize Winsock 2.2 WSADATA wsaData; WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData); hostent* host = gethostbyname(argv[1]); char *ip = inet_ntoa(*reinterpret_cast<in_addr*>(*host->h_addr_list)); std::cout << " ipv4 Address = " << ip << std::endl; std::cout << " hostname = " << host->h_name << std::endl; std::cout << " Address type = " << host->h_addrtype << std::endl; WSACleanup(); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Compiling and runnign with MSVC:
$ cl.exe showIP.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /Fe:out.exe ws2_32.lib && showip.exe
Compiling and runnign with Mingw/GCC:
$ g++ showIP.cpp -o showip.exe -std=c++11 -lws2_32 && showip.exe
Running:
$ showip.exe
Usage: showip.exe <hostname>
$ showip.exe www.google.co
ipv4 Address = 172.217.29.110
hostname = www3.l.google.com
Address type = 2
$ showip.exe www.yandex.com
ipv4 Address = 213.180.204.62
hostname = www.yandex.com
Address type = 2
$ showip.exe www.bing.ca
ipv4 Address = 204.79.197.219
hostname = a-0016.a-msedge.net
Address type = 2
1.27.3 CODE - Basic Socket Client
- Setup and usage
Source:
Source Files
FIle: client-socket-shell1.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <windows.h> #pragma comment (lib, "Ws2_32.lib") // #pragma comment (lib, "Mswsock.lib") // #pragma comment (lib, "AdvApi32.lib") int main(int argc, char** argv){ if(argc < 3){ std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " [HOSTNAME or ADDRESS] [PORT]" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } // Client configuration const char* host = argv[1]; unsigned int port = std::stoi(argv[2]); //Start up Winsock… WSADATA wsadata; int error = WSAStartup(0x0202, &wsadata); if(error){ std::cerr << "Error: failed to initialize WinSock." << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } // Create client socket SOCKET client = ::socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP); if(client == INVALID_SOCKET){ std::cerr << "Error, I cannot create socket" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } SOCKADDR_IN addr; memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr)); addr.sin_family = AF_INET; addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(host); addr.sin_port = htons(port); // Attemp to connect to server and exit on failure. int connval = connect(client, reinterpret_cast<sockaddr*>(&addr), sizeof(addr)); if(connval == SOCKET_ERROR){ std::cerr << "Error: cannot connect to server." << std::endl; //Returns status code other than zero return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::string msgClientConnect = " [CLIENT] Connected to server OK.\n"; ::send(client, msgClientConnect.c_str(), msgClientConnect.size(), 0); std::string msg = " [CLIENT SHELL]>> "; std::string echo; bool flag = true; while(flag){ ::send(client, msg.c_str(), msg.size(), 0); // Create a buffer with 2024 bytes or 2kb std::string buffer(2024, 0); //Returns the number of received bytes int n = ::recv(client, &buffer[0], buffer.size()-1, 0); echo = " => [ECHO] " + buffer + "\n"; ::send(client, echo.c_str(), echo.size(), 0); if(WSAGetLastError() == SOCKET_ERROR){ std::cerr << "Disconnected OK." << std::endl; flag = false; break; } else { buffer.resize(n); if(buffer == "exit\n" ){ std::string exitMessage = " [CLIENT] Disconnect gracefully - OK.\n"; ::send(client, exitMessage.c_str(), exitMessage.size(), 0); std::cerr << "[LOG] I got an exit message. Shutdowing socket now!" << "\n"; std::cerr << "[LOG] Gracifully disconnecting application" << "\n"; std::cerr.flush(); break; } std::cout << " [SERVER SENT] >> " << buffer ; //<< std::endl; // Force writing buffer to the stdout std::cout.flush(); } } std::cerr << "Finished." << std::endl; ::closesocket(client); ::WSACleanup(); // Returns status code 0 return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Build
- MSVC:
$ cl.exe client-socket-shell1.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo
- Mingw/GCC
λ g++ client-socket-shell1.cpp -o winsock-client-shell1.exe -std=c++1z -lws2_32Usage:
STEP 1 - Set up a server with netcat from local computer or remote machine. In this case netcat is set up from a Linux box.
- Note: The IP address from the server side can be obtained with the command $ ipconfig on Windows NT and $ ifconfig on Linux, Android, MacOSX, BSD and so on.
$ nc -v -l 9090 Ncat: Version 7.60 ( https://nmap.org/ncat ) Ncat: Generating a temporary 1024-bit RSA key. Use --ssl-key and --ssl-cert to use a permanent one. Ncat: SHA-1 fingerprint: 00D2 1683 8C75 26DC 74CD 6B3C 52BF D3DE 1FD0 18F5 Ncat: Listening on :::9090 Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:9090
STEP 2 - Connect to server from Windows by runnign the client program.
λ client-socket-shell1.exe Usage: client-socket-shell1.exe [HOSTNAME or ADDRESS] [PORT] λ client-socket-shell1.exe 192.168.18.90 9090 [SERVER SENT] >>
If the netcat server is running in the same machine, the address is 127.0.0.1 or localhost and the command for connecting to the server is:
λ client-socket-shell1.exe localhost 9090 # OR: λ client-socket-shell1.exe 127.0.0.1 9090
STEP 3 - Send commands to client program from server terminal (netcat).
$ nc -v -l 9090 Ncat: Version 7.60 ( https://nmap.org/ncat ) Ncat: Generating a temporary 1024-bit RSA key. Use --ssl-key and --ssl-cert to use a permanent one. Ncat: SHA-1 fingerprint: 00D2 1683 8C75 26DC 74CD 6B3C 52BF D3DE 1FD0 18F5 Ncat: Listening on :::9090 Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:9090 Ncat: Connection from 192.168.18.161. Ncat: Connection from 192.168.18.161:50278. [CLIENT] Connected to server OK. [CLIENT SHELL]>> => [ECHO] [CLIENT SHELL]>>
STEP 4 - Type any commands from server side and they will be to the client side which will echo it back to the server.
Ncat: Connection from 192.168.18.161. Ncat: Connection from 192.168.18.161:50278. [CLIENT] Connected to server OK. [CLIENT SHELL]>> => [ECHO] [CLIENT SHELL]>> command arg0 arg1 arg2 arg3 => [ECHO] command arg0 arg1 arg2 arg3 [CLIENT SHELL]>> ls -la => [ECHO] ls -la [CLIENT SHELL]>> cd / => [ECHO] cd / [CLIENT SHELL]>> uname -a => [ECHO] uname -a [CLIENT SHELL]>> reverse shell - echo shell => [ECHO] reverse shell - echo shell [CLIENT SHELL]>> exit => [ECHO] exit [CLIENT] Disconnect gracefully - OK.
STEP 5 - Output in the client terminal (Windows):
λ client-socket-shell1.exe 192.168.18.90 9090 [SERVER SENT] >> [SERVER SENT] >> command arg0 arg1 arg2 arg3 [SERVER SENT] >> ls -la [SERVER SENT] >> cd / [SERVER SENT] >> uname -a [SERVER SENT] >> reverse shell - echo shell
- Parts
Get client socket configuration from command line:
int main(int argc, char** argv){ if(argc < 3){ std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " [HOSTNAME or ADDRESS] [PORT]" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } // Client configuration const char* host = argv[1]; unsigned int port = std::stoi(argv[2]); ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
Start up Winsock data structure:
- Note: WSAStartup(0x0202, &wsadata) => Intializes Winsock 2.2 API.
//Start up Winsock… WSADATA wsadata; int error = WSAStartup(0x0202, &wsadata); if(error){ std::cerr << "Error: failed to initialize WinSock." << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; }
Create client socket:
// Create client socket SOCKET client = ::socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP); if(client == INVALID_SOCKET){ std::cerr << "Error, I cannot create socket" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } SOCKADDR_IN addr; memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr)); addr.sin_family = AF_INET; addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(host); addr.sin_port = htons(port);
Attemp to connect to server and exit if there is any failure:
// Attemp to connect to server and exit on failure. int connval = connect(client, reinterpret_cast<sockaddr*>(&addr), sizeof(addr)); if(connval == SOCKET_ERROR){ std::cerr << "Error: cannot connect to server." << std::endl; //Returns status code other than zero return EXIT_FAILURE; }
Send message "[CLIENT] Connected to server OK" to server once the client is connected:
std::string msgClientConnect = " [CLIENT] Connected to server OK.\n"; ::send(client, msgClientConnect.c_str(), msgClientConnect.size(), 0); std::string msg = " [CLIENT SHELL]>> "; std::string echo;
Main loop:
- Send prompt string to server "[CLIENT SHELL]>> "
- Receive command from server typed in the server terminal by the user.
- Echo command back to server.
- If server send command "exit", the client exits the main loop and diconnets from server sending the message " [CLIENT] Disconnect gracefully - OK".
bool flag = true; while(flag){ ::send(client, msg.c_str(), msg.size(), 0); // Create a buffer with 2024 bytes or 2kb std::string buffer(2024, 0); //Returns the number of received bytes int n = ::recv(client, &buffer[0], buffer.size()-1, 0); echo = " => [ECHO] " + buffer + "\n"; ::send(client, echo.c_str(), echo.size(), 0); if(WSAGetLastError() == SOCKET_ERROR){ std::cerr << "Disconnected OK." << std::endl; flag = false; break; } else { buffer.resize(n); if(buffer == "exit\n" ){ std::string exitMessage = " [CLIENT] Disconnect gracefully - OK.\n"; ::send(client, exitMessage.c_str(), exitMessage.size(), 0); std::cerr << "[LOG] I got an exit message. Shutdowing socket now!" << "\n"; std::cerr << "[LOG] Gracefully disconnecting application" << "\n"; std::cerr.flush(); break; } std::cout << " [SERVER SENT] >> " << buffer ; //<< std::endl; // Force writing buffer to the stdout std::cout.flush(); } }
Cleanup Winsock, release resource and exit application.
std::cerr << "Finished." << std::endl; ::closesocket(client); ::WSACleanup(); // Returns status code 0 return EXIT_SUCCESS;
1.28 WinlNet and UrlMon - APIs for HTTP and FTP protocol
1.28.1 Overview
Windows provides many ready-to-use high level APIs for accessing most used internet procols such as Http and Ftp, which makes easier to deal with those protocols without reiventing the whell and caring about their implementation or low level details. Those APIs are exposed through the DLLs wininet.dll and urlmon.dll.
See: WinINet Functions | Microsoft Docs
Functions in wininet.dll
- InternetOpen
- Initializes Winnet environment. This function must be called before any other Winnet function.
HINTERNET WINAPI InternetOpen( LPCTSTR lpszAgent, DWORD dwAccessType, LPCTSTR lpszProxyName, LPCTSTR lpszProxyBypass, DWORD dwFlags );
- InternetConnect
- Starts new HTTP or FTP session
HINTERNET InternetConnect( HINTERNET hInternet, LPCTSTR lpszServerName, INTERNET_PORT nServerPort, LPCTSTR lpszUsername, LPCTSTR lpszPassword, DWORD dwService, DWORD dwFlags, DWORD_PTR dwContext );
- HttpOpenRequest
- HttpQueryInfo
- HttpAddRequestHeaders
- HttpSendRequest
- HttpSendRequest
- InternetReadFile
- InternetCloseHandle
- Close internet connection and ends any ongoing operation.
BOOL InternetCloseHandle( HINTERNET hInternet );
- InternetReadFile
BOOL InternetReadFile( HINTERNET hFile, LPVOID lpBuffer, DWORD dwNumberOfBytesToRead, LPDWORD lpdwNumberOfBytesRead );
1.28.2 Example
Source:
- File: file:src/windows/winlNet-basic.cpp
- GIST: winlNet-basic.cpp
File
File: winlNet-basic.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <cstdio> #include <windows.h> #include <urlmon.h> //Provides URLDownloadToFileW #include <wininet.h> #include <tchar.h> // Only for MSVC #pragma comment(lib, "urlmon.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "wininet.lib") auto launchedFromConsole() -> bool; // Simple C++ wrapper for the function: URLDownloadToFileA HRESULT downloadFile(std::string url, std::string file); void testHTTPRequest(); int main(){ // ================== File Download ========================= // // HRESULT hr; hr = downloadFile("http://httpbin.org/image/jpeg", "image.jpeg"); if(SUCCEEDED(hr)) std::cout << "Download successful OK." << '\n'; else std::cout << "Download failed." << '\n'; hr = downloadFile("httpxpabin.org/image/jpeg-error", "image2.jpeg"); if(SUCCEEDED(hr)) std::cout << "Download sucessful OK." << '\n'; else std::cout << "Download failed." << '\n'; //=============== HTTP Protocol ===================================// // testHTTPRequest(); if(!launchedFromConsole()){ std::cout << "Type RETURN to exit" << std::endl; std::cin.get(); } return 0; } auto launchedFromConsole() -> bool { DWORD procIDs[2]; DWORD maxCount = 2; DWORD result = GetConsoleProcessList((LPDWORD)procIDs, maxCount); return result != 1; } HRESULT downloadFile(std::string url, std::string file){ HRESULT hr = URLDownloadToFileA( // (pCaller) Pointer to IUknown instance (not needed) NULL // (szURL) URL to the file that will be downloaded ,url.c_str() // (szFileName) File name that the downloaded file will be saved. ,file.c_str() // (dwReserved) Reserverd - always 0 ,0 // (lpfnCB) Status callback ,NULL ); return hr; } void testHTTPRequest(){ // Reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/forum/beginner/75062/ HINTERNET hConnect = InternetOpen("Fake browser",INTERNET_OPEN_TYPE_PRECONFIG,NULL, NULL, 0); if(!hConnect){ std::cerr << "Error: Connection Failure."; return; } HINTERNET hAddr = InternetOpenUrl( hConnect ,"http://www.httpbin.org/get" ,NULL ,0 ,INTERNET_FLAG_PRAGMA_NOCACHE | INTERNET_FLAG_KEEP_CONNECTION ,0 ); if ( !hAddr ) { DWORD errorCode = GetLastError(); std::cerr << "Failed to open URL" << '\n' << "Error Code = " << errorCode; InternetCloseHandle(hConnect); return; } // Buffer size - 4kb or 4096 bytes char bytesReceived[4096]; DWORD NumOfBytesReceived = 0; while(InternetReadFile(hAddr, bytesReceived, 4096, &NumOfBytesReceived) && NumOfBytesReceived ) { std::cout << bytesReceived; } InternetCloseHandle(hAddr); InternetCloseHandle(hConnect); } //
Compiling and running:
Compile with MSVC:
$ cl.exe winlNet-basic.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /Fe:winlNet.exe
Compile with Mingw/GCC:
$ g++ winlNet-basic.cpp -o winlNet-basic.exe -lwininet -lurlmon -std=c++14
Running:
$ winlNet-basic.exe
Download successful OK.
Download failed.
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Cache-Control": "no-cache",
"Connection": "close",
"Host": "www.httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "Fake browser"
},
"origin": "177.36.10.17",
"url": "http://www.httpbin.org/get"
}
Öa/
Compilation finished at Mon Sep 3 09:53:07
Parts
- Function downloadFile - Wrappers WinlNet function URLDownloadToFileA (ANSI version of URLDownloadToFile) to make it more C++-friendly. This function just downloads a file from a URL.
HRESULT downloadFile(std::string url, std::string file){ HRESULT hr = URLDownloadToFileA( // (pCaller) Pointer to IUknown instance (not needed) NULL // (szURL) URL to the file that will be downloaded ,url.c_str() // (szFileName) File name that the downloaded file will be saved. ,file.c_str() // (dwReserved) Reserverd - always 0 ,0 // (lpfnCB) Status callback ,NULL ); return hr; }
Tests HTTP GET request to http:://www.httpbin.org/get
void testHTTPRequest(){ // Reference: http://www.cplusplus.com/forum/beginner/75062/ HINTERNET hConnect = InternetOpen("Fake browser",INTERNET_OPEN_TYPE_PRECONFIG,NULL, NULL, 0); if(!hConnect){ std::cerr << "Error: Connection Failure."; return; } HINTERNET hAddr = InternetOpenUrl( hConnect ,"http://www.httpbin.org/get" ,NULL ,0 ,INTERNET_FLAG_PRAGMA_NOCACHE | INTERNET_FLAG_KEEP_CONNECTION ,0 ); if ( !hAddr ) { DWORD errorCode = GetLastError(); std::cerr << "Failed to open URL" << '\n' << "Error Code = " << errorCode; InternetCloseHandle(hConnect); return; } // Buffer size - 4kb or 4096 bytes char bytesReceived[4096]; DWORD NumOfBytesReceived = 0; while(InternetReadFile(hAddr, bytesReceived, 4096, &NumOfBytesReceived) && NumOfBytesReceived ) { std::cout << bytesReceived; } InternetCloseHandle(hAddr); InternetCloseHandle(hConnect); } // --- EoF testHTTPRequest() --- //
Main function:
// ================== File Download ========================= // // HRESULT hr; hr = downloadFile("http://httpbin.org/image/jpeg", "image.jpeg"); if(SUCCEEDED(hr)) std::cout << "Download successful OK." << '\n'; else std::cout << "Download failed." << '\n'; hr = downloadFile("httpxpabin.org/image/jpeg-error", "image2.jpeg"); if(SUCCEEDED(hr)) std::cout << "Download sucessful OK." << '\n'; else std::cout << "Download failed." << '\n'; //=============== HTTP Protocol ===================================// // testHTTPRequest(); if(!launchedFromConsole()){ std::cout << "Type RETURN to exit" << std::endl; std::cin.get(); } return 0;
1.29 Remote repl - telnet-like application
The following remote repl (Read-Eval-Print-Loop) application allows accessing Windows shells, such as Powershell or cmd.exe, from remote machines, including Linux or MacOSX machines. The application can work in server-mode, which the programs waits for remote client to connect, or in client-mode, which the program connects to an already running netcat server. The sample application was used for remotely accessing a Windows 10 virtual machine from Linux through a NAT (Network Address Translator) network interface.
Project Files
File: CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0) project(cpp-windows) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON) set(CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON) add_executable(remote-repl remote-repl.cpp) target_link_libraries(remote-repl ws2_32)
File: remote-repl.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> // #include <exception> // #include <new> #include <winsock2.h> #include <windows.h> class Socket { private: std::string m_host; bool m_cleanup; int m_port; SOCKET m_socket; SOCKADDR_IN m_addr; static bool isInitialized; public: // Disable copy contructor Socket(const Socket& sock) = delete; Socket(Socket&& ) = default; Socket() { // Set up client 2.2 WSADATA wsaData; WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2,2), &wsaData); // m_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP); m_socket = WSASocket( AF_INET ,SOCK_STREAM ,IPPROTO_TCP ,NULL ,static_cast<unsigned int>(NULL) ,static_cast<unsigned int>(NULL) ); if(m_socket == INVALID_SOCKET){ throw std::runtime_error("Error, I cannot create socket"); } memset(&m_addr, 0, sizeof(m_addr)); } Socket(SOCKET sock, SOCKADDR_IN addr) { m_socket = sock; m_addr = addr; } ~Socket() { if(m_cleanup){ std::cerr << " [INFO ] Cleanup OK." << std::endl; closesocket(m_socket); WSACleanup(); } } bool isValid() const { return m_socket != -1; } void setNotCleanup() { m_cleanup = false; } // For client-socket only void connect(std::string hostname, int port) { std::cout << "Connecting to server" << std::endl; // throw std::runtime_error("Connection failure."); m_host = hostname; m_port = port; m_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; m_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(hostname.c_str()); m_addr.sin_port = htons(port); int connval = WSAConnect(m_socket, reinterpret_cast<SOCKADDR*>(&m_addr), sizeof(m_addr), NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL ); if(connval == SOCKET_ERROR){ throw std::runtime_error("Error: cannot connect to server <" + m_host + ":" + std::to_string(m_port) + ">"); // throw std::runtime_error("Error: cannot connect to server"); } std::cout << "I am connected. OK." << std::endl; } // For server-socket (aka listening socket only) void bind(std::string hostname, int port, int backlog = 5) { m_host = hostname; m_port = port; m_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; m_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(hostname.c_str()); m_addr.sin_port = htons(port); // TODO => Implement error handler assert( ::bind( m_socket, (SOCKADDR*) &m_addr , sizeof(m_addr)) != -1 ); assert( listen(m_socket, backlog) != -1 ); // int enable = 1; // int result = setsockopt( m_socket, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &enable, sizeof(int) ); // assert( resutl != -1); } // For server socket only =>> // Block current thread and wait for new client connection. Socket accept() { SOCKET client ; SOCKADDR_IN addr; int len = sizeof(addr); client = ::accept(m_socket, (SOCKADDR*) &addr, &len); // assert( client != -1); return Socket(client, addr); } void disconnect() { closesocket(m_socket); } void send(const char* buffer, size_t len, int flags = 0) const { ::send(m_socket, buffer, len, flags); } int recev(char* buffer, size_t len, int flags = 0) const { return ::recv(m_socket, buffer, len , flags); } void sendText(const std::string& text) const { ::send(m_socket, text.c_str(), text.size(), 0); } void sendLine(const std::string& line) const { this->sendText(line + "\n"); } std::string recevText(size_t size) { std::string buffer(size, 0); int n = ::recv(m_socket, &buffer[0], size , 0); buffer.resize(n); return buffer; } HANDLE handle() const { return reinterpret_cast<HANDLE>(m_socket); } }; //---- EoF class ClientSocket ---- // void makeRemoteRepl(const Socket& sock, const std::string& cmdline, bool waitFlag = false); int main(int argc, char** argv) { if( argc < 5 ) { std::cout << " [TRACE] Usage " << " \n $ client " << argv[0] << " <HOSTNAME> <PORT> <PROGRAM> " << " \n $ server " << argv[0] << " <HOSTNAME> <PORT> <PROGRAM> " << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } const std::string command = argv[1]; const std::string address = argv[2]; const DWORD port = std::stoi(argv[3]); const std::string shell = argv[4]; std::cerr << "Running main" << std::endl; if( command == "server" ) { Socket server; server.bind(address, port, 5); // Socket server infinite loop for(;;) { std::cout << " [TRACE] Waiting client connection. " << std::endl; Socket client = server.accept(); if(! client.isValid() ){ continue; } makeRemoteRepl(client, shell, true); } } if( command == "client") { for (;;) { Socket client; client.setNotCleanup(); while (true) { try { std::cerr << "Trying to connect to server" << std::endl; client.connect(address, port); break; } catch (const std::exception &e) { std::cerr << e.what() << std::endl; //exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } } std::cout << "Socket connected OK." << std::endl; client.sendLine(" [LOG] Client socket running OK!"); makeRemoteRepl(client, shell, true); } } // Connection loop - std::cerr << "End successfully" << std::endl; // Returns status code 0 return EXIT_SUCCESS; } // ----------------------------------------------------- // void makeRemoteRepl( const Socket& sock , const std::string& cmdline , bool waitFlag ) { // Create process PROCESS_INFORMATION pi; STARTUPINFO sui; memset(&sui, 0, sizeof(sui)); sui.cb = sizeof(sui); sui.dwFlags = STARTF_USESTDHANDLES ; // | STARTF_USESHOWWINDOW; sui.wShowWindow = SW_HIDE; sui.hStdInput = sock.handle(); sui.hStdOutput = sock.handle(); sui.hStdError = sock.handle(); int bSuccess = CreateProcessA( NULL, const_cast<LPSTR>(cmdline.c_str()) , NULL, NULL, TRUE, CREATE_NO_WINDOW, NULL, NULL, &sui, &pi); if(bSuccess) { sock.sendLine(" [INFO ] Remote repl session started OK.!"); sock.sendLine(" [INFO ] Success code = " + std::to_string(bSuccess)); DWORD pid = GetProcessId(pi.hProcess); sock.sendLine(" [INFO ] Process ID <PID> = " + std::to_string(pid)); } else { sock.sendLine(" [ERROR] Failed to create process."); } if(waitFlag){ WaitForSingleObject( pi.hProcess, INFINITE ); CloseHandle( pi.hProcess ); CloseHandle( pi.hThread ); sock.sendLine(" [LOG] Process finished."); } }
Building
$ cmake -B_build -G "MinGW Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug
$ cmake --build --target all
Running application in client mode
Linux Remote terminal: (netcat server)
# User types commands here that are sent to Windows machine. # Run netcat as server $ rlwrap nc -nlvp 9010 Listening on 0.0.0.0 9010 Connection received on 192.168.1.105 53950 [LOG] Client socket running OK! [INFO ] Remote repl session started OK.! [INFO ] Success code = 1 [INFO ] Process ID <PID> = 1552 Windows PowerShell Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Try the new cross-platform PowerShell https://aka.ms/pscore6 PS C:\> whoami whoami desktop-36ar81f\nixuserp PS C:\> netstat -a netstat -a Active Connections Proto Local Address Foreign Address State TCP 0.0.0.0:135 184-86-53-99:0 LISTENING TCP 0.0.0.0:445 184-86-53-99:0 LISTENING TCP 0.0.0.0:5357 184-86-53-99:0 LISTENING TCP 0.0.0.0:5985 184-86-53-99:0 LISTENING TCP 0.0.0.0:47001 184-86-53-99:0 LISTENING TCP 0.0.0.0:49664 184-86-53-99:0 LISTENING ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... PS C:\> exit exit [LOG] Process finished.
Windows terminal: (client)
$ remote-repl.exe client 192.168.1.115 9010 powershell Running main Trying to connect to server Connecting to server I am connected. OK. Socket connected OK.
Running application in server mode
Windows terminal: (server)
$ remote-repl.exe server 0.0.0.0 9010 powershell Running main [TRACE] Waiting client connection.
Linux remote terminal (client)
# User types commands here that are sent to Windows machine. $ rlwrap nc 192.168.1.105 9010 [INFO ] Remote repl session started OK.! [INFO ] Success code = 1 [INFO ] Process ID <PID> = 4912 Windows PowerShell Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Try the new cross-platform PowerShell https://aka.ms/pscore6 PS C:\> whoami whoami desktop-36ar81f\nixuserp PS C:\> PS C:\> ls -Force / ls -Force / Directory: C:\ Mode LastWriteTime Length Name ---- ------------- ------ ---- d--hs- 9/19/2021 9:47 AM $Recycle.Bin d--hs- 9/27/2021 11:53 AM Config.Msi d--hsl 9/19/2021 9:40 AM Documents and Settings d----- 3/18/2019 9:52 PM PerfLogs d-r--- 9/27/2021 11:53 AM Program Files d-r--- 9/27/2021 11:53 AM Program Files (x86) d--h-- 9/27/2021 11:53 AM ProgramData d--hs- 9/19/2021 9:41 AM Recovery d--hs- 9/27/2021 11:46 AM System Volume Information d-r--- 9/19/2021 6:02 AM Users d----- 9/19/2021 9:48 AM Windows -a-hs- 9/27/2021 5:58 PM 872415232 pagefile.sys -a-hs- 9/27/2021 5:58 PM 268435456 swapfile.sys
1.30 Embed Resources into Executables
The Windows API has several facilities for loading embedded resource, such data such as strings, icon, menus and any arbitrary data from PE32 executables and dynamic linked libraries DLLs. Cross platform applications should avoid using the Windows APIs be listed in this section, since they are specific to Windows, therefore they not portable to other operatingss systems. Applications aiming portability should libraries such as incbin libraries cmrc (CMake-Resource Compiler) and also resource compilers from frameworks such as Qt and WxWidgets.
Windows APIs for dealing with resources:
- Menus and Other Resources
- FindResourceA()
- "Determines the location of a resource with the specified type and name in the specified module."
- LockResource
- "Retrieves a pointer to the specified resource in memory."
- LoadResource()
- "Retrieves a handle that can be used to obtain a pointer to the first byte of the specified resource in memory."
- SizeofResource()
- "Retrieves the size, in bytes, of the specified resource."
Project Files
File: CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0) project(cpp-windows) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON) set(CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON) add_executable(winapp app.cpp myresource.rc VERSIONINFO.rc)
File: app.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> struct Buffer{ char* ptr; size_t size; }; Buffer find_resouce(HMODULE hMod, const char* name, const char* type) { HRSRC rsrc = FindResourceA(hMod, name, type); assert( rsrc != nullptr ); HGLOBAL hGlobal = LoadResource(hMod, rsrc); assert( hGlobal != nullptr ); // Pointer to first byte of resource in memory LPVOID pRes = LockResource(hGlobal); assert( pRes != nullptr ); // Size of resource in bytes DWORD size = SizeofResource(hMod, rsrc); return { static_cast<char*>(pRes), size }; } std::string find_resouce_text(HMODULE hMod, const char* name, const char* type) { Buffer b = find_resouce(hMod, name, type); auto data = std::string(b.ptr, b.ptr + b.size); return data; } void enumerate_resources(HMODULE hMod, const char* type) { auto callback = [](HMODULE hMod, const char* type, char* name, LONG_PTR param) { std::cout << " [*] Resource type = " << type << " ; name = " << name << std::endl; return TRUE; }; long long int status = 0; BOOL result = EnumResourceNamesA(hMod, type, callback, status); } int main() { HMODULE hMod = GetModuleHandleA(nullptr); assert( hMod != nullptr ); enumerate_resources(hMod, RT_RCDATA); std::cout << "\n ----- Display ASCII Art Resource -----" << std::endl; auto data = find_resouce_text(hMod, "MYRESOURCE", RT_RCDATA); std::cout << " [*] Resource data = \n" << data << std::endl; std::cin.get(); return 0; }
File: myresource.rc (Resource script - processed by the resource compiler)
MYRESOURCE RCDATA "myresource.txt"
File: myresource.txt (resource to be embedded).
File with this resource. "At vero eos et accusamus et iusto odio dignissimos ducimus qui blanditiis praesentium voluptatum deleniti atque corrupti quos dolores et quas molestias excepturi sint occaecati cupiditate non provident, similique sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollitia animi, id est laborum et dolorum fuga. Et harum quidem rerum facilis est et expedita distinctio. Nam libero tempore, cum soluta nobis est eligendi optio cumque nihil impedit quo minus id quod maxime placeat facere possimus, omnis voluptas assumenda est, omnis dolor repellendus. Temporibus autem quibusdam et aut officiis debitis aut rerum necessitatibus saepe eveniet ut et voluptates repudiandae sint et molestiae non recusandae. Itaque earum rerum hic tenetur a sapiente delectus, ut aut reiciendis voluptatibus maiores alias consequatur aut perferendis doloribus asperiores repellat."
File: VERSIONINFO.rc (Contains metadata indicating version, vendor, product name and so on.)
#include <winver.h> #include <ntdef.h> #ifdef RC_INVOKED #if DBG #define VER_DBG VS_FF_DEBUG #else #define VER_DBG 0 #endif VS_VERSION_INFO VERSIONINFO FILEVERSION 1,0,0,0 // 1.0.0.0 - Application version PRODUCTVERSION 1,0,0,0 // 1.0.0.0 - Produce version FILEFLAGSMASK VS_FFI_FILEFLAGSMASK FILEFLAGS VER_DBG FILEOS VOS_NT FILETYPE VFT_DRV FILESUBTYPE VFT2_DRV_SYSTEM BEGIN BLOCK "StringFileInfo" BEGIN BLOCK "040904b0" BEGIN VALUE "Comments", "SomeProduct awesome" VALUE "CompanyName", "Some company XYZWK, Inc." VALUE "FileDescription", "MyProduct" VALUE "FileVersion", "V1.0.0.0" VALUE "InternalName", "Some super product" VALUE "LegalCopyright", "(C)2018 Some company XYZWK .Incorporated." VALUE "OriginalFilename", "winapp.exe" VALUE "ProductName", "SomeProduct" VALUE "ProductVersion", "V1.2.3.0" END END BLOCK "VarFileInfo" BEGIN VALUE "Translation", 0x0409,1200 END END #endif
Building and running
Building:
$ cmake -B_build -G "MinGW Makefiles"
$ cmake --build _build --target all
Running:
$ _build\winapp.exe [*] Resource type = ----- Display ASCII Art Resource ----- [*] Resource data = File with this resource. "At vero eos et accusamus et iusto odio dignissimos ducimus qui blanditiis praesentium voluptatum deleniti atque corrupti quos dolores et quas molestias excepturi sint occaecati cupiditate non provident, similique sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollitia animi, id est laborum et dolorum fuga. Et harum quidem rerum facilis est et expedita distinctio. Nam libero tempore, cum soluta nobis est eligendi optio cumque nihil impedit quo minus id quod maxime placeat facere possimus, omnis voluptas assumenda est, omnis dolor repellendus. Temporibus autem quibusdam et aut officiis debitis aut rerum necessitatibus saepe eveniet ut et voluptates repudiandae sint et molestiae non recusandae. Itaque earum rerum hic tenetur a sapiente delectus, ut aut reiciendis voluptatibus maiores alias consequatur aut perferendis doloribus asperiores repellat."
1.31 Graphical User Interfaces - WinAPI
1.31.1 Minimal GUI Program - "hello world"
- Overview
This code contains a minimal graphical user interface with Windows API.
Source:
- File: file:src/windows/gui-basic1.cpp
- GIST: gui-basic1.cpp
Full Code
File: gui-basic1.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <map> #include <set> #include <sstream> #include <windows.h> LRESULT CALLBACK windowProcedure( HWND hwnd, UINT msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam); auto WinMessageToString(UINT msg) -> std::string; int WINAPI WinMain( // Handle to current application isntance HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, // Command line LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow ){ OutputDebugString("Starting WinMain Application"); std::puts("It will not print to Console - Starting WinMain Application"); //Window class name must be unique const char wincClassName [] = "NameOfWindow"; // Win32 Window class structure WNDCLASSEX wc; // Win32 message structure MSG Msg; // Name to identify the class with. wc.lpszClassName = wincClassName; //Pointer to the window procedure for this window class. wc.lpfnWndProc = windowProcedure; // 1 - Register Windows Size wc.cbSize = sizeof(WNDCLASSEX); wc.style = 0; //Amount of extra data allocated for this class in memory. Usually 0 wc.cbClsExtra = 0; //Amount of extra data allocated in memory per window of this type. Usually 0. wc.cbWndExtra = 0; //Handle to application instance (that we got in the first parameter of WinMain()). wc.hInstance = hInstance; // Large (usually 32x32) icon shown when the user presses Alt+Tab. wc.hIcon = LoadIcon(NULL, IDI_APPLICATION); // Cursor that will be displayed over our window. wc.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW); // Background Brush to set the color of our window. wc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW+1); // (HBRUSH) CreateSolidBrush(RGB(10, 20, 30)); // // Background Brush to set the color of our window. wc.lpszMenuName = NULL; // Small (usually 16x16) icon to show in the taskbar and in the top left corner of the window. wc.hIconSm = LoadIcon(NULL, IDI_APPLICATION); OutputDebugString("Registered Window Class OK."); if(!RegisterClassEx(&wc)) { MessageBox( NULL, "Window Registration Failed!", "Error!", MB_ICONEXCLAMATION | MB_OK); //Error status code return -1; } std::cout << "Class Registered" << std::endl; int width = 500, height = 400; int pos_left = 400, pos_top = 100; HWND hwnd = CreateWindowA( wc.lpszClassName, "Title of Window", WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, pos_left, pos_top, width, height, nullptr, nullptr, hInstance, nullptr ); OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Window created OK"); if(hwnd == NULL){ MessageBox(NULL, "Error: Failure to create Window", "Error Report", MB_ICONEXCLAMATION | MB_OK); return -1; } ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow); std::cout << "nCmdShow = " << nCmdShow << std::endl; UpdateWindow(hwnd); //---- Message Loop ----------// while(GetMessage(&Msg, NULL, 0, 0) > 0 ){ TranslateMessage(&Msg); DispatchMessage(&Msg); } OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Exiting application. OK."); // Success status code return 0; } // ------------ End of Main ------------------------- // // Window Procedure - Process window messages or events LRESULT CALLBACK windowProcedure ( HWND hwnd // Window Handle (Window object) ,UINT msg // Window Message ,WPARAM wParam // Additional message information ,LPARAM lParam // Additional message information ){ // Variable initialized one. static auto ignored_messages = std::set<UINT>{ WM_MOUSEMOVE, WM_NCHITTEST, WM_SETCURSOR, WM_IME_NOTIFY }; // Ignore messages which can flood the logging // if(msg != WM_MOUSEMOVE && msg != WM_NCMOUSEMOVE // && msg != WM_QUIT && msg != WM_NCHITTEST ) if(ignored_messages.find(msg) == ignored_messages.end()) OutputDebugString(WinMessageToString(msg).c_str()); // Process messages switch(msg) { case WM_CREATE: SetWindowTextA(hwnd, "Change Window Title"); OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Window created. OK."); break; case WM_CLOSE: OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Window closed. OK."); DestroyWindow(hwnd); break; case WM_DESTROY: OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Exiting application. OK."); PostQuitMessage(0); break; case WM_MOVE: std::cerr << " [INFO] Move window." << std::endl; break; case WM_PAINT: { // GDI - Graphics Devices Interface Here //-------------------------------------------- PAINTSTRUCT ps; HDC hdc; // std::cerr << " [INFO] Windown painting" << std::endl; hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps); std::string text = "Hello world Window!"; TextOutA(hdc, 125, 200, text.c_str(), text.size()); Ellipse(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); Rectangle(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); EndPaint(hwnd, &ps); } break; default: return DefWindowProc(hwnd, msg, wParam, lParam); } return 0; } /** Get a human-readable description of a Windows message as a string */ auto WinMessageToString(UINT msg) -> std::string { /** Database of Windows messages - full list of messages here: * https://wiki.winehq.org/List_Of_Windows_Messages */ static auto WindowMessages = std::map<UINT, std::string>{ {1, "WM_CREATE"}, {2, "WM_DESTROY"}, {5, "WM_SIZE"}, {6, "WM_ACTIVATE"}, {13, "WM_SIZE"}, {22, "WM_SETVISIBLE"}, {23, "WM_ENABLE"}, {29, "WM_PAINT"}, {3, "WM_MOVE"}, {30, "WM_CLOSE"}, {32, "WM_SETCURSOR"}, {72, "WM_FULLSCREEN"}, {85, "WM_COPYDATA"}, {512, "WM_MOUSEMOVE"},{132, "WM_NCHITTEST"}, {641, "WM_IME_SETCONTEXT"}, {8, "WM_KILLFOCUS"}, {134, "WM_NCACTIVATE"}, {28, "WM_ACTIVATEAPP"}, {160, "WM_NCMOUSEMOVE"}, {161, "WM_NCLBUTTONDOWN"}, {36, "WM_GETMINMAXINFO"}, {642, "WM_IME_NOTIFY"}, {433, "WM_CAPTURECHANGED"}, {534, "WM_MOVING"}, {674, "WM_NCMOUSELEAVE"}, {675, "WM_MOUSELEAVE"}, {532, "WM_SIZING"}, {533, "WM_CAPTURECHANGED"}, {127, "WM_GETICON"}, {20, "WM_ERASEBKGND"}, {70, "WM_WINDOWPOSCHANGING"}, {71, "WM_WINDOWPOSCHANGED"}, {273, "WM_COMMAND"}, {274, "WM_SYSCOMMAND"}, {275, "WM_TIMER"}, {513, "WM_LBUTTONDOWN"}, {514, "WM_LBUTTONUP"} }; // Code for debugging messages sent to Window static std::stringstream ss; ss.str(""); ss << " [TRACE] WNPROC Message => " << " Code = " << msg; if(WindowMessages.find(msg) != WindowMessages.end()) ss << " ; Message = " << WindowMessages[msg]; else ss << " ; Message = Unknown "; return ss.str(); }
Compiling:
- MSVC
# Build $ cl.exe gui-basic1.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /Fe:gui-basic1.exe user32.lib gdi32.lib
- Mingw/GCC:
$ g++ gui-basic1.cpp -o gui-basic1.exe -std=c++1z -g -lgdi32 -luser32Running:
The executable gui-basic1.exe can be run by clicking on it or by launching it from console (cmd.exe). However, it will not open any console and program statements for printing to stdout will have no effect since the program was compiled for the Windows subsystem rather than for the console subsystem.
- Parts
- Main Function
- Window subsystem entry point
The entry point of a GUI program is no longer the main function, it is now the WinMain function which is the entry point of the window subsystem. The name 'WINAPI' is just a macro which is expanded to
__stdcall, a calling convention qualifier.Parameters:
- hInstance => Handler to current program.
- hPrevInstance => Legacy and used for backward compatibility reasons.
- lpCmdLine => Command line
- nCmdShow =>
int WINAPI WinMain( // Handle to current application isntance HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, // Command line LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow ){ ... .... ... return 0; }
- Logging with OutputDebugString
It is not possible to visualize the output printed to stdout or stderr of a program compiled for the Window subystem since no terminal is opened and even launching the program in the console (cmd.exe or cmder) does not print anything. A workaround to this hurdle is to print to a file or redirect stdout or stderr to a file stream. Another better solution is to use the API OutputDebugString as its output is sent to shared memory and can be captured with the DebugView (download) sysinternals tool.
int WINAPI WinMain( ... ){ OutputDebugString("Starting WinMain Application"); std::puts("It will not print to Console - Starting WinMain Application"); ... ... ... OutputDebugString("Registered Window Class OK."); ... ... OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Exiting application. OK."); // Success status code return 0; }
The sysinternal tool DebugView is useful for debugging and visualizing logging of any program not able to print to console such as graphical programs compiled to window subsystem, DLL (Dynamic Linked Libraries), services (aka daemons), servers and etc.
Intialize Window class structure:
// ---------- Within WinMain function ----------// //Window class name must be unique const char wincClassName [] = "NameOfWindow"; // Win32 Window class structure WNDCLASSEX wc; // Win32 message structure MSG Msg; // Name to identify the class with. wc.lpszClassName = wincClassName; //Pointer to the window procedure for this window class. wc.lpfnWndProc = windowProcedure; // 1 - Register Windows Size wc.cbSize = sizeof(WNDCLASSEX); wc.style = 0; //Amount of extra data allocated for this class in memory. Usually 0 wc.cbClsExtra = 0; //Amount of extra data allocated in memory per window of this type. Usually 0. wc.cbWndExtra = 0; //Handle to application instance (that we got in the first parameter of WinMain()). wc.hInstance = hInstance; // Large (usually 32x32) icon shown when the user presses Alt+Tab. wc.hIcon = LoadIcon(NULL, IDI_APPLICATION); // Cursor that will be displayed over our window. wc.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW); // Background Brush to set the color of our window. wc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW+1); // (HBRUSH) CreateSolidBrush(RGB(10, 20, 30)); // // Background Brush to set the color of our window. wc.lpszMenuName = NULL; // Small (usually 16x16) icon to show in the taskbar and in the top left corner of the window. wc.hIconSm = LoadIcon(NULL, IDI_APPLICATION); OutputDebugString("Registered Window Class OK.");
Register Window Class:
if(!RegisterClassEx(&wc)) { MessageBox(NULL, "Window Registration Failed!", "Error!", MB_ICONEXCLAMATION | MB_OK); //Error status code return -1; } std::cout << "Class Registered" << std::endl;
Create Window object (hwnd - which is a handler to window object)
int width = 500, height = 400; int pos_left = 400, pos_top = 100; HWND hwnd = CreateWindowA( wc.lpszClassName, "Title of Window", WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, pos_left, pos_top, width, height, nullptr, nullptr, hInstance, nullptr ); OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Window created OK");
Display Window:
ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow); std::cout << "nCmdShow = " << nCmdShow << std::endl; UpdateWindow(hwnd);
Start message loop and processing events:
- The message loops receives messages (akas event) from the operating systems and relays them to the window procedure function or callback which processes the message. In most graphical programs, the program is not in control of the control flow, instead the operating system or window system which calls the program by sending events to it.
//---- Message Loop ----------// while(GetMessage(&Msg, NULL, 0, 0) > 0 ){ TranslateMessage(&Msg); DispatchMessage(&Msg); }
Print message when program ends:
OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Exiting application. OK.");
- Windows Procedure and WinMessageToString
Whenever the window is minimized, moved or resized or dragged, the operating system sends messages to the program by calling the registered window procedure (callback), in this case the function windowProcedure is called whenever an event happens.
In this type of event-driven program, the program does not manage the control the control flow, instead is the operating system which determines the controls by sending events and the program only responds the events.
Notes:
- The name 'CALLBACK' is just a macro for
__stdcallcalling convention. - The parameter hwnd is the Window handler and is the Window registered in the WinMain function.
- The parameter msg is the message sent by the operating system
whenever an event happens, when the Window is created, it sends a
WM_CREATEmessage; when the user clicks at the close button at top right corner, the operating system sends a messageWM_CLOSE. - As in any event-driven GUI API, no blocking function calls or any function call which can take any significant dealay should be executed inside the Window Procedure or callback as it is supposed to return as fast as possible. Otherwise, the GUI will freeze and become unresponsive while the blocking call is being executed. Those blocking calls such as read line from console, download file, process a huge file and so on should be carried out in another thread or that will compromise the GUI usability.
- The full list of messages that the operating sytem can sed can be
found at:
- List Of Windows Messages - https://wiki.winehq.org/List_Of_Windows_Messages
- List of Windows Messages - https://autohotkey.com/docs/misc/SendMessageList.htm
- List of windows messages with their description WM
// Window Procedure - Process window messages or events LRESULT CALLBACK windowProcedure ( HWND hwnd // Window Handle (Window object) ,UINT msg // Window Message ,WPARAM wParam // Additional message information ,LPARAM lParam // Additional message information ){ // Variable initialized one. static auto ignored_messages = std::set<UINT>{ WM_MOUSEMOVE, WM_NCHITTEST, WM_SETCURSOR, WM_IME_NOTIFY }; // Ignore messages which can flood the logging // if(msg != WM_MOUSEMOVE && msg != WM_NCMOUSEMOVE // && msg != WM_QUIT && msg != WM_NCHITTEST ) if(ignored_messages.find(msg) == ignored_messages.end()) OutputDebugString(WinMessageToString(msg).c_str()); ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... // Process messages switch(msg) { case WM_CREATE: SetWindowTextA(hwnd, "Change Window Title"); OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Window created. OK."); break; case WM_CLOSE: OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Window closed. OK."); DestroyWindow(hwnd); break; } ... return 0; }
Full message (events) processing:
// Process messages switch(msg) { case WM_CREATE: SetWindowTextA(hwnd, "Change Window Title"); OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Window created. OK."); break; case WM_CLOSE: OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Window closed. OK."); DestroyWindow(hwnd); break; case WM_DESTROY: OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Exiting application. OK."); PostQuitMessage(0); break; case WM_MOVE: std::cerr << " [INFO] Move window." << std::endl; break; case WM_PAINT: { // GDI - Graphics Devices Interface Here //-------------------------------------------- PAINTSTRUCT ps; HDC hdc; // std::cerr << " [INFO] Windown painting" << std::endl; hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps); std::string text = "Hello world Window!"; TextOutA(hdc, 125, 200, text.c_str(), text.size()); Ellipse(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); Rectangle(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); EndPaint(hwnd, &ps); } break; default: return DefWindowProc(hwnd, msg, wParam, lParam); }
Paint message and GDI - Graphics Device Interface
- The paint message is sent to the program whenever the window is moved, resized, minimized, maximized, overlaped and so on. This case WM_PAINT statement uses GDI for drawing a text and square to the screen.
case WM_PAINT: { // GDI - Graphics Devices Interface Here //-------------------------------------------- PAINTSTRUCT ps; HDC hdc; // std::cerr << " [INFO] Windown painting" << std::endl; hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps); std::string text = "Hello world Window!"; TextOutA(hdc, 125, 200, text.c_str(), text.size()); Ellipse(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); Rectangle(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); EndPaint(hwnd, &ps); }
Function WinMessageToString - this function called in the beggining of the window procedure takes a WM message as parameter and returns a human-readable description of the message code as parameter. The window procedure uses this function and the WinAPI function OutputDebugString to log the received messages (events) which can visualized with the DebugView sysinteral tool.
// Window Procedure - Process window messages or events LRESULT CALLBACK windowProcedure ( ... ){ // Variable initialized one. static auto ignored_messages = std::set<UINT>{ WM_MOUSEMOVE, WM_NCHITTEST, WM_SETCURSOR, WM_IME_NOTIFY }; // Ignore messages which can flood the logging // if(msg != WM_MOUSEMOVE && msg != WM_NCMOUSEMOVE // && msg != WM_QUIT && msg != WM_NCHITTEST ) if(ignored_messages.find(msg) == ignored_messages.end()) OutputDebugString(WinMessageToString(msg).c_str()); ... ... ...
Function WinMessageToString
/** Get a human-readable description of a Windows message as a * string */ auto WinMessageToString(UINT msg) -> std::string { /** Database of Windows messages - full list of messages here: * https://wiki.winehq.org/List_Of_Windows_Messages */ static auto WindowMessages = std::map<UINT, std::string>{ {1, "WM_CREATE"}, {2, "WM_DESTROY"}, {5, "WM_SIZE"}, {6, "WM_ACTIVATE"}, {13, "WM_SIZE"}, {22, "WM_SETVISIBLE"}, {23, "WM_ENABLE"}, {29, "WM_PAINT"}, {3, "WM_MOVE"}, {30, "WM_CLOSE"}, {32, "WM_SETCURSOR"}, {72, "WM_FULLSCREEN"}, {85, "WM_COPYDATA"}, {512, "WM_MOUSEMOVE"},{132, "WM_NCHITTEST"}, {641, "WM_IME_SETCONTEXT"}, {8, "WM_KILLFOCUS"}, {134, "WM_NCACTIVATE"}, {28, "WM_ACTIVATEAPP"}, {160, "WM_NCMOUSEMOVE"}, {161, "WM_NCLBUTTONDOWN"}, {36, "WM_GETMINMAXINFO"}, {642, "WM_IME_NOTIFY"}, {433, "WM_CAPTURECHANGED"}, {534, "WM_MOVING"}, {674, "WM_NCMOUSELEAVE"}, {675, "WM_MOUSELEAVE"}, {532, "WM_SIZING"}, {533, "WM_CAPTURECHANGED"}, {127, "WM_GETICON"}, {20, "WM_ERASEBKGND"}, {70, "WM_WINDOWPOSCHANGING"}, {71, "WM_WINDOWPOSCHANGED"}, {273, "WM_COMMAND"}, {274, "WM_SYSCOMMAND"}, {275, "WM_TIMER"}, {513, "WM_LBUTTONDOWN"}, {514, "WM_LBUTTONUP"} }; // Code for debugging messages sent to Window static std::stringstream ss; ss.str(""); ss << " [TRACE] WNPROC Message => " << " Code = " << msg; if(WindowMessages.find(msg) != WindowMessages.end()) ss << " ; Message = " << WindowMessages[msg]; else ss << " ; Message = Unknown "; return ss.str(); }
- The name 'CALLBACK' is just a macro for
- Main Function
1.31.2 GUI without WinMain
This code presents a minimal Win32 GUI graphical user interface without the WinMain function entry point.
Source:
This code is similar to the previous example, the difference is the changing of the entry point function from non-standard WinMain to main.
- Before - gui-basic1.cpp
int WINAPI WinMain( // Handle to current application isntance HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, // Command line LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow ){ ... .... ... return 0; }
- After - gui-without-winmain.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv){ //---- Get WinMain Parameters ----// HINSTANCE hInstance = GetModuleHandle(NULL); STARTUPINFO si; GetStartupInfo(&si); int nCmdShow = si.wShowWindow; ... ... ... ... return 0 }
Files
File: CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0) project(WindowsGUI_WINAPI) set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17) set(CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON) add_executable( mygui WIN32 gui-without-winmain.cpp ) IF(MSVC) target_link_options( mygui PUBLIC "/ENTRY:mainCRTStartup" ) ENDIF()
File: gui-without-winmain.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <windows.h> LRESULT windowProcedure( HWND hwnd, UINT msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam); int main(int argc, char** argv){ //---- Get WinMain Parameters ----// HINSTANCE hInstance = GetModuleHandle(NULL); STARTUPINFO si; GetStartupInfo(&si); int nCmdShow = si.wShowWindow; // -------------------------// OutputDebugString("Starting WinMain Application"); std::puts("Starting WinMain Application"); //Window class name must be unique const char wincClassName [] = "NameOfWindow"; // Win32 Window class structure WNDCLASSEX wc; // Win32 message structure MSG Msg; wc.lpszClassName = wincClassName; wc.lpfnWndProc = windowProcedure; wc.cbSize = sizeof(WNDCLASSEX); wc.style = 0; wc.cbClsExtra = 0; wc.cbWndExtra = 0; wc.hInstance = hInstance; wc.hIcon = LoadIcon(NULL, IDI_APPLICATION); wc.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW); wc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW+1); // (HBRUSH) CreateSolidBrush(RGB(10, 20, 30)); // wc.lpszMenuName = nullptr; wc.hIconSm = LoadIcon(nullptr, IDI_APPLICATION); if(!RegisterClassEx(&wc)) { MessageBox(nullptr, "Window Registration Failed!", "Error!", MB_ICONEXCLAMATION | MB_OK); //Error status code return -1; } std::cout << "Class Registered" << std::endl; int width = 500, height = 400; int pos_left = 400, pos_top = 100; HWND hwnd = CreateWindowA( wc.lpszClassName, "Title of Window", WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, pos_left, pos_top, width, height, nullptr, nullptr, hInstance, nullptr ); constexpr size_t buttonID = 1001; OutputDebugString(" [INFO] Window created OK"); if(hwnd == NULL){ MessageBox( NULL, "Error: Failure to create Window", "Error Report", MB_ICONEXCLAMATION | MB_OK); return -1; } ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow); UpdateWindow(hwnd); //---- Message Loop ----------// while(GetMessage(&Msg, NULL, 0, 0) > 0 ) { TranslateMessage(&Msg); DispatchMessage(&Msg); } // Success status code return 0; } // ------------ End of Main ------------------------- // // Window Procedure - Process window messages or events LRESULT windowProcedure ( HWND hwnd // Window Handle (Window object) ,UINT msg // Window Message ,WPARAM wParam // Additional message information ,LPARAM lParam // Additional message information ){ // Process messages switch(msg) { case WM_CREATE: break; case WM_CLOSE: DestroyWindow(hwnd); break; case WM_DESTROY: PostQuitMessage(0); break; case WM_MOVE: break; case WM_PAINT: { // GDI - Graphics Devices Interface Here //-------------------------------------------- PAINTSTRUCT ps; HDC hdc; // std::cerr << " [INFO] Windown painting" << std::endl; hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps); std::string text = "Hello world Window!"; TextOutA(hdc, 125, 200, text.c_str(), text.size()); Ellipse(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); Rectangle(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); EndPaint(hwnd, &ps); } break; default: return DefWindowProc(hwnd, msg, wParam, lParam); } return 0; }
Building with CMake and MSVC Compiler
# ---- Build -------------# $ cmake -H. -B_build_msvc -G "Visual Studio 16 2019" -A x64 -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug $ cmake --build _build_msvc --target # ---- Run --------------# $ _build_msvc\Debug\mygui.exe
Building with CMake and MINGW Compiler
# ----- Build --------------# $ cmake -B_build_mingw -G "MinGW Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug $ cmake --build _build_mingw --target #------ Run ---------------# $ _build_mingw\mygui.exe
Compiling with MSVC for console subsystem
Produces: gui-without-winmain.exe
When the user clicks at the application's executable file, a terminal is opened alongside the window where it is possible to view the printed messages.
$ cl.exe gui-without-winmain.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo user32.lib gdi32.lib
By clicking at the program the Window is opened with a terminal:
Compiling with MSVC for window subsystem
When the program is compiled for the window subsystem, no terminal is opened as any Window's GUI application.
$ cl.exe gui-without-winmain.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /link /subsystem:windows /entry:mainCRTStartup user32.lib gdi32.lib
Note: the compiler flags.
- /subsystem:windows => Compiles for Windows subsystem no terminal is opened. It actually, just changes a flag in the PE32 executable file.
- /entry:mainCRTStartup => Changes program entry-point
Compiling with Mingw/GCC for console subsystem
Any program is compiled for the console subystem by default.
$ g++ gui-without-winmain.cpp -o gui-without-winmain.exe -std=c++1z -g -lgdi32 -luser32
Compiling with Mingw/GCC for window subsystem
The flag (-Wl,-subsystem,windows) is required for compiling sources to the windows subsystem.
$ g++ gui-without-winmain.cpp -o gui-without-winmain.exe -std=c++1z -g -lgdi32 -luser32 -Wl,-subsystem,windows
1.31.3 GUI without WinMain in DLang (D)
Note: In this rewrite, the D language version of the code became longer than the C++ version because it is not possible to use include statements as in C or C++, as a result, all declaration of structs and functions from Windows API must to be rewritten in D.
Documentation of Windows APIs used:
- Windows Data Types
- CreateWindowExA() function (winuser.h)
- WindowProc callback function
- STARTUPINFOA structure
- WNDCLASSEXA structure
- Note: In order to view messages sent by the OutputDebugString subroutine, it is necessary the tool DebugView from sysinternal.
- React OS header file: winuser.h contains all constants WM_MOVE,
WM_CLOSE, … and the source of many macros.
- Note: The operating system vendor does not provide the header file winuser.h on the internet. The only way to view this file other than the accessing React OS source, is to install the Windows SDK (Software Development Kit).
Files:
File: wingui.d
import std.stdio; import core.stdc.stdio; import std.range: empty; import std.string; import core.stdc.string: strlen; import std.conv : to; void message_box_error(string message, string title) { MessageBoxA( null , std.string.toStringz(message) , std.string.toStringz(title) , MB_ICONEXCLAMATION | MB_OK ); } extern(C) LRESULT window_message_callback(HWND hwnd, UINT msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam ) { // Process messages switch(msg) { case WM_CREATE: break; case WM_CLOSE: DestroyWindow(hwnd); break; case WM_DESTROY: PostQuitMessage(0); break; case WM_MOVE: break; case WM_PAINT: { // GDI - Graphics Devices Interface Here //-------------------------------------------- PAINTSTRUCT ps; HDC hdc; // std::cerr << " [INFO] Windown painting" << std::endl; hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps); const char* text = std.string.toStringz("Hello world Window!"); TextOutA(hdc, 125, 200, text, cast(int) strlen(text) ); Ellipse(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); Rectangle(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); EndPaint(hwnd, &ps); } break; default: return DefWindowProcA(hwnd, msg, wParam, lParam); } return null; } int main() { printf(" [TRACE] Started D application. Ok \n\n"); HINSTANCE hInstance = GetModuleHandleA(null); assert( hInstance != null ); STARTUPINFO_A si; GetStartupInfoA(&si); int nCmdShow = si.wShowWindow; // -------------------------// OutputDebugStringA("Starting WinMain Application"); const char* wincClassName = std.string.toStringz("NameOfWindow"); // Win32 Window class structure WNDCLASSEXA wc; // Win32 message structure MSG Msg; wc.lpszClassName = cast(char*) wincClassName; wc.lpfnWndProc = &window_message_callback; wc.cbSize = WNDCLASSEXA.sizeof; wc.style = 0; wc.cbClsExtra = 0; wc.cbWndExtra = 0; wc.hInstance = hInstance; wc.hIcon = LoadIconA(null, cast(LPCSTR) IDI_APPLICATION); wc.hCursor = LoadCursorA(null, cast(LPCSTR) IDC_ARROW); wc.hbrBackground = cast(HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW+1); wc.hIconSm = LoadIconA(null, cast(LPCSTR) IDI_APPLICATION); if( !RegisterClassExA(&wc) ) { message_box_error("Window Registration Failed!", "Error!"); //Error status code return -1; } int width = 500, height = 400; int pos_left = 400, pos_top = 100; HWND hwnd = CreateWindowExA( 0 , wc.lpszClassName , "Title of Window" , WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW , pos_left , pos_top , width , height , null , null , hInstance , null ); assert( hwnd != null ); OutputDebugStringA(" [INFO] Window created OK"); if(hwnd == null) { message_box_error( "Error: Failure to create Window", "Error Report"); return -1; } ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow); UpdateWindow(hwnd); //---- Message Loop ----------// while( GetMessageA(&Msg, null, 0, 0) > 0 ) { TranslateMessage(&Msg); DispatchMessageA(&Msg); } message_box_error("Program terminated Ok.", "Information:"); return 0; } // ========== I M P L E M E N T A T I O N S =================== // // Useful Type aliases //----------------------------------// // Alias for C or C++ void* void pointer (opaque pointer) alias LPVOID = void*; // Windows handle's alias aliases alias HINSTANCE = LPVOID; alias HANDLE = LPVOID; alias HWND = LPVOID; alias HDC = LPVOID; alias HMODULE = LPVOID; alias HICON = LPVOID; alias HCURSOR = LPVOID; alias HBRUSH = LPVOID; alias HMENU = LPVOID; // Aliases for string aliass alias LPCSTR = const char*; alias LPSTR = char*; // Operation status code alias HRESULT = long; // Return code of COM interfaces alias BOOL = int; // Boolean status code (0 - false), (1 or anything else is true) alias LPRESULT = const HRESULT*; // Non Categorized aliases alias UINT = uint; alias LONG = long; alias BYTE = char; alias LPBYTE = char*; alias WORD = short; alias DWORD = int; alias WPARAM = UINT*; alias LPARAM = long*; alias LRESULT = long*; alias ATOM = WORD; // Type alias for C function pointer (Function with C linkage) // ,in other words, function with C-calling convention. alias WNDPROC = extern(C) LRESULT function( HWND hwnd , UINT uMsg , WPARAM wParam , LPARAM lParam ); struct RECT { LONG left; LONG top; LONG right; LONG bottom; } struct POINT { LONG x; LONG y; }; struct MSG { HWND hwnd; UINT message; WPARAM wParam; LPARAM lParam; DWORD time; POINT pt; DWORD lPrivate; }; struct STARTUPINFO_A { DWORD cb; LPSTR lpReserved; LPSTR lpDesktop; LPSTR lpTitle; DWORD dwX; DWORD dwY; DWORD dwXSize; DWORD dwYSize; DWORD dwXCountChars; DWORD dwYCountChars; DWORD dwFillAttribute; DWORD dwFlags; WORD wShowWindow; WORD cbReserved2; LPBYTE lpReserved2; HANDLE hStdInput; HANDLE hStdOutput; HANDLE hStdError; }; struct WNDCLASSEXA { UINT cbSize; UINT style; WNDPROC lpfnWndProc; int cbClsExtra; int cbWndExtra; HINSTANCE hInstance; HICON hIcon; HCURSOR hCursor; HBRUSH hbrBackground; LPSTR lpszMenuName; LPSTR lpszClassName; HICON hIconSm; }; struct PAINTSTRUCT { HDC hdc; BOOL fErase; RECT rcPaint; BOOL fRestore; BOOL fIncUpdate; BYTE[32] rgbReserved; }; extern(C) int MessageBoxA(HWND hWnd, LPCSTR lpText, LPCSTR lpCaption, UINT uType); extern(C) void OutputDebugStringA(LPCSTR lpOutputString); extern(C) HMODULE GetModuleHandleA(LPCSTR lpModuleName); extern(C) BOOL ShowWindow(HWND hWnd, int nCmdShow); extern(C) BOOL UpdateWindow(HWND hWnd); extern(C) BOOL GetMessageA(MSG* lpMsg, HWND hWnd, UINT wMsgFilterMin, UINT wMsgFilterMax); extern(C) BOOL TranslateMessage(const MSG *lpMsg); extern(C) BOOL DestroyWindow(HWND hWnd); extern(C) HWND CreateWindowExA( DWORD dwExStyle, LPCSTR lpClassName, LPCSTR lpWindowName, DWORD dwStyle, int X, int Y, int nWidth, int nHeight, HWND hWndParent, HMENU hMenu, HINSTANCE hInstance, LPVOID lpParam ); extern(C) ATOM RegisterClassExA(const WNDCLASSEXA *unnamedParam1); extern(C) void GetStartupInfoA(STARTUPINFO_A* lpStartupInfo); extern(C) HICON LoadIconA (HINSTANCE hInstance, LPCSTR lpIconName); extern(C) HCURSOR LoadCursorA(HINSTANCE hInstance, LPCSTR lpCursorName); extern(C) LRESULT DispatchMessageA(const MSG *lpMsg); extern(C) void PostQuitMessage(int nExitCode); extern(C) LRESULT DefWindowProcA( HWND hWnd, UINT Msg , WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam); extern(C) HDC BeginPaint(HWND hWnd, PAINTSTRUCT* lpPaint); extern(C) BOOL EndPaint (HWND hWnd, const PAINTSTRUCT* lpPaint); extern(C) BOOL TextOutA(HDC hdc, int x, int y, LPCSTR lpString, int c); extern(C) BOOL Ellipse(HDC hdc, int left, int top, int right, int bottom); extern(C) BOOL Rectangle(HDC hdc, int left, int top, int right, int bottom); const int IDI_APPLICATION = 32512; const int IDI_HAND = 32513; const int IDI_QUESTION = 32514; const int IDI_EXCLAMATION = 32515; const int IDI_ASTERISK = 32516; const int IDI_WINLOGO = 32517; const int IDC_ARROW = 32512; const DWORD WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW = 0xcf0000; const DWORD WM_NULL = 0; const DWORD WM_CREATE = 1; const DWORD WM_DESTROY = 2; const DWORD WM_ENABLE = 10; const DWORD WM_CLOSE = 16; const DWORD WM_QUIT = 18; const DWORD WM_PAINT = 15; const DWORD WM_MOVE = 3; const DWORD COLOR_WINDOW = 5; const DWORD MB_USERICON = 128; const DWORD MB_ICONASTERISK = 64; const DWORD MB_ICONEXCLAMATION = 0x30; const DWORD MB_ICONWARNING = 0x30; const DWORD MB_ICONERROR = 16; const DWORD MB_ICONHAND = 16; const DWORD MB_ICONQUESTION = 32; const DWORD MB_OK = 0; const DWORD MB_ABORTRETRYIGNORE = 2; const DWORD MB_APPLMODAL = 0; const DWORD MB_DEFAULT_DESKTOP_ONLY = 0x20000; const DWORD MB_HELP = 0x4000; const DWORD MB_RIGHT = 0x80000; const DWORD MB_RTLREADING = 0x100000; const DWORD MB_TOPMOST = 0x40000; const DWORD MB_DEFBUTTON1 = 0; const DWORD MB_DEFBUTTON2 = 256; const DWORD MB_DEFBUTTON3 = 512; const DWORD MB_DEFBUTTON4 = 0x300; const DWORD MB_ICONINFORMATION = 64; const DWORD MB_ICONSTOP = 16; const DWORD MB_OKCANCEL = 1;
Building
Building for console subsystem: (default)
$ dmd wingui.d -of=wingui_console_subsystem.exe -m64 Kernel32.lib Ntdll.lib User32.lib Gdi32.lib
Building for window subsystem:
$ dmd wingui.d -of=wingui_window_subsystem.exe -m64 -L/SUBSYSTEM:WINDOWS -L/ENTRY:mainCRTStartup Kernel32.lib Ntdll.lib User32.lib Gdi32.lib
Runninng
# Console subsystem =>> Opens a terminal window when user clicks # at the executable. $ .\wingui_console_subsystem.exe # Window subsystem version => Prints nothing in the terminal. $ .\wingui_window_subsystem.exe
1.31.4 GUI without WinMain in Rust
Note: This Rust rewrite shows a blank GUI window and a message box when the window is closed. This code is still incomplete and still needs porting the GDI structs for 2D drawing on the window.
Files:
File: rust-wingui.rs
// Build for the "window" subsystem instead of console subsystem. // Comment the next uncommented line to enable the console subsystem and view // the stdout and stderr output. #![windows_subsystem = "windows"] use std::os::raw::{c_int, c_char, c_long, c_void, c_uint, c_short}; use std::ffi::CString; use std::mem; const IDI_APPLICATION: c_int = 32512; const IDI_HAND: c_int = 32513; const IDI_QUESTION: c_int = 32514; const IDI_EXCLAMATION: c_int = 32515; const IDI_ASTERISK: c_int = 32516; const IDI_WINLOGO: c_int = 32517; const IDC_ARROW: c_int = 32512; const WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW: DWORD = 0xcf0000; const WM_NULL: UINT = 0; const WM_CREATE: UINT = 1; const WM_DESTROY: UINT = 2; const WM_ENABLE: UINT = 10; const WM_CLOSE: UINT = 16; const WM_QUIT: UINT = 18; const WM_PAINT: UINT = 15; const WM_MOVE: UINT = 3; extern "C" fn window_message_callback( hwnd: HWND, msg: UINT , wParam: WPARAM, lParam: LPARAM) -> LRESULT { let zero_ptr = std::ptr::null_mut(); if msg == WM_CLOSE { output_debug_string("Message WM_CLOSE sent. => Shutdown application"); unsafe { DestroyWindow(hwnd); } return zero_ptr; } if msg == WM_DESTROY { output_debug_string("Message WM_DESTROY sent."); unsafe{ PostQuitMessage(0); } return zero_ptr; } if msg == WM_MOVE { output_debug_string("Message WM_MOVE sent."); return zero_ptr; } if msg == WM_PAINT { // TODO - Port the following code for the GDI // (GDI - Graphics Device Interface) /** * PAINTSTRUCT ps; * HDC hdc; * // std::cerr << " [INFO] Windown painting" << std::endl; * hdc = BeginPaint(hwnd, &ps); * std::string text = "Hello world Window!"; * TextOutA(hdc, 125, 200, text.c_str(), text.size()); * Ellipse(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); * Rectangle(hdc, 100, 100, 160, 160); * EndPaint(hwnd, &ps); -------------------------------------------------*/ // output_debug_string("TODO - Finish the GDI code"); return zero_ptr; } return unsafe{ DefWindowProcA(hwnd, msg, wParam, lParam) }; //return std::ptr::null_mut(); } fn main() { println!(" [TRACE] Hello world Rust! on Windows NT."); output_debug_string("Hello world from a Rust process!!"); output_debug_string("You can see those messages using Sysinternals tool"); let c_null_ptr = std::ptr::null_mut(); let c_null_ptr_u8 = std::ptr::null_mut() as *mut u8; let hInstance: HINSTANCE = unsafe { GetModuleHandleA(std::ptr::null_mut()) }; assert!( hInstance != c_null_ptr ); // Initialize struct let mut si: STARTUPINFO_A = STARTUPINFO_A { cb: 0 , lpReserved: std::ptr::null_mut() , lpDesktop: c_null_ptr_u8 , lpTitle: c_null_ptr_u8 , dwX: 0 , dwY: 0 , dwXSize: 0 , dwYSize: 0 , dwXCountChars: 0 , dwYCountChars: 0 , dwFillAttribute: 0 , dwFlags: 0 , wShowWindow: 0 , cbReserved2: 0 , lpReserved2: std::ptr::null_mut() , hStdInput: c_null_ptr , hStdOutput: c_null_ptr , hStdError: c_null_ptr }; unsafe { GetStartupInfoA( &mut si as *mut _ ) }; let nCmdShow: WORD = si.wShowWindow; let className: &str = "NameOfWIndow"; let className_: CString = CString::new(className).unwrap(); let COLOR_WINDOW: c_int = 5; let mut wc = WNDCLASSEXA { cbSize: mem::size_of::<WNDCLASSEXA>() as u32 , style: 0 , lpfnWndProc: window_message_callback , cbClsExtra: 0 , cbWndExtra: 0 , hInstance: hInstance , hIcon: unsafe{ LoadIconA( c_null_ptr , IDI_APPLICATION) } , hCursor: unsafe{ LoadCursorA( c_null_ptr, IDC_ARROW) } , hbrBackground: (COLOR_WINDOW + 1) as *mut _ , lpszMenuName: std::ptr::null_mut() , lpszClassName: className_.as_ptr() , hIconSm: std::ptr::null_mut() }; let mut result: ATOM = 0; // False result = unsafe { RegisterClassExA(&wc as *const _) }; assert!( result != 0); let pos_left: DWORD = 400; let pos_top: DWORD = 100; let width: DWORD = 500; let height: DWORD = 400; let title = CString::new("Title of Window").unwrap() ; let hwnd: HWND = unsafe { CreateWindowExA( 0 // dwExStyle , wc.lpszClassName // lpClassName , title.as_ptr() // lpWindowName , WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW // dwStyle , pos_left, pos_top // X, Y , width, height // nWidth, nHeight , c_null_ptr // hWndParent , c_null_ptr // hMenu , hInstance // hInstance , c_null_ptr // lpParam ) }; assert!( hwnd != c_null_ptr ); unsafe { ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow as i32); UpdateWindow(hwnd); } // Dummy initialization => This struct is initialized // by GetMessage(), however rust does not provide // any means to default initialize this struct. let mut msg: MSG = MSG { hwnd: c_null_ptr , message: 0 , wParam: std::ptr::null_mut() , lParam: std::ptr::null_mut() , time: 0 , pt: POINT{ x: 0, y: 0 } , lPrivate: 0 }; // ---- Window event loop --- loop { let cond = unsafe { GetMessageA(&mut msg as *mut _, c_null_ptr, 0, 0) }; if cond <= 0 { break; } unsafe { TranslateMessage(&msg); DispatchMessageA(&msg); } } // message_box_info("Application terminated Ok", "Notification"); println!(" [TRACE] Terminated. Ok!"); } // --- End of main() --- // // ===== I M P L E M E N T A T I O N S ============= // //****************************************************// // Useful Type aliases //----------------------------------// // Alias for C or C++ void* void pointer (opaque pointer) type LPVOID = *mut c_void; // Windows handle's type aliases type HINSTANCE = LPVOID; type HANDLE = LPVOID; type HWND = LPVOID; type HMODULE = LPVOID; type HICON = LPVOID; type HCURSOR = LPVOID; type HBRUSH = LPVOID; type HMENU = LPVOID; // Aliases for string types type LPCSTR = *const c_char; type LPSTR = *mut u8; // Operation status code type HRESULT = c_long; // Return code of COM interfaces type BOOL = c_int; // Boolean status code (0 - false), (1 or anything else is true) type LPRESULT = *const HRESULT; // Non Categorized aliases type UINT = c_uint; type LPBYTE = *mut u8; type WORD = c_short; type DWORD = c_int; type WPARAM = *mut UINT; type LPARAM = *mut c_long; type LRESULT = *mut c_long; type LONG = c_long; type ATOM = WORD; // Type alias for C function pointer (Function with C linkage) // ,in other words, function with C-calling convention. type WindowProc = unsafe extern "C" fn( hwnd: HWND , uMsg: UINT , wParam: WPARAM , lParam: LPARAM) -> LRESULT; #[repr(C)] struct STARTUPINFO_A { cb: DWORD , lpReserved: LPSTR , lpDesktop: LPSTR , lpTitle: LPSTR , dwX: DWORD , dwY: DWORD , dwXSize: DWORD , dwYSize: DWORD , dwXCountChars: DWORD , dwYCountChars: DWORD , dwFillAttribute: DWORD , dwFlags: DWORD , wShowWindow: WORD , cbReserved2: WORD , lpReserved2: LPBYTE , hStdInput: HANDLE , hStdOutput: HANDLE , hStdError: HANDLE } type LPSTARTUPINFO_A = *mut STARTUPINFO_A; #[repr(C)] struct WNDCLASSEXA { cbSize: UINT , style: UINT // Callback function 'lpfnWndProc' (function pointer) , lpfnWndProc: WindowProc , cbClsExtra: c_int , cbWndExtra: c_int , hInstance: HINSTANCE , hIcon: HICON , hCursor: HCURSOR , hbrBackground: HBRUSH , lpszMenuName: LPCSTR , lpszClassName: LPCSTR , hIconSm: HICON } #[repr(C)] struct POINT { x: LONG , y: LONG } #[repr(C)] struct MSG { hwnd: HWND , message: UINT , wParam: WPARAM , lParam: LPARAM , time: DWORD , pt: POINT , lPrivate: DWORD } type LPMSG = *mut MSG; #[link(name = "user32")] extern "C" { fn GetModuleHandleA(lpModuleName: LPCSTR) -> HMODULE; fn RegisterClassExA(unnamedParam1: *const WNDCLASSEXA) -> ATOM; fn LoadIconA(hInstance: HINSTANCE, lpIconName: c_int) -> HICON; // fn LoadIconA(hInstance: HINSTANCE, lpIconName: LPCSTR) -> HICON; // HCURSOR LoadCursorA(HINSTANCE hInstance, LPCSTR lpCursorName); // fn LoadCursorA(hInstance: HINSTANCE, lpCursorName: LPCSTR) -> HCURSOR; fn LoadCursorA(hInstance: HINSTANCE, lpCursorName: c_int) -> HCURSOR; fn ShowWindow(hWnd: HWND , nCmdShow: c_int ) -> BOOL; fn UpdateWindow(hWnd: HWND) -> BOOL; fn GetMessageA( lpMsg: LPMSG ,hWnd: HWND , wMsgFilterMin: UINT , wMsgFilterMax: UINT) -> BOOL; fn GetStartupInfoA(lpStartupInfo: LPSTARTUPINFO_A ) -> c_void; fn DefWindowProcA(hWnd: HWND, Msg: UINT, wParam: WPARAM, lParam: LPARAM) -> LRESULT; fn TranslateMessage(lpMsg: *const MSG) -> BOOL; fn DispatchMessageA(lpMsg: *const MSG) -> LRESULT; fn DestroyWindow(hWnd: HWND) -> BOOL; fn PostQuitMessage(nExitCode: c_int) -> c_void; // Note: CreateWindowA is a macro. fn CreateWindowExA( dwExStyle: DWORD , lpClassName: LPCSTR , lpWindowName: LPCSTR , dwStyle: DWORD , X: c_int , Y: c_int , nWidth: c_int , nHeight: c_int , hWndParent: HWND , hMenu: HMENU , hInstance: HINSTANCE , lpParam: LPVOID ) -> HWND; fn OutputDebugStringA(message: LPCSTR) -> c_void; fn MessageBoxA(hWnd: HWND, lpText: LPCSTR, lpCaption: LPCSTR, uType: UINT) -> c_int; } fn output_debug_string(message: &str) { let cstr: CString = CString::new(message).unwrap(); unsafe { OutputDebugStringA(cstr.as_ptr()); } } fn message_box(text: &str, caption: &str, u_type: c_uint) { let text_ = CString::new(text).unwrap(); let caption_ = CString::new(caption).unwrap(); // Unsafe functions can only be called from // unsafe blocks. unsafe { MessageBoxA( std::ptr::null_mut() , text_.as_ptr() , caption_.as_ptr() , u_type); } } fn message_box_info(text: &str, caption: &str) { message_box(text, caption, 0x00020000 | 0x00000040); }
Building:
$ rustc rust-wingui.rs $ rustc rust-wingui.rs -A warnings # Build supressing warnings
Running:
$ .\rust-wingui.exe
1.32 Cross-compiling WxWidgets for Windows from Linux
WxWidget is a C++ full-featured cross-platform platform graphics interface framework based on MFC - Microsoft Foundations Classes, that supports native controls and platform-specific look and feel of several operating systems, including Microsoft Windows NT, Linux and Mac-OSX. WxWidgets framework also supports many different gaphics backends, including: Gtk (wxGtk); Windows API (win32) controls (wxMSW); MacOSX Cocoa (wxOSX/Cocoa); X11 - X Windows Systems (wX11); Qt Framework (wxQt) and Motiff (obsolete) wxMotiff. In addition to gaphics interfaces features, this framework also provide support for basic C++ containers, sockets, multithreading, clipboard and sound and video playback. WxWidgets is released under wxWindows License (based on L-GPL) with an exception clause allowing the application to be either dynamically or statically linked against WxWidgets libraries without the need to redistribute application source code. This section presents how to cross-compile WxWidgets applications from Linux to Windows (Win32 API) using a reproducible development environment based on a docker image.
Advatanges:
- Full-featured and cross-platform framework, just-like Qt Framework.
- Based on MFC - Microsoft Foundation Classes
- Supports many different operating systems and graphics backends
- More commercially friendly than Qt
- Closed-source and commercial applications can be statically linked against WxWidgets without the need to disclose the source code.
- Suitable for porting applications based on MFC (Microsoft Foundation Classes) or Windows Win32 API.
Drawbacks:
- The documentation is not as good as Qt documentation.
- The library uses lots of macro (C++/C preprocessor) magic.
- WxWidgets does not use modern C++ features.
- Library in C++98, C with-classes style.
- Unlike Qt, this framework don't support embedded and mobile plaforms.
Building the docker image (Reproducible Development and building environment)
File: wxwidgets-windows-docker.conf
- This docker image provides is based on dockcross base image and provides a reproducible development environment that allows cross-compiling WxWidgets applications for Windows NT.
# Command to build this docker image: # $ docker build . -t wxwidgets-windows -f wxwidgets-windows-docker.conf # FROM dockcross/windows-static-x64 # ---------- Install XMake Building System --------------# # ENV XMAKE_ROOT y # Download Xmake installation script RUN curl -fsSL https://xmake.io/shget.text > /tmp/install.sh # Execute the installation script RUN env CC= CXX= CPP= bash /tmp/install.sh # ---------- Install WxWidgets Library for Windows Cross-Compilation --------# # RUN mkdir -p /build WORKDIR /build RUN git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/wxWidgets/wxWidgets.git WORKDIR wxWidgets RUN mkdir -p build-debug WORKDIR build-debug # Create symbolic link to windres RUN ln -s /usr/src/mxe/usr/bin/x86_64-w64-mingw32.static-windres /bin/windres # Run configuration step RUN ../configure --enable-debug --host=x86_64-w64-mingw32 \ --with-msw --disable-shared --enable-monolithic --build=x86_64-linux --disable-xrc \ --disable-sys-libs --enable-unicode # Run building step => Build and install WxWidgets RUN make -j4 && make install RUN mkdir -p /cwd WORKDIR /cwd RUN rm -rf /build
Build the docker image (Wait a while, drink a coffee …):
$ docker build . -t wxwidgets-windows -f wxwidgets-windows-docker.conf
Checking the docker image:
$ docker run --rm -it --user=(id -u):(id -g) --workdir=/cwd --volume=$PWD:/cwd wxwidgets-windows bash I have no name!@3c84b2b8cb95:/cwd$ I have no name!@3c84b2b8cb95:/cwd$ export PS1=" $ " $ echo $CC /usr/src/mxe/usr/bin/x86_64-w64-mingw32.static-gcc $ echo $CXX /usr/src/mxe/usr/bin/x86_64-w64-mingw32.static-g++ $ echo $LD /usr/src/mxe/usr/bin/x86_64-w64-mingw32.static-ld $ echo $CPP /usr/src/mxe/usr/bin/x86_64-w64-mingw32.static-cpp $ echo $DEFAULT_DOCKCROSS_IMAGE dockcross/windows-static-x64:latest $ echo $CROSS_TRIPLE x86_64-w64-mingw32.static $ echo $AR /usr/src/mxe/usr/bin/x86_64-w64-mingw32.static-ar $ echo $AS /usr/src/mxe/usr/bin/x86_64-w64-mingw32.static-as $ echo $CMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE /usr/src/mxe/usr/x86_64-w64-mingw32.static/share/cmake/mxe-conf.cmake $ which wx-config /usr/local/bin/wx-config $ wx-config --cxxflags --libs -I/usr/local/lib/wx/include/x86_64-w64-mingw32-msw-unicode-static-3.3 -I/usr/local/include/wx-3.3 -D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64 -D__WXMSW__ -L/usr/local/lib -Wl,--subsystem,windows -mwindows /usr/local/lib/libwx_mswu-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32.a -limm32 -lwxtiff-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lwxjpeg-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lwxpng-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lwxregexu-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lwxscintilla-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lwxexpat-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lwxzlib-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lrpcrt4 -loleaut32 -lole32 -luuid -luxtheme -lwinspool -lwinmm -lshell32 -lshlwapi -lcomctl32 -lcomdlg32 -ladvapi32 -lversion -lws2_32 -lgdi32 -loleacc -lwinhttp
Output of wx-config version:
$ wx-config --version 3.3.0
Output of command $ wx-config –cxxflags –libs
$ docker run --rm -it --user=(id -u):(id -g) --workdir=/cwd --volume=$PWD:/cwd \
wxwidgets-windows wx-config --cxxflags --libs
Output of command: $ wx-config --cxxflags --libs
Include Paths:
-I/usr/local/lib/wx/include/x86_64-w64-mingw32-msw-unicode-static-3.3
-I/usr/local/include/wx-3.3
Compiling definitions:
-D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64 -D__WXMSW__
Linking Directories:
-L/usr/local/lib
Linker Commands:
-Wl,--subsystem,windows -mwindows
Libraries to Link against:
/usr/local/lib/libwx_mswu-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32.a
-limm32 -lwxtiff-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lwxjpeg-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lwxpng-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32
-lwxregexu-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lwxscintilla-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lwxexpat-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32
-lwxzlib-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 -lrpcrt4 -loleaut32 -lole32 -luuid -luxtheme -lwinspool -lwinmm -lshell32
-lshlwapi -lcomctl32 -lcomdlg32 -ladvapi32 -lversion -lws2_32 -lgdi32 -loleacc -lwinhttp
Files
File: CMakeLists.txt
project(WxProject-Cross-Compile) cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0) set(CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON) # DOES NOT WORK!!: find_package(wxWidgets COMPONENTS core base REQUIRED) # Note: Obtained from the output of command: $ wx-config --cxxflags --libs set(wxWidgets_LIBRARIES /usr/local/lib/libwx_mswu-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32.a imm32 wxtiff-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 wxjpeg-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 wxpng-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 wxregexu-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 wxscintilla-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 wxexpat-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 wxzlib-3.3-x86_64-w64-mingw32 rpcrt4 oleaut32 ole32 uuid uxtheme winspool winmm shell32 shlwapi comctl32 comdlg32 advapi32 version ws2_32 gdi32 oleacc winhttp ) # Note: Obtained from the output of command: $ wx-config --cxxflags --libs set(wxWidgets_INCLUDES /usr/local/lib/wx/include/x86_64-w64-mingw32-msw-unicode-static-3.3 /usr/local/include/wx-3.3 ) add_executable(SimpleWindow SimpleWindow.cpp) target_compile_definitions(SimpleWindow PRIVATE _FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64 __WXMSW__ ) target_include_directories(SimpleWindow PRIVATE ${wxWidgets_INCLUDES}) link_directories(SimpleWindow PRIVATE /usr/local/lib ) target_link_libraries(SimpleWindow PRIVATE ${wxWidgets_LIBRARIES}) target_link_options(SimpleWindow PRIVATE -mwindows -Wl,--subsystem,windows)
File: SimpleWindow.cpp (Moritzolch.com)
#include <wx/wx.h> class MyFrame : public wxFrame { public: MyFrame() : wxFrame(NULL, wxID_ANY, _("Test")) {} }; class MyApp : public wxApp { public: virtual bool OnInit() override { myFrame.Show(); return true; } private: MyFrame myFrame; }; IMPLEMENT_APP(MyApp)
Building Aproach 1 => Manual compilation
$ docker run --rm -it --user=(id -u):(id -g) --workdir=/cwd \ --volume=$PWD:/cwd wxwidgets-windows bash I have no name!@4cca88463e97:/cwd$ export PS1="$ " $ echo $CXX /usr/src/mxe/usr/bin/x86_64-w64-mingw32.static-g++ $ $CXX SimpleWindow.cpp -v -o SimpleWindow.exe `wx-config --cxxflags --libs` $ ls CMakeLists.txt Dockerfile.conf SimpleWindow.cpp SimpleWindow.exe _build out.log winhello.cpp
Building Aproach 2 => Using CMake
# Configuration step $ docker run --rm -it --user=(id -u):(id -g) --workdir=/cwd --volume=$PWD:/cwd \ wxwidgets-windows cmake -B_build -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug # Building step $ docker run --rm -it --user=(id -u):(id -g) --workdir=/cwd --volume=$PWD:/cwd \ wxwidgets-windows cmake --build _build --target SimpleWindow
Check CMake output:
$ tree _build -L 1
_build
├── CMakeCache.txt
├── CMakeFiles
├── cmake_install.cmake
├── Makefile
└── SimpleWindow.exe
1 directory, 4 files
$ file _build/SimpleWindow.exe
_build/SimpleWindow.exe: PE32+ executable (GUI) x86-64, for MS Windows
$ du -h _build/SimpleWindow.exe
96M _build/SimpleWindow.exe
Run the application using Wine:
$ wine _build/SimpleWindow.exe
Screenshot:
Further Reading
- https://www.wxwidgets.org (Official Website)
- https://www.wxwidgets.org/about
- https://www.wxwidgets.org/about/licence/
- https://www.wxwidgets.org/about/history/
- Introduction to wxWidgets
- Note: Show the similarity between WxWidgets and MFC
- https://docs.wxwidgets.org/trunk/overview_install.html
- https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Downloading_and_installing_wxWidgets
- https://docs.wxwidgets.org/trunk/overview_install.html
- https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Cross-Compiling_Under_Linux
- https://wiki.codeblocks.org/index.php/Cross_Compiling_wxWidgets_Applications_on_Linux
- Moritzolch.com - A guide to set up wxWidgets with MinGW on Windows
- Using wxWidgets with MinGW and Code::Blocks
- https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Writing_Your_First_Application-Adding_A_Button
- Using wxWidgets under Windows
1.33 Loading DLLs - shared libraries at runtime
1.33.1 Example 1 - Basic Dynamic Loading DLL
This example demonstrates how to dynamic load functions from a shared library at runtime with WinAPIs Loadlibrary, GetProcAddress and FreeLibrary.
Source:
FIle: dynamic-loading.cpp
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------- #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <windows.h> int main(){ /** Reference: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/ie/ms775123(v=vs.94) Function Signature: HRESULT URLDownloadToFile( LPUNKNOWN pCaller, LPCTSTR szURL, LPCTSTR szFileName, _Reserved_ DWORD dwReserved, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK lpfnCB ); ---------------------------------------------- */ // Wide-unicode strings std::wstring fileURL = L"http://httpbin.org/image/jpeg"; std::wstring file1 = L"download-file1.jpeg"; std::wstring file2 = L"download-file2.jpeg"; // Wide unicode version for LoadLibrary API HMODULE hLib = ::LoadLibraryW(L"urlmon.dll"); if(hLib == nullptr){ std::cerr << " [ERROR] Error: failed to load shared library" << std::endl; // Early return on Error. return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::cerr << " [INFO] DLL Loaded OK" << std::endl; std::cout << "============ EXPERIMENT 1 ===================" << std::endl; // The function pointer must have the same // signature of the function to be dynamically loaded // // Note: Windows function pointer should include calling convention // If omitted, the default calling convention is __cdcel // Possible Calling Conventions: __cdcel, __stdcall, __fastcall and so on. //--------------------------- // C+11 type alias for function pointer using FunptrType = HRESULT (__cdecl *)(LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK); // Alternative 2 for type alias (C++98/03) typedef HRESULT (__cdecl * FunptrTypeTypedef)(LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK); FARPROC hFunc = ::GetProcAddress(hLib, "URLDownloadToFileW"); if(hFunc == nullptr){ std::cerr << " [Error] Failed to load function from DLL" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::cerr << " [INFO] Function loaded OK" << std::endl; // Functin Pointer FunptrType URLDownloadToFileFunPTR = reinterpret_cast<FunptrType>(hFunc); HRESULT result1 = URLDownloadToFileFunPTR(nullptr, fileURL.c_str(), file1.c_str(), 0, nullptr); if(SUCCEEDED(result1)) std::cerr << " [INFO] Download successful OK. " << std::endl; else std::cerr << " [ERROR] Download failure. " << std::endl; std::cout << "============ EXPERIMENT 2 ===================" << std::endl; // Same cast as reinterpret_cast void* hFunc2 = (void*) ::GetProcAddress(hLib, "URLDownloadToFileW"); // Omit error checking if(hFunct2 == nullptr){ ... } // Note: Calling convention __cdecl can be omitted using URLDownloadToFileW_t = auto __cdecl (LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK) -> HRESULT; // auto (LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK) -> HRESULT; auto DownloadFile = reinterpret_cast<URLDownloadToFileW_t*>(hFunc2); HRESULT hresult2 = DownloadFile(nullptr, fileURL.c_str(), file2.c_str(), 0, nullptr); if(SUCCEEDED(result1)) std::cerr << " [INFO] Download successful OK. " << std::endl; else std::cerr << " [ERROR] Download failure. " << std::endl; // WARNING: Code NOT Safe - prone to resource leaking // in case of exception or forget to call this function. ::FreeLibrary(hLib); std::cerr << " [INFO] Application ended gracefully. OK." << std::endl; return 0; }
Types of loading:
- Implicit loading (static loading) - the DLL is linked at compile-time and the application doesn't refer to the DLL file directly.
- Explicit loading (dynamic loading) - the DLL is linked at runtime or loaded at runtime and the application refer to the DLL file and its function explicitly using the WinAPIs - LoadLibrary, GetProcAddress and FreeLibrary.
This code loads the function URLDownloadToFile at runtime from the DLL (Dynamically Linked Library) or shared library urlmon.dll. This function is used to donwload the image file from the URL http://httpbin.org/image/jpeg as file1.jpeg and file2.jpeg.
Signature of URLDownloadToFileW (wide unicode version) of URLDownloadToFile.
HRESULT URLDownloadToFile( LPUNKNOWN pCaller, LPCTSTR szURL, LPCTSTR szFileName, _Reserved_ DWORD dwReserved, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK lpfnCB ); HRESULT URLDownloadToFileW( LPUNKNOWN pCaller, LPCWSTR szURL, LPCWSTR szFileName, _Reserved_ DWORD dwReserved, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK lpfnCB );
Compiling and running with MSVC:
$ cl.exe dynamic-linking1.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /Fe:out.exe && out.exe dynamic-linking1.cpp [INFO] DLL Loaded OK ============ EXPERIMENT 1 =================== [INFO] Function loaded OK [INFO] Download successful OK. ============ EXPERIMENT 2 =================== [INFO] Download successful OK. [INFO] Application ended gracefully. OK.
Compiling and running with Mingw/GCC (GNU C/C++ Compiler):
$ g++ dynamic-loading1.cpp -o out2.exe -std=c++1z && out2.exe [INFO] DLL Loaded OK ============ EXPERIMENT 1 =================== [INFO] Function loaded OK [INFO] Download successful OK. ============ EXPERIMENT 2 =================== [INFO] Download successful OK. [INFO] Application ended gracefully. OK.
Parts inside the main function
- Function parameters that will be used later.
// Wide-unicode strings std::wstring fileURL = L"http://httpbin.org/image/jpeg"; std::wstring file1 = L"download-file1.jpeg"; std::wstring file2 = L"download-file2.jpeg";
- Load shared library (aka module) urlmon.dll at runtime using LoadLibraryW API
and perform error checking and exiting the application on
error. The mentioned DLL is loaded into the current process address space.
- Note: If the application is 64 bits, the DLL must be compiled for 64 bits, otherwise it will not work. The same happens if the application is 32 bits.
- Signature: HMODULE LoadLibraryW (LPCWSTR lpLibFileName);
- The file urlmon.dll is at
C:\Windows\System32\urlmon.dll. - If the extension of the DLL is omitted, the function automatically appends .dll to the file name, therefore it is also possible to load the DLL using just "urlmon" instead of "urlmon.dll".
- If the DLL is provided without absolute path as
C:\Windows\System32\urlmon.dll, the DLL is searched in the following order:- Directory where is the underlying application
- System directory -
%SystemRoot%\system32orC:\Windows\System32\ - Current Working Directory (CWD) - Note: The process current working directory may not be the same as the application.
- Directories listed in the $PATH environment variable.
// Wide unicode version for LoadLibrary API HMODULE hLib = ::LoadLibraryW(L"urlmon.dll"); if(hLib == nullptr){ std::cerr << " [ERROR] Error: failed to load shared library" << std::endl; // Early return on Error. return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::cerr << " [INFO] DLL Loaded OK" << std::endl;
- Loading function - In order to load the function
URLDownloadToFileW, it is necessary to know: the function symbol
and its its exact type signature and calling convention. In
general, the symbol has the same name of the function to be
loaded. Windows Applications and DLLs of 32 bits supports the
calling conventions
__cdecl(default),__stdcalland__fastcall. Windows applications and DLLs of 64 bits have always the same calling conventions__cdecl. The default calling convention can be omitted in the function signature.
Function pointer type alias (FunptrType) with must type signature of the function URLDownloadToFileW:
// C+11 type alias for function pointer using FunptrType = HRESULT (__cdecl *)(LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK); // __cdecl can be omited // HRESULT (__cdecl *)(LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK); // Alternative 2 for type alias (C++98/03) typedef HRESULT (__cdecl * FunptrTypeTypedef)(LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK);
Function is loaded using the WinAPI GetProcAddress
- Signature: FARPROC GetProcAddress(HMODULE hModule, LPCSTR lpProcName);
FARPROC hFunc = ::GetProcAddress(hLib, "URLDownloadToFileW"); if(hFunc == nullptr){ std::cerr << " [Error] Failed to load function from DLL" << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::cerr << " [INFO] Function loaded OK" << std::endl;
The value hFunc must be casted to a function type before usage:
- Note: It is alos possible to use C-style casting. However, it is not encouraged as this type of casting is not explicit as reinterpret_cast which communicates the that operation is unsafe and that it can lead to undefined behavior.
// Functin Pointer FunptrType URLDownloadToFileFunPTR = reinterpret_cast<FunptrType>(hFunc);
- Perform experiment 1 - Use function pointer URLDownloadToFileFunPTR ,which points to the function URLDownloadToFileW, to perform a download of the image http://httpbin.org/image/jpeg and save it to file download-file1.jpeg.
HRESULT result1 = URLDownloadToFileFunPTR(nullptr, fileURL.c_str(), file1.c_str(), 0, nullptr); if(SUCCEEDED(result1)) std::cerr << " [INFO] Download successful OK. " << std::endl; else std::cerr << " [ERROR] Download failure. " << std::endl;
- Experiment 2 - This piece of code is similar to the previous
one. However, it uses a different syntax for the function pointer.
- Note: The function pointer DownloadFile points to the function URLDownloadToFileW.
std::cout << "============ EXPERIMENT 2 ===================" << std::endl; // Same cast as reinterpret_cast void* hFunc2 = (void*) ::GetProcAddress(hLib, "URLDownloadToFileW"); // Omit error checking if(hFunct2 == nullptr){ ... } // Note: Calling convention __cdecl can be omitted using URLDownloadToFileW_t = auto __cdecl (LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK) -> HRESULT; // auto (LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK) -> HRESULT; auto DownloadFile = reinterpret_cast<URLDownloadToFileW_t*>(hFunc2); HRESULT hresult2 = DownloadFile(nullptr, fileURL.c_str(), file2.c_str(), 0, nullptr); if(SUCCEEDED(result1)) std::cerr << " [INFO] Download successful OK. " << std::endl; else std::cerr << " [ERROR] Download failure. " << std::endl;
- Release acquired resource hLib. This operation is unsafe and prone to resource leaking, therefore the code would be safer and more robust if it used RAII (Resource Acquisition Is Initialization) idiom for releasing the resouce.
::FreeLibrary(hLib); std::cerr << " [INFO] Application ended gracefully. OK." << std::endl;
Show symbols (functions) exported by DLL urmon.dll
- Open the MSVC developer shell prompt and use the following commands:
# Print to console $ dumpbin /exports C:\Windows\System32\urlmon.dll # Or print to file redirecting the stdout to a file result.txt $ dumpbin /exports C:\Windows\System32\urlmon.dll > C:\Users\archbox\Desktop\result.txt
Command output:
$ dumpbin /exports C:\Windows\System32\urlmon.dll > C:\Users\archbox\Desktop\result.txt Microsoft (R) COFF/PE Dumper Version 14.12.25835.0 Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Dump of file C:\Windows\System32\urlmon.dll File Type: DLL Section contains the following exports for urlmon.dll 00000000 characteristics F6A98BC3 time date stamp 0.00 version 100 ordinal base 481 number of functions 132 number of names ordinal hint RVA name 121 0 000718E0 AsyncGetClassBits 122 1 000AE7A0 AsyncInstallDistributionUnit 123 2 000A0CD0 BindAsyncMoniker 124 3 000CF110 CAuthenticateHostUI_CreateInstance 125 4 000AF130 CDLGetLongPathNameA 126 5 000AF150 CDLGetLongPathNameW 127 6 00107B70 CORPolicyProvider 128 7 000AE830 CoGetClassObjectFromURL 129 8 000AED90 CoInstall 130 9 00035E90 CoInternetCanonicalizeIUri 131 A 00035FB0 CoInternetCombineIUri ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 227 71 000E48C0 URLDownloadA 228 72 000EDF10 URLDownloadToCacheFileA 229 73 000EE090 URLDownloadToCacheFileW 230 74 000EE200 URLDownloadToFileA 231 75 0006D300 URLDownloadToFileW 232 76 000E4920 URLDownloadW 233 77 000EE350 URLOpenBlockingStreamA 234 78 000EE430 URLOpenBlockingStreamW 235 79 000EE540 URLOpenPullStreamA 236 7A 000EE610 URLOpenPullStreamW 237 7B 000EE6E0 URLOpenStreamA ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Summary D000 .data 1000 .didat 1000 .isoapis F000 .pdata 3D000 .rdata 3000 .reloc 52000 .rsrc 117000 .text
Further Reading:
- WinAPIS: LoadLibraryW, GetProcAddress and FreeLibrary.
- https://github.com/numpy/numpy/wiki/windows-dll-notes
- The LoadLibrary Explorer
- Dynamic-Link Library Search Order
- Dynamic-Link Library Data
- Dynamic-Link Library Redirection
- Dynamic-Link Library Security
- 15.17. ctypes — A foreign function library for Python — Python 2.7.15 documentation
1.33.2 Example 2 - Dynamic loading with a class Wrapper
This code uses a class DLLoader to load a shared library hiding the complexity and implementation detail. It also uses RAII for ensuring that the resource is released.
Source:
Files
FIle: dymaic-loading2.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <windows.h> //========== File: DLLLoader.hpp =======// class DLLLoader { private: HMODULE m_hLib; std::string m_file; public: DLLLoader(const std::string& file); DLLLoader(const DLLLoader&) = delete; DLLLoader(DLLLoader&& rhs); ~DLLLoader(); auto operator=(const DLLLoader&) = delete; auto operator=(DLLLoader&& rhs); auto GetFile() const -> std::string; auto IsLoaded() const -> bool; operator bool() const; template<class FunctionSignature> auto GetFunction(const std::string& functionName ) const -> FunctionSignature* { if(m_hLib == nullptr){ return nullptr; } FARPROC hFunc = ::GetProcAddress(m_hLib, functionName.c_str()); if(hFunc == nullptr){ return nullptr; } return reinterpret_cast<FunctionSignature*>(hFunc); } }; //========== File: Main.cpp =======// int main() { // Wide-unicode strings std::wstring fileURL = L"http://httpbin.org/image/jpeg"; std::wstring file1 = L"download-file1.jpeg"; std::wstring file2 = L"download-file2.jpeg"; auto dll = DLLLoader("urlmon.dll"); if(!dll){ std::cerr << "[Error] failed to load DLL." << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::cerr << "[INFO] DLL loaded OK." << std::endl; // -----------------------------------------------------------------// std::cout << "===== Experiment 1 =========== " << std::endl; auto URLDownloadToFileW = dll.GetFunction<HRESULT (LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK)>("URLDownloadToFileW"); if(URLDownloadToFileW == nullptr){ std::cerr << "[Error] failed to load function. " << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::cerr << "[INFO] Function URLDownloadToFileW loaded OK. " << std::endl; HRESULT result1 = URLDownloadToFileW(nullptr, fileURL.c_str(), file1.c_str(), 0, nullptr); if(SUCCEEDED(result1)) std::cerr << " [INFO] Download successful OK. " << std::endl; else std::cerr << " [ERROR] Download failure. " << std::endl; // -----------------------------------------------------------------// std::cout << "===== Experiment 2 =========== " << std::endl; // Note: Calling convention __cdecl can be omitted using URLDownloadToFileW_t = HRESULT (*) (LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK); auto URLDownloadToFileW2 = dll.GetFunction<URLDownloadToFileW_t>("URLDownloadToFileW"); HRESULT result2 = URLDownloadToFileW(nullptr, fileURL.c_str(), file2.c_str(), 0, nullptr); if(SUCCEEDED(result2)) std::cerr << " [INFO] Download successful OK. " << std::endl; else std::cerr << " [ERROR] Download failure. " << std::endl; return 0; } ///==== Implementations - file: DLLoader.hpp =======// DLLLoader::DLLLoader(const std::string& file): m_file(file), m_hLib(::LoadLibraryA(file.c_str())) { } // Move CTOR DLLLoader::DLLLoader(DLLLoader&& rhs): m_hLib(std::move(rhs.m_hLib)), m_file(std::move(rhs.m_file)) { } // Move assignment operator auto DLLLoader::operator=(DLLLoader&& rhs) { std::swap(this->m_hLib, rhs.m_hLib); std::swap(this->m_file, rhs.m_file); } DLLLoader::~DLLLoader() { std::cerr << " [INFO] DLL handler released OK." << std::endl; if(m_hLib != nullptr) ::FreeLibrary(m_hLib); } auto DLLLoader::GetFile() const -> std::string { return m_file; } auto DLLLoader::IsLoaded() const -> bool { return m_hLib == nullptr; } DLLLoader::operator bool() const { return m_hLib != nullptr; }
Build and run with MSVC
$ cl.exe dynamic-loading2.cpp /EHsc /Zi /nologo /Fe:out.exe && out.exe dynamic-loading2.cpp [INFO] DLL loaded OK. ===== Experiment 1 =========== [INFO] Function URLDownloadToFileW loaded OK. [INFO] Download successful OK. ===== Experiment 2 =========== [INFO] Download successful OK. [INFO] DLL handler released OK.
Build and run with Mingw/GCC
$ g++ dynamic-loading2.cpp -std=c++14 -g -o out-gcc.exe && out-gcc.exe
[INFO] DLL loaded OK.
===== Experiment 1 ===========
[INFO] Function URLDownloadToFileW loaded OK.
[INFO] Download successful OK.
===== Experiment 2 ===========
[INFO] Download successful OK.
[INFO] DLL handler released OK.
Parts
Main function - Load Library:
// Wide-unicode strings std::wstring fileURL = L"http://httpbin.org/image/jpeg"; std::wstring file1 = L"download-file1.jpeg"; std::wstring file2 = L"download-file2.jpeg"; auto dll = DLLLoader("urlmon.dll"); if(!dll){ std::cerr << "[Error] failed to load DLL." << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::cerr << "[INFO] DLL loaded OK." << std::endl;
Main function - Experiment 1:
std::cout << "===== Experiment 1 =========== " << std::endl; auto URLDownloadToFileW = dll.GetFunction<HRESULT (LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK)>("URLDownloadToFileW"); if(URLDownloadToFileW == nullptr){ std::cerr << "[Error] failed to load function. " << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } std::cerr << "[INFO] Function URLDownloadToFileW loaded OK. " << std::endl; HRESULT result1 = URLDownloadToFileW(nullptr, fileURL.c_str(), file1.c_str(), 0, nullptr); if(SUCCEEDED(result1)) std::cerr << " [INFO] Download successful OK. " << std::endl; else std::cerr << " [ERROR] Download failure. " << std::endl;
Main function - Experiment 2:
std::cout << "===== Experiment 2 =========== " << std::endl; // Note: Calling convention __cdecl can be omitted using URLDownloadToFileW_t = HRESULT (*) (LPUNKNOWN, LPCWSTR, LPCWSTR, DWORD, LPBINDSTATUSCALLBACK); auto URLDownloadToFileW2 = dll.GetFunction<URLDownloadToFileW_t>("URLDownloadToFileW"); HRESULT result2 = URLDownloadToFileW(nullptr, fileURL.c_str(), file2.c_str(), 0, nullptr); if(SUCCEEDED(result2)) std::cerr << " [INFO] Download successful OK. " << std::endl; else std::cerr << " [ERROR] Download failure. " << std::endl; return 0;
Class DLLoader:
//========== File: DLLLoader.hpp =======// class DLLLoader { private: HMODULE m_hLib; std::string m_file; public: DLLLoader(const std::string& file); DLLLoader(const DLLLoader&) = delete; DLLLoader(DLLLoader&& rhs); ~DLLLoader(); auto operator=(const DLLLoader&) = delete; auto operator=(DLLLoader&& rhs); auto GetFile() const -> std::string; auto IsLoaded() const -> bool; operator bool() const; template<class FunctionSignature> auto GetFunction(const std::string& functionName ) const -> FunctionSignature* { if(m_hLib == nullptr) return nullptr; FARPROC hFunc = ::GetProcAddress(m_hLib, functionName.c_str()); if(hFunc == nullptr) return nullptr; return reinterpret_cast<FunctionSignature*>(hFunc); } };
Member functions of class DLLoader:
///==== Implementations - file: DLLoader.hpp =======// DLLLoader::DLLLoader(const std::string& file): m_file(file), m_hLib(::LoadLibraryA(file.c_str())) { } // Move CTOR DLLLoader::DLLLoader(DLLLoader&& rhs): m_hLib(std::move(rhs.m_hLib)), m_file(std::move(rhs.m_file)) { } auto DLLLoader::operator=(DLLLoader&& rhs) { std::swap(this->m_hLib, rhs.m_hLib); std::swap(this->m_file, rhs.m_file); } DLLLoader::~DLLLoader() { std::cerr << " [INFO] DLL handler released OK." << std::endl; if(m_hLib != nullptr) ::FreeLibrary(m_hLib); } auto DLLLoader::GetFile() const -> std::string { return m_file; } auto DLLLoader::IsLoaded() const -> bool { return m_hLib == nullptr; } DLLLoader::operator bool() const { return m_hLib != nullptr; }
1.34 Runnable Shared Libraries DLLs - rundll32
1.34.1 Overview
Windows shared libraries DLLs, such as control panel applets, can be executed in a similar way to executable if they contain entry point functions matching the type signature expected by rundll32.exe application.
Some Runnable DLLs
File Explorer Options:
- The following command calls the Options_RunDLL entry point of the DLL shell32.dll which opens a window where is possible to set file explorer options.
$ RunDll32.exe shell32.dll,Options_RunDLL 0
Environment variables control panel applet:
- It opens a Window where is possible to set and add news environment variables.
$ rundll32.exe sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariables
Check DLL locations:
$ where shell32.dll C:\Windows\System32\shell32.dll $ where sysdm.cpl C:\Windows\System32\sysdm.cpl $ file C:\Windows\System32\sysdm.cpl C:\Windows\System32\sysdm.cpl: PE32+ executable (DLL) (GUI) x86-64, for MS Windows
1.34.2 Creating a runnable DLL
File: runnable.cpp
Sample runnable DLL with two entry points.
#include <windows.h> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <sstream> #define DLL_EXPORT extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) #define DLL_EXPORT_STDCALL extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) __stdcall DLL_EXPORT void entryPoint1(HWND hwn, HINSTANCE hinst, LPSTR cmdLine, int nCmdShow) { std::stringstream ss; ss << __FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__ << ":" << "Entry point 1 running!"; // Note: Does not work because the DLL is loaded by a program built for // the window subsystem. std::cout << ss.str() << std::endl; ss << " cmdLine = " << cmdLine; //Print logging to shared memory OutputDebugStringA(ss.str().c_str()); // Show graphical messagebox MessageBoxA(NULL, ss.str().c_str(), "EntryPoint1-DLL", 0); } DLL_EXPORT void entryPoint2(HWND hwn, HINSTANCE hinst, LPSTR cmdLine, int nCmdShow) { // Show graphical messagebox MessageBoxA(nullptr, "Launching Notepad.exe", "EntryPoint2-DLL", 0); // Launch Notepad.exe ::system("notepad.exe"); } /** DLL Entry Point on Windows, similar to main() function */ DLL_EXPORT BOOL APIENTRY DllMain (HINSTANCE hInst, DWORD reason, LPVOID lpReserved) { std::stringstream ss; ss << __FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__ << ": => DLL Loaded OK." << std::endl; OutputDebugString(ss.str().c_str()); ss.clear(); switch (reason) { case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH: ss << __FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__ << ": => DLL attached." << std::endl; OutputDebugString(ss.str().c_str()); ss.clear(); break; case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH: ss << __FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__ << ": => DLL detached." << std::endl; OutputDebugString(ss.str().c_str()); ss.clear(); break; case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH: ss << __FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__ << ": => DLL thread attached." << std::endl; OutputDebugString(ss.str().c_str()); ss.clear(); break; case DLL_THREAD_DETACH: ss << __FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__ << ": => DLL thread detached." << std::endl; OutputDebugString(ss.str().c_str()); ss.clear(); break; } return TRUE; }
File: CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.9) project(RunnableDLL) #----------------------------------------------# set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17) set(CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON) set(CMAKE_CXX_EXTENSIONS OFF) #=========== CMake Functions ===================# # Copy target file to current directory whenerver it is rebuilt function(copy_after_build TARGET_NAME ) # Note: CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR is the directory where is this # CMakeLists.txt file. set(DESTDIR ${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/bin/) file(MAKE_DIRECTORY ${DESTDIR}) # Copy binary file to <CMakeLists.txt didctory>./bin # after target is compiled. add_custom_command(TARGET ${TARGET_NAME} POST_BUILD COMMAND ${CMAKE_COMMAND} -E copy $<TARGET_FILE:${TARGET_NAME}> ${DESTDIR} ) endfunction() #========== Targets Configurations ============# # Generates DLL named: 'applet.cpl' add_library(runnable SHARED runnable.cpp) # Change the DLL name from 'runnable.dll' to 'applet.cpl' set_target_properties( runnable PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME "applet" SUFFIX ".cpl" ) copy_after_build(runnable)
Building
Building:
$ cd <PROJECT-ROOT-DIRECTORY> # Configure $ cmake -H. -B_build -G"Visual Studio 15 2017 Win64" # Compile $ cmake --build _build --target all
Check building system output:
- Note: The tools 'ls' and 'file' are not native to Windows, they come bundled with GIT.
$ ls bin applet.cpl* $ file bin\applet.cpl bin\applet.cpl: PE32+ executable (DLL) (console) x86-64, for MS Windows
Running
Check where is rundll32:
$ where rundll32
C:\Windows\System32\rundll32.exe
Execute entryPoint1 function
- As the DLL applet.cpl is loaded by an executable compiled to the Window-subsystem, the cout output is not displayed in the terminal. A workaround to this issue is logging to a file; redirect std::cout to a file output stream or using the OutputDebugString API and DebugView application from SysInternals.
$ rundll32 bin\applet.cpl,entryPoint1 arg0 arg1 arg2
DebugView Output:
[5276] C:\Users\dummy-user\Desktop\Runnable-DLL\runnable.cpp:41: => DLL Loaded OK. [5276] C:\Users\dummy-user\Desktop\Runnable-DLL\runnable.cpp:41: => DLL Loaded OK. [5276] C:\Users\dummy-user\Desktop\Runnable-DLL\runnable.cpp:47: => DLL attached. [5276] C:\Users\dummy-user\Desktop\Runnable-DLL\runnable.cpp:41: => DLL Loaded OK. [5276] C:\Users\dummy-user\Desktop\Runnable-DLL\runnable.cpp:41: => DLL Loaded OK. [5276] C:\Users\dummy-user\Desktop\Runnable-DLL\runnable.cpp:57: => DLL thread attached. [5276] C:\Users\dummy-user\Desktop\Runnable-DLL\runnable.cpp:13:Entry point 1 running! cmdLine = arg0 arg1 arg2 [5276] C:\Users\dummy-user\Desktop\Runnable-DLL\runnable.cpp:41: => DLL Loaded OK. [5276] C:\Users\dummy-user\Desktop\Runnable-DLL\runnable.cpp:41: => DLL Loaded OK. [5276] C:\Users\dummy-user\Desktop\Runnable-DLL\runnable.cpp:52: => DLL detached.
Execute entryPoint2 function
- The entryPoint2 launches notepad.exe application.
$ rundll32 bin\applet.cpl,entryPoint2
1.34.3 Creating a DLL runner
The following code is a DLL runner, akin to rundll32.exe built-in application. It can run any DLL containing entry rundll32 entry points or the functions with the same type signature as Rundll32EntryPoint_t.
File: dll-runner.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cassert> #include <windows.h> #define DLL_EXPORT extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) #define DLL_EXPORT_STDCALL extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) __stdcall using Rundll32EntryPoint_t = void (*) ( HWND hwn , HINSTANCE hinst , LPSTR cmdLine , int nCmdShow); int main(int argc, const char* argv[]) { if(argc < 4) { std::cerr << " Usage: " << argv[0] << " <DLL-FILE> <ENTRY-POINT> <ENTRY_COMMAND_LINE> " << std::endl; std::cerr << " [ERROR] Invalid arguments. Abort." << std::endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } /// Shared library that will be executed std::string dll_file = argv[1]; /// Entry point that will be called std::string entry_point = argv[2]; /// Command line arguments to the called entry point std::string command_line = argv[3]; // Wide unicode version for LoadLibrary API HMODULE hLib = ::LoadLibraryA(dll_file.c_str()); assert(hLib != nullptr); FARPROC hFunc = ::GetProcAddress(hLib, entry_point.c_str()); assert(hFunc != nullptr); //--- Execute Entry Point ----// HINSTANCE hInstance = GetModuleHandle(NULL); auto entry_point_handler = reinterpret_cast<Rundll32EntryPoint_t>(hFunc); entry_point_handler(nullptr, hInstance, command_line.data(), 1); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Testing
Show usage:
$ bin\dll-runner.exe Usage: bin\dll-runner.exe <DLL-FILE> <ENTRY-POINT> <ENTRY_COMMAND_LINE> [ERROR] Invalid arguments. Abort.
Execute EditEnvironmentvariables entry point of sysdm.cpl DLL (Control Panel Applet).
# $ RunDll32.exe sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariables $ dll-runner.exe sysdm.cpl EditEnvironmentVariables "" $ dll-runner.exe C:\\Windows\system32\sysdm.cpl EditEnvironmentVariables ""
Execute Options_RunDLL entry point of shell32.dll which opens File Explorer Options window.
# $ RunDll32.exe shell32.dll,Options_RunDLL 0 $ dll-runner.exe shell32.dll Options_RunDLL "0" $ dll-runner.exe C:\\Windows\system32\shell32.dll Options_RunDLL "0"
1.35 Read metadata from Windows PE Portable Executable files
PE (Portable Executable), which main variants are PE-32 and PE-64, is the binary file format used by Windows executable (.exe files), shared libraries (.dll files); device drivers (.sys files) and also Windows kernel.
More infor about PE32 files:
- Five PE Analysis Tools Worth Looking At
- http://www.pelib.com/resources/luevel.txt
- https://wiki.osdev.org/PE
- PE Format - Microsft Docs
- Wikibooks - x86 Disassembly/Windows Executable Files
- Portable Executable
- The Portable Executable File Format from Top to Bottom
- PE File Format Offsets - by Sunshine
- PE-Portable-executable - aldeid
- Portable Executable File Format - blog kowalczyk
- Question - Pulling PE32 header info
- Tiny PE - Creating the smallest possible PE executable
- Reverse Engineering III: PE Format
- Undestanding PE Structure - Part 2
- https://formats.kaitai.io/uefi_te/index.html
Project Files
GIST:
File: CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.9) project(pe-metadata) #========== Global Configurations =============# #----------------------------------------------# set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17) set(CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON) add_executable(pe-info pe-info.cpp pe_data.hpp)
File: pe_data.hpp
#ifndef _PE_DATA_ #define _PE_DATA_ //#include <windows.h> //#include <winnt.h> constexpr size_t IMAGE_SIZEOF_SHORT_NAME = 8; constexpr size_t IMAGE_NUMBEROF_DIRECTORY_ENTRIES = 16; // using LONG = long; using LONG = std::int32_t; using WORD = std::uint16_t; // unsigned short; using DWORD = std::uint32_t; // unsigned long; using BYTE = std::uint8_t; //unsigned char; using ULONGLONG = std::uint64_t; // unsigned long long // Source: <winttt.h> => Original: typedef struct _IMAGE_DOS_HEADER struct IMAGE_DOS_HEADER { WORD e_magic; WORD e_cblp; WORD e_cp; WORD e_crlc; WORD e_cparhdr; WORD e_minalloc; WORD e_maxalloc; WORD e_ss; WORD e_sp; WORD e_csum; WORD e_ip; WORD e_cs; WORD e_lfarlc; WORD e_ovno; WORD e_res[4]; WORD e_oemid; WORD e_oeminfo; WORD e_res2[10]; // Offset to the PE header from the beginning of the file. LONG e_lfanew; }; struct PE_HEADER { DWORD Signature; WORD Machine; WORD NumberOfSections; DWORD TimeDateStamp; DWORD PointerToSymbolTable; DWORD NumberOfSymbols; WORD SizeOfOptionalHeader; WORD Characteristics; }; struct PE_IMAGE_DATA_DIRECTORY { DWORD VirtualAddress; DWORD Size; }; struct PE_OPTIONAL_HEADER64 { WORD Magic; BYTE MajorLinkerVersion; BYTE MinorLinkerVersion; DWORD SizeOfCode; DWORD SizeOfInitializedData; DWORD SizeOfUninitializedData; DWORD AddressOfEntryPoint; DWORD BaseOfCode; ULONGLONG ImageBase; DWORD SectionAlignment; DWORD FileAlignment; WORD MajorOperatingSystemVersion; WORD MinorOperatingSystemVersion; WORD MajorImageVersion; WORD MinorImageVersion; WORD MajorSubsystemVersion; WORD MinorSubsystemVersion; DWORD Win32VersionValue; DWORD SizeOfImage; DWORD SizeOfHeaders; DWORD CheckSum; WORD Subsystem; WORD DllCharacteristics; ULONGLONG SizeOfStackReserve; ULONGLONG SizeOfStackCommit; ULONGLONG SizeOfHeapReserve; ULONGLONG SizeOfHeapCommit; DWORD LoaderFlags; DWORD NumberOfRvaAndSizes; PE_IMAGE_DATA_DIRECTORY DataDirectory[IMAGE_NUMBEROF_DIRECTORY_ENTRIES]; }; // source: winnt.h header struct PE_SECTION_HEADER { BYTE Name[IMAGE_SIZEOF_SHORT_NAME]; union { DWORD PhysicalAddress; DWORD VirtualSize; } Misc; DWORD VirtualAddress; DWORD SizeOfRawData; DWORD PointerToRawData; DWORD PointerToRelocations; DWORD PointerToLinenumbers; WORD NumberOfRelocations; WORD NumberOfLinenumbers; DWORD Characteristics; }; #endif
File: pe-info.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstdint> #include <fstream> #include <cassert> #include <optional> // C++17 #include <algorithm> #include "pe_data.hpp" /** Read binary data from a input stream at a given offset. * * @param tref Reference to type that will be read from input stream * @param ifs Input stream * @param offset Offset from the beggining of the input stream or file. */ template<typename T> void read_at( T& tref , std::istream& ifs , std::optional<size_t> offset = {}) { if(offset) ifs.seekg(offset.value()); ifs.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&tref), sizeof (T)); } int main(int argc, char** argv) { if(argc < 2) { std::cout << "Usage: $ pe-info <FILE> " << "\n"; return EXIT_FAILURE; } auto file_path = std::string{ argv[1] } ; std::cout << " File: " << file_path << "\n"; auto ifs = std::ifstream (file_path, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary ); assert( ifs.good() ); IMAGE_DOS_HEADER dos_header; // Position cursor at beggining of file read_at(dos_header, ifs, 0x00 ); assert( dos_header.e_magic == 0x5A4D ); // Offset of PE-Header from the beggining of the file auto e_lfanew = dos_header.e_lfanew; char magic[3] = { dos_header.e_magic & 0xFF // Fist byte , (dos_header.e_magic >> 8) & 0xff // Second byte , 0x00 // Null character }; std::printf("\n ------ DOS HEADER ---------------\n"); std::printf(" [DOS_HEADER] MAGIC NUMBER = 0x%X (hex) \n", dos_header.e_magic); std::printf(" [DOS_HEADER] MAGIC NUMBER = %s (str) \n", magic); std::printf(" [DOS_HEADER] e_lfanew = 0x%X \n", e_lfanew); //--------------------------------------------------// // PE HEADER // //--------------------------------------------------// PE_HEADER pe_header; read_at(pe_header, ifs, dos_header.e_lfanew); //The signature should always have this value (0x4550) assert( pe_header.Signature == 0x4550 ); std::printf("\n -------- PE - Header ----------------------\n\n"); std::printf(" Note: if machine is 0x8664 => the processor is AMD-Intel x86-64 \n"); std::printf("\n"); std::printf(" Signature = 0x%X \n", pe_header.Signature); std::printf(" Machine = 0x%X \n", pe_header.Machine); std::printf(" Number of sections = %d \n", pe_header.NumberOfSections); //--------------------------------------------------// // PE OPTIONAL HEADER // //--------------------------------------------------// PE_OPTIONAL_HEADER64 pe_opt; read_at(pe_opt, ifs); std::string subsystem = [&pe_opt]() { if(pe_opt.Subsystem == 1) return "No subsystem required (device drivers)"; if(pe_opt.Subsystem == 2) return "gui / graphical"; if(pe_opt.Subsystem == 3) return "console"; if(pe_opt.Subsystem == 9) return "Windows CE system"; if(pe_opt.Subsystem == 10) return "EFI - Extensible Firmware Interfgace"; if(pe_opt.Subsystem == 16) return "Windows Boot"; return "Unknown"; }(); std::printf("\n -------- PE Optional Header ----------------------\n\n"); std::printf(" Magic = 0x%X \n", pe_opt.Magic); std::printf(" Subsystem = 0x%X \n", pe_opt.Subsystem); std::printf(" Subsystem = %s \n", subsystem.c_str()); std::printf(" Address of Entrypoint = 0x%X \n", pe_opt.AddressOfEntryPoint); std::printf(" Major link version = 0x%X \n", pe_opt.MajorLinkerVersion); std::printf(" Size of code = 0x%X \n", pe_opt.SizeOfCode); std::printf(" Major Operating System Version = 0x%X \n", pe_opt.MajorOperatingSystemVersion); std::printf(" Minor Operating System Version = 0x%X \n", pe_opt.MinorOperatingSystemVersion); //--------------------------------------------------// // DATA SECTIONS // //--------------------------------------------------// std::printf("\n -------- PE Sections ---------------\n\n"); PE_SECTION_HEADER sec; for(int i = 0; i < pe_header.NumberOfSections; i++) { read_at(sec, ifs); std::printf(" [%d] section name = %s \n", i, sec.Name); std::printf(" => Virtual Address = 0x%X \n", sec.VirtualAddress); std::printf(" => Raw Address = 0x%X \n", sec.PointerToRawData); std::printf("\n"); } return 0; }
Building
- This proof-of-concept application is cross-platform and does not depend on the Windows API, therefore, it can also be built on Linux or any Unix-like operating system.
Build on Windows
$ git clone https://gist.github.com/f5edeaa4d929f5acf258d71caf6915cd pe-info && cd pe-info $ cmake -H. -B_build -G "Visual Studio 16 2019" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug $ cmake --build _build --target all
Build on Linux
$ git clone https://gist.github.com/f5edeaa4d929f5acf258d71caf6915cd pe-info && cd pe-info
$ cmake -H. -B_build_linux -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug
$ cmake --build _build_linux --target
Running
Note: the following results can be checked with the application CFF Explorer which allows viewing PE32 files in intuitive and lightweight GUI.
Inspect: ipconfig.exe
$ pe-info.exe C:\Windows\System32\ipconfig.exe
File: C:\Windows\System32\ipconfig.exe
------ DOS HEADER ---------------
[DOS_HEADER] MAGIC NUMBER = 0x5A4D (hex)
[DOS_HEADER] MAGIC NUMBER = MZ (str)
[DOS_HEADER] e_lfanew = 0xE8
-------- PE - Header ----------------------
Note: if machine is 0x8664 => the processor is AMD-Intel x86-64
Signature = 0x4550
Machine = 0x8664
Number of sections = 6
-------- PE Optional Header ----------------------
Magic = 0x20B
Subsystem = 0x3
Subsystem = console
Address of Entrypoint = 0x4EB0
Major link version = 0xE
Size of code = 0x4800
Major Operating System Version = 0xA
Minor Operating System Version = 0x0
-------- PE Sections ---------------
[0] section name = .text
=> Virtual Address = 0x1000
=> Raw Address = 0x400
[1] section name = .rdata
=> Virtual Address = 0x6000
=> Raw Address = 0x4C00
[2] section name = .data
=> Virtual Address = 0x9000
=> Raw Address = 0x7600
[3] section name = .pdata
=> Virtual Address = 0xA000
=> Raw Address = 0x7800
[4] section name = .rsrc
=> Virtual Address = 0xB000
=> Raw Address = 0x7C00
[5] section name = .reloc
=> Virtual Address = 0xC000
=> Raw Address = 0x8600
Inspect: notepad.exe
$ pe-info.exe C:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe File: C:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe ------ DOS HEADER --------------- [DOS_HEADER] MAGIC NUMBER = 0x5A4D (hex) [DOS_HEADER] MAGIC NUMBER = MZ (str) [DOS_HEADER] e_lfanew = 0xF8 -------- PE - Header ---------------------- Note: if machine is 0x8664 => the processor is AMD-Intel x86-64 Signature = 0x4550 Machine = 0x8664 Number of sections = 7 -------- PE Optional Header ---------------------- Magic = 0x20B Subsystem = 0x2 Subsystem = gui / graphical Address of Entrypoint = 0x20110 Major link version = 0xE Size of code = 0x20600 Major Operating System Version = 0xA Minor Operating System Version = 0x0 -------- PE Sections --------------- [0] section name = .text => Virtual Address = 0x1000 => Raw Address = 0x400 [1] section name = .rdata => Virtual Address = 0x22000 => Raw Address = 0x20A00 [2] section name = .data => Virtual Address = 0x2B000 => Raw Address = 0x29600 [3] section name = .pdata => Virtual Address = 0x2E000 => Raw Address = 0x2A200 [4] section name = .didat => Virtual Address = 0x2F000 => Raw Address = 0x2B200 [5] section name = .rsrc => Virtual Address = 0x30000 => Raw Address = 0x2B400 [6] section name = .reloc => Virtual Address = 0x31000 => Raw Address = 0x2C000
1.36 Install Development Tools and Compilers
1.36.1 C++ Compilers
- Install GCC/Mingw + a couple of GNU tools
Migw - gcc/g++ GNU C/C++ Compiler ported for Windows - mingw
Tools:
- gcc => GNU C compiler
- g++ => GNU C++ compiler
- gfortran => GNU Fortran Compiler
$ choco install -f mingw
Note the tools are installed at:
C:\tools\mingw64\bin\Check installed tools:
λ dir C:\tools\mingw64\bin Volume in drive C has no label. Volume Serial Number is CEFD-3D70 Directory of C:\tools\mingw64\bin 12/28/2015 08:49 PM <DIR> . 12/28/2015 08:49 PM <DIR> .. 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,003,008 addr2line.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,029,120 ar.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,781,248 as.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,812,480 c++.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,001,472 c++filt.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,810,944 cpp.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,061,888 dlltool.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 55,296 dllwrap.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 3,037,696 dwp.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 41,984 elfedit.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,812,480 g++.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 62,464 gcc-ar.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 61,952 gcc-nm.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 61,952 gcc-ranlib.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,809,920 gcc.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,391,616 gcov-tool.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,409,536 gcov.exe 12/28/2015 08:47 PM 58,333 gdb.exe 12/28/2015 08:47 PM 7,786,103 gdborig.exe 12/28/2015 08:47 PM 412,003 gdbserver.exe 12/28/2015 07:34 PM 57,856 gendef.exe 12/28/2015 07:34 PM 75,264 genidl.exe 12/28/2015 07:34 PM 31,232 genpeimg.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,811,968 gfortran.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,069,568 gprof.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,419,264 ld.bfd.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,419,264 ld.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 4,806,144 ld.gold.exe 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 37,888 libatomic-1.dll 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 82,944 libgcc_s_seh-1.dll 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 1,293,312 libgfortran-3.dll 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 112,640 libgomp-1.dll 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 17,920 libgomp-plugin-host_nonshm-1.dll 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 333,824 libquadmath-0.dll 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 19,968 libssp-0.dll 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 1,424,896 libstdc++-6.dll 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 16,384 libvtv-0.dll 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 16,384 libvtv_stubs-0.dll 12/28/2015 07:33 PM 83,456 libwinpthread-1.dll 12/28/2015 08:49 PM 219,648 mingw32-make.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,013,760 nm.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,171,456 objcopy.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 2,101,760 objdump.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,029,120 ranlib.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 490,496 readelf.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,004,032 size.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,003,520 strings.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,171,456 strip.exe 12/28/2015 07:35 PM 437,760 widl.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,027,072 windmc.exe 12/28/2015 05:51 PM 1,115,648 windres.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,812,480 x86_64-w64-mingw32-c++.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,812,480 x86_64-w64-mingw32-g++.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,809,920 x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc-5.3.0.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 62,464 x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc-ar.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 61,952 x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc-nm.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 61,952 x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc-ranlib.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,809,920 x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc.exe 12/28/2015 07:32 PM 1,811,968 x86_64-w64-mingw32-gfortran.exe 59 File(s) 62,660,535 bytes 2 Dir(s) 19,433,713,664 bytes freeSee:
- Install Visual Studio + Microsft MSVC C++ Compiler
Installing Visual Studio building tools directly is hassle as Microsoft doesn't provide an easy and quick way to install it as Linux development tools which can be quick installed by using the command line and trusted repositories. However chocolately package manager provides a Linux-like solution to install those development tools in an automatic and seamlessly way.
Visual Studio Build Tools 2015 - Visual C++ Build Tools 2015 14.0.25420.1
$ choco install visualcppbuildtools
Visual C++ 2017 - Visual Studio 2017 Build Tools 15.2.26430.20170650
$ choco install hoco install visualstudio2017buildtools
1.36.2 IDEs and Text Editors
- Install Visual Studio Code
Package: https://chocolatey.org/packages/vscode
$ choco install -y vscode
More:
- Code Runner - Visual Studio Marketplace - Compile and run single file. However, it is not so fast and flexible as Emacs' M-x compile.
- Building your C++ application with Visual Studio Code | Visual C++ Team Blog
- Install Codeblocks
Package: https://chocolatey.org/packages/codeblocks
$ choco install -y codeblocks
- Install QTCreator Standalone
Install QTCreator quasi-IDE. This 'IDE' can work with CMake projects and provides code completion on the fly, without any configuration.
$ choco install -y qtcreator
1.36.3 Essential Windows Instrospection and Debugging Tools
- Install SysInternals
SysInterals - https://chocolatey.org/packages/sysinternals
$ choco install sysinternals
Process Explorer - https://chocolatey.org/packages/procexp
$ choco install procexp
- Install CMDER Terminal Emulator
CMDER Is decent ANSI/VT100 compliant terminal emulator which supports ANI Escape sequences, ANSI colors and Emacs Keybindigns used on bash.
$ choco install cmder
- COM, OLE and RPC Views
- Oleview.exe
- Oleview.exe => Tool for viewing system COM Components. It comes with Visual studio tools. It can be launched from development prompt by typing oleview.exe
# Tested for MSVC - 2017 tools: C:\Users\archbox > where oleview C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.17763.0\x64\oleview.exe
For MSVC - 2017, it can be launched directly by running oleview.exe with absolute path:
Windows Key + R + "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.17763.0\x64\oleview.exe"
- RPCView
- "A free and powerful tool to explore and decompile all RPC functionalities present on a Microsoft system."
- http://rpcview.org/
- API Monitor - Monitor WinAPI and system calls
"Monitor is a free software that lets you monitor and control API calls made by applications and services. Its a powerful tool for seeing how applications and services work or for tracking down problems that you have in your own applications."
- Oleview.exe
1.36.4 Other Tools
- Install JOM - NMake Clone
JOM is a NMake clone created by the QT company which allows faster and parallel building:
$ choco install jom
- Install IDA Free Disassembler
IDA - Free - Famous Disassembler - https://chocolatey.org/packages/ida-free
$ choco install ida-free
1.37 WINAPI Map
1.37.1 Misc.
Source Codes:
- Repository: https://github.com/Microsoft/Windows-classic-samples
- Windows Registry - RegExplorer.c
- Windows Service - Service.c
- Repository: https://github.com/strobejb/winspy/ (Winspy++ Tool) for inspecting Windows Messages.
General:
- https://www.pinvoke.net/
- Note: Lists of Windows API functions grouped by system DLLs. It has better discoverability and usability than MSDN docs.
- kernel32.dll
- advapi32.dll
- wininet.dll - High level functions for Http and Ftp protocol.
- Win32 Structured Exception Handler
- Calling WinRT Components from a Win32 process via the Desktop Bridge
1.37.2 Header Files
1.37.3 Common HRESULT values
Reference: Common HRESULT Values - Windows applications | Microsoft Docs
| Name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| S_OK | Operation successful | 0x00000000 |
| E_ABORT | Operation aborted | 0x80004004 |
| E_ACCESSDENIED | General access denied error | 0x80070005 |
| E_FAIL | Unspecified failure | 0x80004005 |
| E_HANDLE | Handle that is not valid | 0x80070006 |
| E_INVALIDARG | One or more arguments are not valid | 0x80070057 |
| E_NOINTERFACE | No such interface supported | 0x80004002 |
| E_NOTIMPL | Not implemented | 0x80004001 |
| E_OUTOFMEMORY | Failed to allocate necessary memory | 0x8007000E |
| E_POINTER | Pointer that is not valid | 0x80004003 |
| E_UNEXPECTED | Unexpected failure | 0x8000FFFF |
1.37.4 Typedefs
WINAPI (several headers)
- Macro used fro main function entry point.
#define WINAPI __stdcall
CALLBACK macro used for Window procedure callback.
#define CALLBACK __stdcall
Boolean (WinBase.h)
#define FALSE 0 #define TRUE 1
Handle types - (opaque pointers) - (WinBase.h)
typedef void* HANDLE; typedef void* HMODULE; typedef void* HINSTANCE; typedef void* HTASK; typedef void* HKEY; typedef void* HDESK; typedef void* HMF; typedef void* HEMF; typedef void* HPEN; typedef void* HRSRC; typedef void* HSTR; typedef void* HWINSTA; typedef void* HKL; typedef void* HGDIOBJ; typedef HANDLE HDWP; typedef HANDLE* LPHANDLE;
Graphical Hadles - used by GUI functions. (WinBase.h)
typedef void* HWND; typedef void* HMENU; typedef void* HACCEL; typedef void* HBRUSH; typedef void* HFONT; typedef void* HDC; typedef void* HICON; typedef void* HRGN; typedef void* HMONITOR;
HRESULT macros and definitions (winerror.h)
#define SUCCEEDED(hr) (((HRESULT)(hr)) >= 0) #define FAILED(hr) (((HRESULT)(hr)) < 0) #define HRESULT_CODE(hr) ((hr) & 0xFFFF) #define HRESULT_FACILITY(hr) (((hr) >> 16) & 0x1fff) #define HRESULT_SEVERITY(hr) (((hr) >> 31) & 0x1) // Create an HRESULT value from component pieces #define MAKE_HRESULT(sev,fac,code) \ ((HRESULT) (((unsigned long)(sev)<<31) | ((unsigned long)(fac)<<16) | ((unsigned long)(code))) ) #define _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(_sc) _sc #define _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(_sc) ((HRESULT)_sc) #define E_UNEXPECTED _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x8000FFFFL) #define E_NOTIMPL _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80004001L) #define E_OUTOFMEMORY _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x8007000EL) #define E_INVALIDARG _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80070057L) #define E_NOINTERFACE _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80004002L) #define E_POINTER _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80004003L) #define E_HANDLE _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80070006L) #define E_ABORT _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80004004L) #define E_FAIL _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80004005L) #define E_ACCESSDENIED _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80070005L) #define E_NOTIMPL _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80000001L) #define E_OUTOFMEMORY _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80000002L) #define E_INVALIDARG _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80000003L) #define E_NOINTERFACE _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80000004L) #define E_POINTER _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80000005L) #define E_HANDLE _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80000006L) #define E_ABORT _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80000007L) #define E_FAIL _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80000008L) #define E_ACCESSDENIED _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x80000009L) #define E_PENDING _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x8000000AL) #define E_BOUNDS _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x8000000BL) #define E_CHANGED_STATE _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x8000000CL) #define E_ILLEGAL_STATE_CHANGE _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x8000000DL) #define E_ILLEGAL_METHOD_CALL _HRESULT_TYPEDEF_(0x8000000EL)
Window Messages (Winuser.h)
... ... #define WM_NULL 0x0000 #define WM_CREATE 0x0001 #define WM_DESTROY 0x0002 #define WM_MOVE 0x0003 #define WM_SIZE 0x0005 #define WM_ACTIVATE 0x0006 #define WM_SETFOCUS 0x0007 #define WM_KILLFOCUS 0x0008 #define WM_ENABLE 0x000A #define WM_SETREDRAW 0x000B #define WM_SETTEXT 0x000C #define WM_GETTEXT 0x000D #define WM_GETTEXTLENGTH 0x000E #define WM_PAINT 0x000F #define WM_CLOSE 0x0010 #define WM_DEVMODECHANGE 0x001B #define WM_ACTIVATEAPP 0x001C #define WM_FONTCHANGE 0x001D #define WM_TIMECHANGE 0x001E #define WM_CANCELMODE 0x001F #define WM_SETCURSOR 0x0020 #define WM_MOUSEACTIVATE 0x0021 #define WM_CHILDACTIVATE 0x0022 #define WM_QUEUESYNC 0x0023 #define WM_GETMINMAXINFO 0x002 #define WM_COPYDATA 0x004A #define WM_CANCELJOURNAL 0x004B ... ... ...
1.37.5 Console
APIs:
- GetConsoleCP
- MSDN: "Retrieves the input code page used by the console associated with the calling process. A console uses its input code page to translate keyboard input into the corresponding character value."
- GetConsoleTitle
- "Retrieves the title for the current console window."
- AttachConsole
- MSDN: "Attaches the calling process to the console of the specified process."
- AllocConsole -
- MSDN: "Allocates a new console for the calling process."
- FreeConsole
- MSDN: "Detaches the calling process from its console."
Console Information
1.37.6 Memory Allocation
- Heap Functions - Windows applications | Microsoft Docs
- HeapAlloc
- MSDN: "Allocates a block of memory from a heap. The allocated memory is not movable."
- HeapCreate
- MSDN: "Creates a private heap object that can be used by the calling process. The function reserves space in the virtual address space of the process and allocates physical storage for a specified initial portion of this block."
1.37.7 File
Ref:
CreateFile.
HANDLE CreateFile( LPCTSTR lpFileName, // pointer to name of the file DWORD dwDesiredAccess, // access (read-write) mode DWORD dwShareMode, // share mode LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpSecurityAttributes, // pointer to security descriptor DWORD dwCreationDistribution, // how to create DWORD dwFlagsAndAttributes, // file attributes HANDLE hTemplateFile // handle to file with attributes to copy );
ReadFile:
BOOL ReadFile( HANDLE hFile, // handle of file to read LPVOID lpBuffer, // address of buffer that receives data DWORD nNumberOfBytesToRead, // number of bytes to read LPDWORD lpNumberOfBytesRead, // address of number of bytes read LPOVERLAPPED lpOverlapped // address of structure for data );
WriteFile:
BOOL WriteFile( HANDLE hFile, // handle to file to write to LPCVOID lpBuffer, // pointer to data to write to file DWORD nNumberOfBytesToWrite, // number of bytes to write LPDWORD lpNumberOfBytesWritten, // pointer to number of bytes written LPOVERLAPPED lpOverlapped // pointer to structure needed for overlapped I/O );
Copy File:
BOOL CopyFile( LPCTSTR lpExistingFileName, // name of an existing file LPCTSTR lpNewFileName, // name of new file BOOL bFailIfExists // operation if file exists );
Delete File:
BOOL DeleteFile( LPCTSTR lpFileName // file name );
Move File:
BOOL MoveFile( LPCTSTR lpExistingFileName, // file name LPCTSTR lpNewFileName // new file name );
Create Directory:
BOOL CreateDirectory( LPCTSTR lpPathName, // directory name LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpSecurityAttributes // SD );
Remove Directory:
BOOL RemoveDirectory( LPCTSTR lpPathName // directory name );
1.37.8 Handle - Kernel "Objects"
1.37.9 Process Creation
- system, _wsystem
- Note: This functions always shows a console window.
// ANSI int system(const char* command); // Wide-unicode version int _wsystem(const wchar_t* command);
FILE *_popen( const char *command, const char *mode ); FILE *_wpopen( const wchar_t *command, const wchar_t *mode );
- CreateProcessA (ANSI Version)
- MSDN: "Creates a new process and its primary thread. The new process runs in the security context of the calling process."
BOOL CreateProcessA( LPCSTR lpApplicationName, // const char* LPSTR lpCommandLine, // char* LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes, // SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES* LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, // SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES* BOOL bInheritHandles, // DWORD dwCreationFlags, // DWORD - int LPVOID lpEnvironment, // void* LPCSTR lpCurrentDirectory, // const char* LPSTARTUPINFOA lpStartupInfo, // STARTUPINFOA* LPPROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation // PROCESS_INFORMATION* );
- CreateProcessW (wide Unicode version)
BOOL CreateProcessW( LPCWSTR lpApplicationName, // const wchar_t* LPWSTR lpCommandLine, // wchar_t* LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes, // SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES* LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, // SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES* BOOL bInheritHandles, // C++ bool DWORD dwCreationFlags, // DWORD / int LPVOID lpEnvironment, // void* LPCWSTR lpCurrentDirectory, // const wchar_t* LPSTARTUPINFOW lpStartupInfo, // STARTUPINFOW* LPPROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation // PPROCESS_INFORMATION* );
1.37.10 Process Information
DWORD GetCurrentProcessId();
- GetCurrentProcess
- Returns handle to current process.
HANDLE GetCurrentProcess();
1.37.11 Process Manipulation
- CreateProcessA and CreateProcessW
- MSDN: "Creates a new process and its primary thread. The new process runs in the security context of the calling process."
- TerminateProcess
- MSDN: "Terminates the specified process and all of its threads."
BOOL TerminateProcess( HANDLE hProcess, UINT uExitCode );
- OpenProcess
- MSDN: "Opens an existing local process object."
HANDLE OpenProcess( DWORD dwDesiredAccess, BOOL bInheritHandle, DWORD dwProcessId );
- ReadProcessMemory
- MSDN: "Reads data from an area of memory in a specified process. The entire area to be read must be accessible or the operation fails."
BOOL WINAPI ReadProcessMemory( _In_ HANDLE hProcess, _In_ LPCVOID lpBaseAddress, _Out_ LPVOID lpBuffer, _In_ SIZE_T nSize, _Out_ SIZE_T *lpNumberOfBytesRead );
- CreateRemoteThread
- MSDN: "Use the CreateRemoteThreadEx function to create a thread that runs in the virtual address space of another process and optionally specify extended attributes."
HANDLE CreateRemoteThread( HANDLE hProcess, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, SIZE_T dwStackSize, LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE lpStartAddress, LPVOID lpParameter, DWORD dwCreationFlags, LPDWORD lpThreadId );
1.37.12 GUI _ Graphical User Interface
1.37.13 Dynamic Linking or Runtime Linking
- LoadLibraryA and LoadLibraryW
- MSDN: "Loads the specified module into the address space of the calling process. The specified module may cause other modules to be loaded."
// ANSI API HMODULE LoadLibraryA( LPCSTR lpLibFileName); // Unicode API HMODULE LoadLibraryW(LPCWSTR lpLibFileName);
- GetProcAddress
- MSDN: "Retrieves the address of an exported function (function pointer) or variable from the specified dynamic-link library (DLL)."
FARPROC GetProcAddress(HMODULE hModule, LPCSTR lpProcName);
- FreeLibrary
- MSDN: "Frees the loaded dynamic-link library (DLL) module and, if necessary, decrements its reference count. When the reference count reaches zero, the module is unloaded from the address space of the calling process and the handle is no longer valid."
BOOL FreeLibrary(HMODULE hLibModule);
1.38 Books
Books:
- Mark Russinovitch et al - Windows Internals - 5th edition - Microsft Press 2000.
- Windows Operating System Internals Curriculum Development Kit, developed by David A. Solomon and Mark E. Russinovich with Andreas Polze.
- Penny Orwick and Guy Smith. Developing Drivers with Windows Driver Foundation.
- Charles Petzold: Windows Programming - Microsoft Press.
- Visual Basic - Programmer’s Guide to the Win32 API, The Authoritative Solution by Dan Appleman
- Johnson M. Hart, Win32 System Programming: A Windows® 2000 -
Application Developer's Guide, 2nd Edition, Addison -
Wesley, 2000.
- Note: This book discusses select Windows programming problems and addresses the problem of portable programming by comparing Windows and Unixapproaches.
- Jeffrey Richter, Programming Applications for Microsoft Windows,
4th Edition, Microsoft Press, September 1999.
- Note: This book provides a comprehensive discussion of the Windows API suggested reading.